Abstract
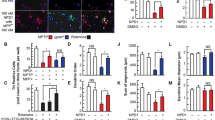
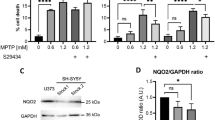
We have tested the idea that oxidative metabolism of dopamine may be involved in MPTP toxicity using the RCSN-3 cell line derived from the substantia nigra of an adult rat. Treatment with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) (10 μM), MPTP combined with 40 μM dicoumarol (an inhibitor of DT-diaphorase) and dicoumarol alone, did not induce toxicity in RCSN-3 cells after 72 h incubation. The lack of toxicity MPTP-treated RCSN-3 cells may be explained by the fact that they are unable to metabolize MPTP to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridinium ion (MPP+) as determined by HPLC. Incubation for 72 h with 100 μM MPP+ induced 6.6±1.4% cell death of RCSN-3 cells compared to 3.5±0.4 observed in control cells. However, when the cells were treated with 100 μM MPP+ and 40 μM dicoumarol, cell death increased 4-fold compared to that of cells treated solely with MPP+ (27±2%;P<0.001). Underthese conditions, a significant increase in DNA fragmentation (3-fold compared to MPP+ alone;P<0.01) and in calpain activation (P <0.05 compared to control) was evident. The inhibition of DT-diaphorase by dicoumarol supports the idea that oxidative metabolism of dopamine is involved in MPP+ toxicity in RCSN-3 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arriagada C, J Salazar, T Shimahara, R Caviedes and P Caviedes (2002) An immortalized neuronal cell line derived from the substantia nigra of an adult rat: application to cell transplant therapy, In: Ronken E, and G van Scharrenburg (Eds.)Parkinson's Disease (IOS Press, Amsterdam, Netherlands) pp 120–132.
Baez S, Y Linderson and J Segura-Aguilar (1995) Superoxide dismutase and catalase enhance autoxidation during one-electron reduction of aminochrome by NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase.Biochem. Mol. Med. 54, 12–18.
Burns RS, CC Chiueh, SP Markey, MH Ebert, DM Jacobowitz and IJ Kopin (1983) A primate model of parkinsonism: selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra byN-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 4546–4550.
Duthie SJ and MH Grant (1989) The role of reductive and oxidative metabolism in the toxicity of mitoxantrone, adriamycin and menadione in human liver derived Hep G2 hepatoma cells.Br. J. Cancer 60, 566–571.
Herrero MT, EC Hirsch, A Kastner, MR Luquin, F Javoy-Agid, LM Gonzalo, JA Obeso and Y Agid (1993a) Neuromelanin accumulation with age in catecholaminergic neurons fromMacaca fascicularis brainstem.Dev. Neurosci. 15, 37–48.
Herrero MT, EC Hirsch, A Kastner, M Ruberg, MR Luquin, J Laguna, F Javoy-Agid, JA Obeso and Y Agid (1993b) Does neuromelanin contribute to the vulnerability of catecholaminergic neurons in monkeys intoxicated with MPTP?Neuroscience 56, 499–511.
Hirsch EC, AM Graybiel and Y Agid (1988) Melanized dopaminergic neurons are differentially susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson's disease.Nature 334, 345–348.
Knepper-Nicolai B, J Savill and SB Brown (1998) Constitutive apoptosis in human neutrophils requires synergy between calpains and the proteasome downstream of caspases.J. Biol. Chem. 273, 30530–30536.
Kostrzewa RM and J Segura-Aguilar (2002) Neurotoxicological and neuroprotective elements in Parkinson's disease.Neurotox. Res. 4, 83–86.
Langston JW and PA Ballard Jr (1983) Parkinson's disease in a chemist working with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine.N. Engl. J. Med. 309, 310.
Li X, MR Melamed and Z Darzynkiewics (1996) Detection of apoptosis and DNA replication by differential labeling of DNA strand breaks with fluorochromes of different color.Exp. Cell. Res. 222, 28–37.
Mann DM and PO Yates (1983) Possible role of neuromelanin in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.Mech. Ageing Dev. 21, 193–203.
Marsden CD (1983) Neuromelanin and Parkinson's disease.J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 19, 121–141.
Paris I, A Dagnino-Subiabre, K Marcelain, LB Bennett, P Caviedes, R Caviedes, C Olea-Azar and J Segura-Aguilar (2001) Copper neurotoxicity is dependent on dopamine-mediated copper uptake and one-electron reduction of aminochrome in a rat substantia nigra neuronal cell line.J. Neurochem. 77, 519–529.
Preusch PC and DM Smalley (1990) Vitamin K1 2,3-epoxide and quinone reduction: mechanism and inhibition.Free Radic. Res. Commun. 8, 401–415.
Prota G (2000) Melanins, melanogenesis and melanocytes: looking at their functional significance from the chemist's viewpoint.Pigment Cell Res. 13, 283–293.
Rosser BG, SP Powers and GJ Gores (1993) Calpain activity increases in hepatocytes following addition of ATP. Demonstration by a novel fluorescent approach.J. Biol. Chem. 268, 23593–23600.
Segura-Aguilar J and C Lind (1989) On the mechanism of Mn3+ induced neurotoxicity of dopamine: prevention of quinone derived oxygen toxicity by DT-diaphorase and superoxide dismutase.Chem. Biol. Interact. 72, 309–324.
Segura-Aguilar J, V Barreiro and C Lind (1986) Dicoumarol-sensitive glucuronidation of benzo(a)pyrene metabolites in rat liver microsomes.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 251, 266–275.
Segura-Aguilar J, D Metodiewa and CJ Welch (1998) Metabolic activation of dopamine o-quinones too-semiquinones by NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase may play an important role in oxidative stress and apoptotic effects.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1381, 1–6.
Segura-Aguilar J, D Metodiewa and S Baez (2001) The possible role of one electron reduction of aminochrome in the neurode-generative processes of the dopaminergic systems.Neurotox. Res. 3, 157–166.
Shao M, Z Liu, E Tao and B Chen (2001) Polymorphism of MAOB gene and NAD.Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 18, 122–124.
Sies H (1987) Intact organ spectrophotometry and single-photon counting.Arch. Toxicol. 60, 138–143.
Sulzer D, J Bogulavsky, KE Larsen, G Behr, E Karatekin, MH Kleinman, N Turro, D Krantz, RH Edwards, LA Greene and L Zecca (2000) Neuromelanin biosynthesis is driven by excess cytosolic catecholamines not accumulated by synaptic vesicles.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11869–11874.
Wood DE and EW Newcomb (1999) Caspase-dependent activation of calpain during drug-induced apoptosis.J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8309–8315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández, R.A., Sánchez De Las Matas, M.J., Arriagada, C. et al. MPP+-induced degeneration is potentiated by dicoumarol in cultures of the RCSN-3 dopaminergic cell line. Implications of neuromelanin in oxidative metabolism of dopamine neurotoxicity. neurotox res 5, 407–410 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033169
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033169