Abstract
Splenosis is defined as the heterotopic autotransplantation of splenic tissue. The main cause of splenosis is splenic rupture following abdominal trauma, in which fragments of splenic tissue are seeded throughout the peritoneal cavity.
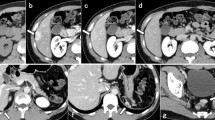
Demonstration of splenosis by scintigraphy or CT imaging has been reported, but there is no previous report of simultaneous demonstration by SPECT and CT imaging. Autotransplantation of splenic tissue in the abdominal cavity forms a solid tumor-like image on CT and is difficult to differentiate from other abdominal masses. In such cases, SPECT demonstration of splenosis is very important for identification of its exact site.
A case report of splenosis is presented, in which simultaneous demonstration by SPECT and CT was performed. This was confirmed at laparotomy for gastrectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchbinder JH, Lipkoff CJ: Multiple peritoneal splenic implants following abdominal injury.Surgery 6: 927–934, 1939
Lindell RG, Brown JM, Lindgren RD: Splenosis: CT demonstration of heterotopic autotransplantation of splenic tissue.J Comput Assist Tomogr 6: 1184–1187, 1982
Mandelson DS, Cohen BA, Armas RD: CT appearance of splenosis.J Comput Assist Tomogr 6: 1188–1190, 1982
Stewart CA, Sakimura IT, Siegel ME: Scintigraphic demonstration of splenosis.Clin Nucl Med 11: 161–164, 1986
Schiff RG, Leonidas J, Shende A, et al: The noninvasive diagnosis of intrathoracic splenosis using Technetium-99m Heat-Damaged Red Blood cells.Clin Nucl Med 12: 785–787, 1987
Atkins HL, Eckelman WC, Hauser W, et al: Splenic sequestration of Tc-99m-labelled red blood cells.J Nucl Med 21: 579–583, 1972
Jacobson SJ, De Naldo GL: Splenosis demonstrated by splenic scan.J Nucl Med 12: 570–572, 1971
Abu-Nema T, Nawaz K, Sadek S, et al: Splenic implants evaluation with radionuclide methods.Radiology 163: 641–643, 1986
Bidet AC, Schmidt GD, Mas J, et al: Diagnosis of splenosis: The advantage of splenic scintiscanning with Tc-99m-heat damaged red blood cells.Eur J Nucl Med 12: 357–358, 1986
Davis HH, Varki A, Heaton WA, et al: Detection of accessory spleens with Indium-111-labeled autologous platelets.Am J Hematol 8: 81–86, 1980
Beahrs Jr, Stephans DH: Enlarged accessory spleens: CT appearance in postsplenectomy patients.Am J Radiol 135: 483–486, 1980
Stovall TG, Ling FW: Splenosis: Report of a case and review of the literature.Obstetrical and Gynecological Survey 43: 69–72, 1988
White JD, West AN, Priebat DA: Splenosis mimicking an intra-abdominal malignancy.The American Journal of Medicine 87: 687–690, 1989
Roucos S, Tabet G, Jebara VA, et al: Thoracic splenosis.J Thoracic Cadiovasc Surg 99: 361–363, 1990
Fleming CR, Dickson ER, Harrison EG Jr: Splenosis, Autotransplantation of splenic tissue.Am J Radiol 61: 414–419, 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, S., Suematsu, T., Motohara, T. et al. SPECT demonstration of splenosis. Ann Nucl Med 6, 99–102 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164650
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164650