Abstract
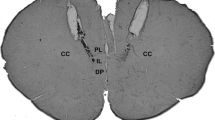
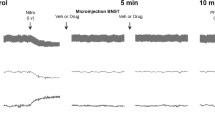
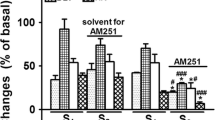
Endothelin-1 (ET-1), a novel and potent vasoconstrictor in blood vessel, is known to have some functions in the rat central nervous system (CNS). In order to investigate the central functions of ET-1, ET-1 was administered to the periaqueductal gray area (PAG) of anesthetized rats to induce barrel rolling and increase the arterial blood pressure (ABP). ET-1 had a modulatory effect on central cardiovascular and behavioral control. The selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist MK-801 (3 μmol/kg, i.p.) blocked the ET-1 induced responses, and both the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (N-nitro-L-arginine methylester 1 mmol/rat) and the nitric oxide (NO) scavenger hemoglobin (15 nmol/rat) had similar effects in reducing the ET-1 (10 pmol/rat)-induced behavioral changes and ABP elevation. However, NO donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP 10 μg, 1 μg/rat) decreased the ET-1 induced ABP elevation, and recovered the ET-1-induced barrel rolling effect that was reduced by MK-801. These results suggest that ET-1 might have neuromodulatory functions such as ABP elevation and barrel rolling induction in the PAG of the rats via the NMDA receptor and NO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandler, R. and Depaulis, A., Midbrain periaqueduactal gray control of defensive behavior in the cat and the rat. In “The midbrain periaqueductal Gray matter: Functional, Anatomical and Neurochemical Organization” 175–98 (1991).
Burke, R. E., Fahn, S., Wagner, H. R. and Smeal, M. Chlorpromazine Methionine-induced barrel rotation: Antimuscarinic effect.Brain Res., 250, 133–42 (1982).
D’Amico, M., Berrino, L., Maione, S., Pizzirusso, A. and Rossi, F., Effects of L-NAME on endothelin-1-induced barrel-rolling in periaqueductal gray area of rats.Life Sci., 57, PL357–60 (1995a).
D’Amico, M., Berrino, L., Maione, S., Fillippelli, A., Pizzirusso, A., Vitagliano, S. and Rossi, F. Endothelin-1 in rat periaqueductal gray area induces hypertension via glutamatergic receptors.Hypertension, 25, 507–10 (1995b).
D’Amico, M., Berrino, L., Maione, S., and Rossi, F. Selective and nonselective ET antagonists reveal and ETB receptors mediated ET-1-induced behavioral effect in conscious rats.Life Science, 58, PL177–80 (1996).
Dawson, V. L., Dawson, T. M., Bartley, D. A., Uhl, G. R., Snyder, S. H. Mechanism of nitric oxide-mediated neurotoxicity in primary brain cultures.J. Neurosci., 13, 2651–61 (1993).
Dawson, T. M. and Dawson, V. L. Nitric oxide synthase: Role as a transmitter/mediator in the brain and endocrine system.Annu. Rev. Med., 47, 219–27 (1996).
Garthwaite, J. and Boulton, C. L., Nitric oxide signaling in the central nervous system.Annu Rev Physiol 57, 683–706 (1995).
George, P. The rat nervous system-Periaqueductal Gray.Academic press 2nd ED. 173–82 (1995).
Gulati, A. and Rebello, S. Characteristics of endothelin receptors in the central nervous system of spontaneously hypertensive rats.Neuropharmacology 31, 243–50 (1992).
Horie K, Morita A, and Yokogoshi H. Endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 modulate dopaminergic neurons through different mechanisms.Life Sci., 57(8), 735–41 (1995).
Kataoka Y, Koizumi S, Kohzuma M, Shibaguchi H, Shigematsu K, Niwa M, and Taniyama K. NMDA receptor involvement in endothelin neurotoxicity in rat striatal slices.Eur J Pharmacol., 273(3), 285–9 (1995).
