Abstract
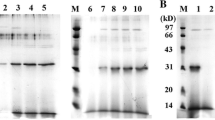
A tetrapeptide, RGDS, was inserted into proUK kringle domain G118-L119 by the construction of a mutant proUK-RGDS gene. The gene was expressed in the baculovirus expression system. Immunoaffinity chromatography was used to purify the chimera and protein with purity over 90% was achieved. The chimera was tested for its platelet membrane binding function and showed a calcium-dependent platelet binding activity. Amidolytic activity of the chimera was tested. The result indicated that specific amidolytic activity of plasmin activated chimera was 62 000 IU/mg, comparable to the previously reported 65 355 IU/mg of plasmin activated natural proUK[1]. Activation of plasminogen by the chimera after plasmin treatment followed Michieal-Menten kinetics, and the Km was 0.97 μmol/L, which was also comparable to 1.64 μmol/L of native urokinase. The chimera also showed intensive ability to inhibit platelet aggregationin vitro. These results indicate that this chimera might be useful as a bifunctional thrombolytic agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The GUSTO Investigators, An international randomized trial comparing four thrombolytic strategies for acute myocardial infarction,New Engl. J. Med., 1993, 329: 673.
Collen, D., Thrombolytic therapy,Throm. Haemost., 1997, 78: 742.
Holvoet, P., Laroche, Y., Lijnen, H. R. et al., Characterization of a chimera plasminogen activator consisting of a singlechain Fv fragment derived from a fibrin fragment D-dimer-specific antibody and a truncated single-chain urokinase,J. Bio. Chem., 1991, 266: 19717.
Tait, J. F., Engelhardt, S., Smith, C. et al., Prourokinase-annexin V chimeras: construction, expression, and characterization of recombinant proteins,J. Bio. Chem., 1995, 270: 21594.
Ruoslahti, E., RGD and other recognition sequence for integrins,Annu. Rev. Cell Biol., 1996, 12: 697.
Smith, J. W., Tachias, K., Madison, E. L., Protein loop grafting to construct a variant of tissue-type plasminogen activator that binds platelet integrin aIIbB3,J. Bio. Chem., 1995, 270: 30486.
Hawrani, A. S. E., Moreton, K.M., Sessions, R. B. et al., Engineering surface loops of proteins-a preferred strategy for obtaining new enzyme function,Trends Biotech., 1994, 12: 207.
Williams, J., Rucinski, B., Holt, J. et al., Elegantin and albolabrin purified peptides from viper venoms; homologies with the RGDS domain of fibrinogen and von Willbrand factor,Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1990, 1039: 81.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., Maniatis, T.,Molecular Cloning; A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed., NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1992.
Xu, Y., Zhang, H. T., Bi, Y. D. et al., Expression of the human pro-urokinase cDNA product in insect cells using Baculovirus system,Chinese Biochem. J. (in Chinese), 1993, 9: 209.
Deckmyn, H., Stanssens, P., Hoet, B. et al., An echistatin-like Arg-Gly-Asp(RGD)-containing sequence in the heavy chain CDR3 of a murine monoclonal antibody that inhibits human platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa function,British J. Haematol., 1994, 87: 562.
Wang, H. L., Bao, C. X., Ran, C. G. et al.,Thrombi and Hemostasis Assay Technology, Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1992.
King, L. A., Kaur, K., Mann, S. G. et al., Secretion of single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator from insect cells,Gene, 1991, 106: 151.
Wun, T., Ossowski, L., Reich, E., A proenzyme form of human urokinase,J. Bio. Chem., 1982, 257: 7262.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, B., Sun, Y., Guo, Y. et al. A prourokinase-RGDS chimera. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 42, 259–266 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183601
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183601