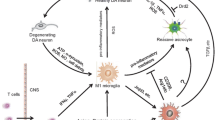
Abstract
In 1988 McGeer and colleagues (Neurology 38, 1285–91) observed an activation of the microglia in substantia nigrapars compacta (SNpc) and striatum of brains from patients with Parkinson's disease. In the years that followed several studies performed in the cerebrospinal fluid and duringpost-mortem analysis in parkinsonian patients revealed increased levels of cytokines, suggesting the activation of a proinflammatory response. Moreover, Langston and his group described the presence of active microglia in the SNpc of three patients who had been exposed to MPTP several years before death. These results suggested that the inflammatory response may increase negative feed-back into the damaged area of the cerebral parenchyma, inducing an imbalance that could perpetuate and/or accelerate neuronal death over a period of years. Similar results have been obtained in parkinsonian monkeys, rats and mice. For these reasons, several groups have treated parkinsonian animals with different anti-inflammatory drugs and obtained promising results. However, it is still not known whether inflammatory changes are responsible for active nerve cell death or whether they play a protective role in neurodegeneration. These changes are putatively related to neuronal loss and suggest that anti-inflammatory treatment for parkinsonian patients could have beneficial effects in the progression of the disease by slowing down the process of neuronal loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akassoglou K, L Probert, G Kontogeorgos and G Kollias (1997) Astrocyte-specific but not neuron-specific transmembrane TNF triggers inflammation and degeneration in the central nervous system of transgenic mice.J. Immunol. 158, 438–445.
Alon T, I Hemo, A Itin, J Pe'er, J Stone and E Keshet (1995) Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity.Nat. Med. 1, 1024–1028.
Barcia C, E Fernández-Villalba, JM Navarro-Ruiz, V Garcia, JL Saez-Cassanelli and MT Herrero (2002a) Active cytokines in chronic parkinsonian monkeys one year after last MPTP exposure. Clinical and post-mortem study.Soc. Neurosci. Prgm. No. 485.16. [Abstract]
Barcia C, A Sánchez-Bahillo, V Bautista-Hernández, JM Navarro-Ruiz, E Fernández-Villalba, B Faucheux, EC Hirsch and MT Herrero (2002b) Blood vessels and neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Study in chronic MPTP-treated monkeys, In: Nicholson and Faull (Eds.),The Basal Ganglia VII (Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York), pp 341–347.
Bauer J, F Berkenbosch, AM Van Dam and CD Dijkstra (1993) Demonstration of interleukin-1 beta in Lewis rat brain during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by immunocytochemistry at the light and ultrastructural level.J. Neuroimmunol. 48, 13–21.
Benjamin LE, I Hemo and E Keshet (1998) A plasticity window for blood vessel remodeling is defined by pericyte coverage of the preformed endothelial network and is regulated by PDGF-B and VEGF.Development 125, 1591–1598.
Benveniste EN (1995)Human Cytokines: Their Role in Research and Therapy, In: Aggarawal B and Puri R. (Eds.), (Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, UK), pp 195–216.
Blum-Degen D, T Muller, W Kuhn, M Gerlach, H Przuntek and P Riederer (1995) Interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 are elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer's and de novo Parkinson's disease patients.Neurosci. Lett. 202, 17–20.
Boka G, P Anglade, D Wallach, F Javoy-Agid, Y Agid and EC Hirsch (1994) Immunocytochemical analysis of tumor necrosis factor and its receptors in Parkinson's disease.Neurosci. Lett. 172, 151–154.
Campbell IL (2001) Cytokine-mediated inflammation and signalling in the intact nervous system, In: Castellano-López B and Nieto-Sampedro M (Eds.),Glial Cell Function (Progress in Brain Research), pp 481–498.
Carmeliet P (2001) Biomedicine. Clotting factors build blood vessels.Science 293, 1602–1604.
Carreno-Muller E, AJ Herrera, RM de Pablos, M Tomas-Camardiel, JL Venero, J Cano and A Machado (2003) Thrombin inducesin vivo degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurones along with the activation of microglia.J. Neurochem. 84, 1201–1214.
Corbin JG, D Kelly, EM Rath, KD Baerwald, K Suzuki and B Popko (1996) Targeted CNS expression of interferon-γ in transgenic mice leads to hypomyelination, reactive gliosis, and abnormal cerebellar development.Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 7, 354–370.
Czlonkowska A, M Kohutnicka, I Kurkowska-Jastrzebska and A Czlonkowski (1996) Microglial reaction in MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) induced Parkinson's disease mice model.Neurodegeneration 5, 137–143.
Dexter DT, CJ Carter, FR Wells, F Javoy-Agid, Y Agid, A Lees, P Jenner and CD Marsden (1989) Basal lipid peroxidation in substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson's disease.J. Neurochem. 52, 381–389.
Dvorak HF, LF Brown, M Detmar and AM Dvorak (1995) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis.Am. J. Pathol. 146, 1029–1039.
Egwuagu CE, J Sztein, CC Chan, R Mahdi, RB Nussenblatt and AB Chepelinsky (1994) γ interferon expression disrupts lens and retinal differentiation in transgenic mice.Dev. Biol. 166, 557–568.
