Abstract
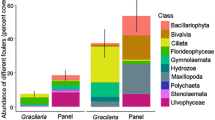
Observations were made on the colonization of test panels (8×5 cm) by fouling organisms in the coastal waters and the cooling circuit (forebay) of Madras Atomic Power Station for a year. In coastal waters, hydroids settled as a pioneer species followed by barnacles and ascidians, whereas at the forebay, sea anemones were the important settlers. Species abundance, diversity indices and fouling biomass showed relatively low values at the forebay as compared to coastal waters. Species richness however was more in forebay than in coastal waters. Low species diversity with high species richness indices observed at the forebay could be attributed to species selection under altered environmental factors (chlorine levels, high flow rates and lack of predators).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hillman R E 1977 The techniques for monitoring reproduction and growth of fouling organisms at power plant intakes; inBiofouling control procedures (ed.) L D Jensen (New York: Marcel Dekkar), pp 5–9
Karande A A 1968 Studies on marine fouling and boring organisms in Bombay harbour; inProc. 2nd Int. Congr. Mar. Foul. Corrosion, Athens, pp 563–569
Karande A A 1983 Marine biofouling in seawater tunnel;NCML Report, Bombay Markowski 1959 The cooling water of power stations: A new factor in the environment of marine and fresh water invertebrates;J. Anim. Ecol. 28 243–258
Nair K V K, Murugan P and Eswaran M S 1988 Macrofoulants in Kalpakkam coastal waters, east coast of India;Indian J. Mar. Sci. 17 341–343
Odum E P 1969 Strategy of ecosystem development;Science 164 262–270
Raymond J E G 1983Plankton productivity in the oceans, volume II:Zooplankton (Oxford: Pergamon Press)
Relini G 1984 Macrofouling in the conduits of a middle Tirrhenian power station; in6th Int. Congr. Mar. Foul. Corrosion, Athens, pp 195–210
Sasikumar N, Rajagopal S and Nair KVK 1989 Seasonal and vertical distribution of macrofoulants in Kalpakkam coastal waters;Indian J. Mar. Sci. 18 270–275
Satyanarayana Rao K and Balaji M 1987Biological fouling at Kakinada, Godavary estuary. Marine biodeterioration (New Delhi: Oxford IBH publishers)
Stirn S 1981 Manual methods in aquatic environment research;FAO fisheries technical paper No. 209, part 8,Ecological assessment of pollution effects, pp 40–50
Sutherland 1981 The fouling community at Buefort, North Carolina: a study in stability;Am. Nat. 118 499–519
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasikumar, N., Nair, K.V.K. & Azariah, J. Colonization of marine foulants at a power plant site. Proc Ani Sci 99, 525–531 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03186416
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03186416