Abstract
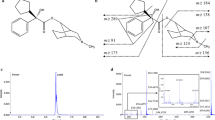
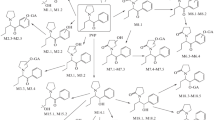
Propentofylline (PPF, 3-methyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-7-propylxanthine) has been reported to be a compound for treatment of both vascular dementia and dementia of the Alzheimer type. The short half-life (about 15 min) of PPF at the terminal elimination phase and poor bioavailability after oral administration of PPF to rabbits (Kimet al., 1992) suggest in part that this drug takes the extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver. In addition, the metabolic pathway for PPF remains unclear. The objective of this experiment is to identify urinary metabolites of PPF in rats. For the identification of the metabolites, rat urine was collected after oral administration of 100 mg/kg PPF. PPF metabolite, 3-methyl-1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-7-propylxanthine, was synthesized and confirmed by gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy (GC/MS) and1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The urinary metabolites of PPF were extracted with diethyl ether and identified by electron impact and chemical ionization GC/MS. One urinary metabolite was confirmed to be 3-methyl-1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-7-propylxanthine by synthesized authentic compound. Several metabolites of monohydroxy- and dihydroxy-PPF were identified based on mass fragmentation of both intact and trimethylsilylated derivatives of PPF metabolites and the novel structure of these metabolites is suggested based on mass spectra.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andine, P., Rudolphi, K. A., Fredholm, B. B., Hagberg, H. Effects of propentofylline (HWA 285) on extracellular purines and excitatory amino acids in CA1 of rat hippocampus during transient ischaemia.Br. J. Pharmacol. 100 (4), 814–818 (1990).
Fredholm, B. B., Lindstrom, K., Wallman-Johansson, A. Propentofylline and other adenosine transport inhibitors increase the efflux of adenosine following electrical or metabolic stimulation of rat hippocampal slices.J. Neurochem., 62 (2), 563–573 (1994).
Fugi, K., Hiramatsu, M., Kameyama, T., Nebeshima, T. Effects of repeated administration of propentofylline on memory impairment produced by basal forebrain lesion in rats.European J. Pharmacol., 236 (3), 411–417 (1993).
Grome, J. J., Hofmann, W., Gojowczyk, G., Stefanovich, V., Effects of a xanthine derivative, propentofylline, on local cerebral blood flow and glucose utilization in the rat.Brain Res. 740 (1–2), 41–46, 1996.
Hignite, C., Chapter 16. Nucleic acids and derivative. InBiochemical applications of mass spectroscopy, Vol. 1; Waller, G. R. and Dermer, O. C. (Eds.). John Willey & Sons, pp. 527–566 (1980).
Kim, N. S., Ito, T., Kawata, M., Uchida, T., Goto, S., Preparation and evaluation of Eudragit gels. IV: Rectal gel preparations for sustained release and avoidance of first-pass metabolism of propentofylline.J. Pharm. Sci., 81 (9), 904–907 (1992).
Meilke, R., Kittner, B., Ghaemi, M., Kessler, J., Szelies, B., Herholz, K., Hiess, W. D. Propentofylline improves regional cerebral.J. Neurol. Sci., 141 (1–2), 59 (1996).
Nabeshima, T. Nerve growth factor strategy and preparation of animal model for Alzheimer-type senile dementia.Yakugaku Zasshi, 115 (7), 499–512 (1995).
Schanzer W., Geyer H. and Donike, M. Metabolism of methandienone in man: identification and synthesis of conjugated excreted urinary metabolites, determination of excretion rates and gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric identification of bis-hydroxylated metabolites.J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 38 (4), 441–464 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, OS., Ryu, JC. Identification of propentofylline metabolites in rats by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Arch Pharm Res 23, 374–380 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975450
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975450