Eriksson U and K Alitalo (1999) Structure, expression and receptor-binding properties of novel vascular endothelial growth factors.Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 237, 41–57.
Fargeas C, CY Wu, T Nakajima, D Cox, T Nutman and G Delespesse (1992) Differential effect of transforming growth factor beta on the synthesis of Th1- and Th2-like lymphokines by human T lymphocytes.Eur. J. Immunol. 22, 2173–2176.
Faucheux BA, AM Bonnet, Y Agid and EC Hirsch (1999) Blood vessels change in the mesencephalon of patients with Parkinson's disease.Lancet 353, 981–982.
Ferrara N (1999) Molecular and biological properties of vascular endothelial growth factor.J. Mol. Med. 77, 527–543.
Fiers W (1991) Tumor necrosis factor. Characterization at the molecular, cellular andin vivo level.FEBS. Lett. 285, 199–212.
Geiger K, E Howes, M Gallina, XJ Huang, GH Travis and N Sarvetnick (1994) Transgenic mice expressing IFN-γ in the retina develop inflammation of the eye and photoreceptor loss.Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 35, 2667–2681.
Giulian D and LB Lachman (1985) Interleukin-1 stimulation of astroglial proliferation after brain injury.Science 228, 497–499.
Gotz ME, G Kunig, P Riederer and MB Youdim (1994) Oxidative stress: free radical production in neural degeneration.Pharmacol. Ther. 63, 37–122.
Graeber MB, KB Bise and P Mehraein (1994) CR 3/43, a marker for activated microglia: aplication to diagnostic neuropathology.Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 20, 406–408.
Hickey WF (1991) Migration of hematogenous cells through the blood-brain barrier and the initiation of CNS inflammation.Brain. Pathol. 1, 97–105.
Hirsch EC, S Hunot, P Damier and B Faucheux (1998) Glial cells and inflammation in Parkinson's disease: a role in neurodegeneration?Ann. Neurol. 44, 115–120.
Horwitz MS, CF Evans, FG Klier and MB Oldstone (1999) Detailedin vivo analysis of interferon-γ induced major histocompatibility complex expression in the the central nervous system: astrocytes fail to express major histocompatibility complex class I and II molecules.Lab. Invest. 79, 235–242.
Hunot S, C Betard, B Faucheux, Y Agid and EC Hirsch (1997) Immunohistochemical analysis of interferon-γ and interleukin-1 beta in substantia nigra of Parkinsonian patients.Mov. Disord. 12, 20 [abstract].
Hunot S and EC Hirsch (2003) Neuroinflammatory processes in Parkinson's disease.Ann. Neurol. 3, 49–58
Jain RK, GC Koenig, M Dellian, D Fukumura, LL Munn and RJ Melder (1996) Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion and angiogenesis in tumors.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 15, 195–204.
Hurwitz AA, WD Lyman, MP Guida, TM Calderon and JW Berman (1992) Tumor necrosis factor α induces adhesion molecule expression on human fetal astrocytes.J. Exp. Med. 176, 1631–1636.
Jenner P and CW Olanow (1998) Understanding cell death in Parkinson's disease.Ann. Neurol. 44, 72–84.
Kerbel RS (2000) Tumor angiogenesis: past, present and the near future.Carcinogenesis 21, 505–515.
Kreutzberg GM (1996) Microglia signalling in neuropathology.Trends. Neurosci. 19, 312–318.
Kiefer R, D Lindholm and GW Kreutzberg (1993) Interleukin-6 and transforming growth factor-beta 1 mRNAs are induced in rat facial nucleus following motoneuron axotomy.Eur. J. Neurosci. 5, 775–781.
Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I, A Wronska, M Kohutnicka, A Czlonkowski and A Czlonkowska (1999) The inflammatory reaction following 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine intoxication in mouse.Exp. Neurol. 156, 50–61.
Langston JW, LS Forno, J Tetrud, AG Reeves, JA Kaplan and D Karluk (1999) Evidence of active nerve cell degeneration in the substantia nigra of humans years after 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine exposure.Ann. Neurol. 46, 598–605.
Le W, D Rowe, W Xie, I Ortiz, Y He and SH Appel (2001) Microglial activation and dopaminergic cell injury: anin vitro model relevant to Parkinson's disease.J. Neurosci. 21, 8447–8455.
Lee S, W Liu, D Dickson, C Brosnan and J Berman (1993) Cytokine production by human foetal microglia and astrocytes. Differential induction by lipopolisacharides and IL-1β.J. Immunol. 150, 2629–2667.
Liu B and JS Hong (2003) Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and strategies for therapeutic intervention.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 304, 1–7.
Liya Y and A Neufeld (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-α: a potentially neurodestructive cytokine produced by glia in the human glaucomatous optic nerve head.Glia 32, 42–50.
Loughlin AJ, MN Woodroofe and ML Cuzner (1993) Modulation of interferon-γ-induced major histocompatibility complex class II and Fc receptor expression on isolated microglia by transforming growth factor-beta 1, interleukin-4, noradrenaline and glucocorticoids.Immunology 79, 125–130.