Koseki, C., Imai, M., Hirata, Y., Yamagisawa, M., and Masaki, T., Autoradiograph distribution in rat tissues of binding sites for endothelin: a neuropeptides.Am. J. Physiol., R858–R866 (1989).
Kuwaki, T., Koshiya, N., Cao, W. H., Takahashi, H., Terui, N., and Kumada, M., Modulatory effects of endothelin-1 on central cardiovascular control in rats.Jpn. J. Physiol., 40, 827–41 (1990).
Lei, S. Z., Pan, Z. H., Aggarwal, S. K., Chen, H. S., Hantman, J., Sucher, N. J., and Lipton, S. A. Effect of nitric oxide production on the redox modulatory site of the NMDA receptor-channel complex.Neuron, 8, 1087–99 (1992).
Maione, S., Berrinol, L., Vitagliano, S., Leyva, J., and Rossi, F. Interactive role of L-glutamte and vasopressin, at the level of the PAG area, for cardiovascular tone and stereotyped behaviour.Brain Res., 597, 166–9 (1992).
Maione, S., D’Amico M., Berrino, L., Filippelli, A., Leyva, J., and Rossi, F. Involvement of periaqueductal gray area NMDA receptors in endothelin-induced behavioural effects.Eur J Pharmacol., 250(1): 209–12 (1993).
Matsumura, K., Abe, I., Tsuchihashi, T., Tominaga, M., Kobayashi, K., and Fujishima, M., Central effects of endothelin on neurohormonal responses in conscious rabbits.Hypertension, 17, 1192–96 (1991).
Minamisawa, K., Hasimoto, R., Ishii, M., and Kimura, F. Complicated central effects of endothelin on blood pressure in rat.Jpn. J. Physiol., 39, 825–32 (1989).
Moser, R. and Pelton, J. T. Behavioral effects of centrally administered endothelin in the rat.British Journal of Pharmacology, 96, 347P (1989).
Mosqueda-Garcia, R., Yates, K., O’Leary, J., and Inagami, T. Cardiovascular and respiratory effects of endothelin in the ventrolateral medulla of the normotensive rat.Hypertension, 26, 263–71 (1995).
Onstott, D., Mayer, B., and Beitz A. J. Nitric oxide synthase immunoreactive neurons anatomically define a longitudinal dorsolateral column within the midbrain periaqueductal gray of the rat: Analysis using laser confocal microscoopy.Brain Research, 610, 317–24 (1993).
Schuman, E. M. and Madisan, D. V. Nitric oxide and synaptic function.Annual Review of Neuroscience, 17, 153–83 (1994).
Snyder, S. H., Nitric oxide: First in a new class of neurotransmitters.Science, 257, 494–6 (1992).
Sripada, S., Gaytan, O., Al-rahim, S., Swann, A., and Dafny, N. Dose-related effects of MK-801 on acute and chronic methyl-phenidate administration.Brain Res. 814(1–2), 78–85 (1998).
Wong, E. H., Kemp, J. A., Priestley, T., Knight, A. R., Woodruff, G. N., and Iversen, L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist.Proc Natl Acad Sci. 83(18), 7104–8 (1986).
Wurpel, J. N., Dundore, R. L., Barbella, Y. R., Balaban, C. D., Keil, L. C. and Servers, W. B. Barrel rotation evoked by intracerebroventricular vasopressin in conscious rats. I Description and general pharmacology.Brain Res., 365, 21–29 (1986).
Yamagisawa, M., Kurihara, H., Kimura, S., Tomobe, Y., Kobayashi, M., Mitsui, Y., Yazaki, Y., Goto, K., and Masaki, T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells.Nature, 332, 411–5 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, J.S., Shin, C.Y., Yang, S.J. et al. NMDA receptor and NO mediate ET-1-induced behavioral and cardiovascular effects in periaqueductal gray matter of rats. Arch Pharm Res 24, 64–68 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976495
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976495