Summary
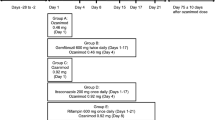
The aim of the study presented here was to determine possible pharmacokinetic interactions of moxonidine and glibenclamide at steady state in 18 healthy male volunteers. Multiple oral doses of 0.2 mg of moxonidine b.i.d. (q. 12 h) and of 2.5 mg of glibenclamide o.i.d. (q. 24 h) were administered alone and in combination in an open, non-randomized, three-treatment design. The preparations were given for 5 days in each of the 3 periods.
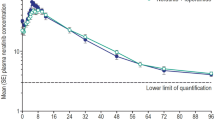
The results of this multiple dose study did not indicate substantial pharmacokinetic interactions of the drugs. Regarding the influence of glibenclamide on the pharmacokinetics of moxonidine, no significant changes were seen at all. In the presence of moxonidine, a minor decrease of bioavailability of glibenclamide was detectable, as could be derived from the AUC and clearance data. The actual differences were small and not considered to be of clinical significance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plänitz V. (1984): Crossover comparison of moxonidine and clonidine in mild to moderate hypertension. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 27, 147–152.
Plänitz V., Stenzel W., Hoffmann K. (1985): Doubleblind crossover comparison of moxonidine and clonidine HCl. Herz-Kreislauf, 17, 420–425.
Amah B.I. (1988): Unique presynaptic α2-receptor selectivity and specificity of the antihypertensive agent moxonidine. Arzneimittelforsch., 38(II), 1435–1442.
Ernsberger P., Giuliano R., Willette R.N., Reis D.J. (1990): Role of imidazole receptors in the vasodepressor response to clonidine analogues in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 253, 408–418.
Bricca G., Dontenwill M., Molines A., Feldman J., Belcourt A., Bousquet P. (1988): Evidence for existence of a homogenous population of imidazoline receptors in the human brainstem. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 150, 401–402.
Ernsberger P. (1990): Moxonidine, a second-generation centrally-acting antihypertensive, binds selectively to imidazole sites in the ventrolateral medulla (VLM) and kidney. Pharmacologist, 32, 191.
Kukovetz W.R., Diembeck W. (1986): Pharmacokinetic study after intravenous and oral administration of14C-moxonidine to humans. Unpublished.
Theodor R.A., Weimann H.J., Weber W., Michaelis K. (1991) Absolute bioavailability of moxonidine. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet., 16, 153–159.
Trenk D., Wagner F., Jähnchen F., Plänitz V. (1987): Pharmacokinetics of moxonidine after single and repeated daily doses in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 27, 988–993.
Kirch W., Hutt H.J., Plänitz V. (1988): The influence of renal function on clinical pharmacokinetics of moxonidine. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 15, 245–253.
Drug Information ’91 American Hospital Formulary Service, American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Bethesda, USA, pp. 1897–1901.
Saller R., Berger Th., Ulmer E.-M., Hellenbrecht D. (1983): Praktische Pharmakologie, 2. Auflage. Schattauer Verlag, Stuttgart/New York, pp. 218–219.
Gröning R. (1988): Generika. Arzneistoffprofile und Bioverfügbarkeits daten von Fertigarzneimitteln. Deutscher Apotheker Verlag, Stuttgart, pp. 1–7.
Häring N., Salama Z.B. (1989): Determination of moxonidine in human plasma by gas chromatography/mass-spectrometry with negative ion chemical ionization. Unpublished L.A.B. GmbH & Co Validation Report
Nieder M., Dilger C., Jaeger H. (1986): Determination of glibenclamide in human serum by HPLC. HRC & CC, 9, 102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, M., Weimann, H.J., Eden, G. et al. Steady state investigation of possible pharmacokinetic interactions of moxonidine and glibenclamide. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 18, 277–283 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03188809
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03188809