McGeer PL, S Itagaki, BE Boyes and EG McGeer (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains.Neurology 38, 1285–1291.
McGeer PL, K Yasojima and EG McGeer (2001) Inflammation in Parkinson's disease.Adv. Neurol. 86, 83–89.
Merrill JE and EN Benveniste (1996) Cytokines in inflammatory brain lesions: helpful and harmful.Trends Neurosci. 19, 331–338.
Mogi M, M Harada, P Riederer, H Narabayashi, K Fujita and T Nagatsu (1994) Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) increases both in the brain and in the cerebrospinal fluid from parkinsonian patients.Neurosci. Lett. 165, 208–210.
Mogi M, M Harada, H Narabayashi, H Inagaki, M Minami and T Nagatsu (1996) Interleukin (IL)-1 beta, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6 and transforming growth factor-α levels are elevated in ventricular cerebrospinal fluid in juvenile parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease.Neurosci. Lett. 211, 13–16.
Mogi M, A Togari, K Tanaka, N Ogawa, H Ichinose and T Nagatsu (1999) Increase in level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned striatum in rats without influence of systemic L-DOPA on the TNF-α induction.Neurosci. Lett. 268, 101–104.
Pinedo HM, HM Verheul, RJ D'Amato and J Folkman (1998) Involvement of platelets in tumour angiogenesis?Lancet 352, 1775–1777.
Renno T, V Taupin, L Bourbonniere, G Verge, E Tran, R De Simone, M Krakowski, M Rodriguez, A Peterson and T Owens (1998) Interferon-γ in progression to chronic demyelination and neurological deficit following acuteEAE.Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 12, 376–389.
Risau W (1997) Mechanisms of angiogenesis.Nature 386, 671–674.
Rosenman SJ, P Shrikant, L Dubb, EN Benveniste and RM Ransohoff (1995) Cytokine-induced expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) by astrocytes and astrocytoma cell lines.J. Immunol. 154, 1888–1899.
Rothwell NJ and SJ Hopkins (1995) Cytokines and the nervous system II: Actions and mechanisms of action.Trends Neurosci. 18, 130–136.
Saez Cassanelli JL, C Barcia, V García-Martínez, JM Navarro-Ruiz and MT Herrero (2002) Increase of blood vessels in substantia nigra pars compacta in acute MPTP-treated mice. Relation with neuronal loss.Fens Forum p476 [Abstract].
Seljelid R, S Jozefowski and B Sveinbjornsson (1999) Tumor stroma.Anticancer Res. 19, 4809–4822.
Stone J, A Itin, T Alon, J Pe'er, H Gnessin, T Chan-Ling and E Keshet (1995) Development of retinal vasculature is mediated by hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression by neuroglia.J. Neurosci. 15, 4738–4747.
Stypula G, J Kunert-Radek, H Stepien, K Zylinska and M Pawlikowski (1996) Evaluation of interleukins, ACTH, cortisol and prolactin concentrations in the blood of patients with parkinson's disease.Neuroimmunomodulation 3, 131–134.
Tani M and RM Ransohoff (1994) Do chemokines mediate inflammatory cell invasion of the central nervous system parenchyma?Brain Pathol. 4, 135–143.
Taupin V, T Renno, L Bourbonniere, AC Peterson, M Rodriguez and T Owens (1997) Increased severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, chronic macrophage/microglial reactivity, and demyelination in transgenic mice producing tumor necrosis factor-α in the central nervous system.Eur. J. Immunol. 27, 905–913.
Teismann P and B Ferger (2001) Inhibition of the cyclooxygenase isoenzymes COX-1 and COX-2 provide neuroprotection in the MPTP-mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Synapse 39, 167–174.
Teismann P, K Tieu, DK Choi, DC Wu, A Naini, S Hunot, M Vila, V Jackson-Lewis and S Przedborski (2003a) Cyclooxygenase-2 is instrumental in Parkinson's disease neurodegeneration.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5473–5478.
Teismann P, K Tieu, O Cohen, DK Choi, du C Wu, D Marks, M Vila, V Jackson-Lewis and S Przedborski (2003b) Pathogenic role of glial cells in Parkinson's disease.Mov. Disord. 18, 121–129.
Tyor WR, JD Glass, N Baumrind, JC McArthur, JW Griffin, PS Becker and DE Griffin (1993) Cytokine expression of macrophages in HIV-1-associated vacuolar myelopathy.Neurology 43, 1002–1009.
Van Dam AM, J Bauer, FJ Tilders and F Berkenbosch (1995) Exdotoxin-induced appearance of immunoreactive interleukin-1 beta in ramified microglia in rat brain: a light and electron microscopic study.Neuroscience 65, 815–826.
Wilms H, P Rosenstiel, J Sievers, G Deuschl, L Zecca and R Lucius (2003) Activation of microglia by human neuromelanin is NF-kappaB dependent and involves p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: implications for Parkinson's disease.FASEB J. 17, 500–502.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barcia, C., Barreiro, A.F., Poza, M. et al. Parkinson's disease and inflammatory changes. neurotox res 5, 411–417 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033170
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033170