Abstract
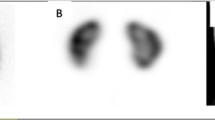
The authors present a comparison of the findings for thallium-201 (Tl-201), Tc-99m MAG3 and Tc-99m MDP in subacute and chronic radiation nephritis in a 9-yr-old boy who was treated by radiation therapy for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma of the left chest wall by a radiation port that partially included the left kidney. Tl-201 imaging three and six months later showed a cortical defect in the left kidney due to radiation nephritis. Tc-99m MDP scan showed increased uptake on both occasions, but more marked in the subacute period than in the chronic period. Tc-99m MAG3 showed decreased concentration and increased cortical retention three months later. Six months after the radiation therapy, a cortical defect corresponding to the cortical area that showed increased parenchymal retention was more prominent in the Tc-99m MAG3 scan.
In the present case, Tc-99m MDP, Tl-201 and Tc-99m MAG3 findings may provide useful information for understanding pathophysiological damage in the kidney after radiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fogelman I. Soft tissue uptake of bone agents. In:Bone Scanning in Clinical Practice. Gray HW (ed), Over Wallop, Hampshire; Bas Printers Limited, 1987; 211–219.
Titelbaum DS, Fowble BF, Powe JE, et al. Renal uptake of technetium-99m methylene diphosphonate following therapeutic radiation for vertebral metastases.J Nucl Med 1989; 30(6): 1113–1116.
Wistow BW, McAfee JG, Sagerman RH, Thomas FD, Grossman ZD. Renal uptake of Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate after radiation therapy.J Nucl Med 1979; 20: 32–34.
Lutrin CL, Goris ML. Pyrophosphate retention by previously irradiated renal tissue.Radiology 1979; 133: 207–209.
Wahner HW, Dewanjee MK. Drug induced modulation of Tc-99m pyrophosphate tissue distribution. What is involved?J Nucl Med 1981; 22: 555–559.
Dewanjee MK, Kahn PC. Mechanisms of localization of Tc99m pyrophosphate and tetracycline in infarcted myocardium.J Nucl Med 1976; 17: 639–646.
DeThrall JH, Ziessman HA. Tumors. In:Nuclear Medicine the Requisites. St. Louis, Missouri: Mosby-Year Book, Inc., 1995: 180–181.
Ugur O, Caner B, Bakkaloglu M, et al. Segmental ARN in a kidney with a single artery transplanted from living related donor.Nuklearmedizin 1996; 35 (5): 190–192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Degirmenci, B., Uysal, K., Bekis, R. et al. Tc-99m MDP, thallium-201 chloride and Tc-99m MAG3 renal uptake in subacute and chronic radiation nephritis compared. Ann Nucl Med 15, 447–449 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02988351
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02988351