Abstract
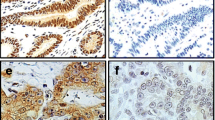
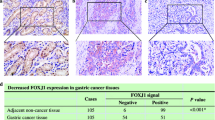
c-fos was first identified as a viral oncoprotein, and has been studied in terms of its oncogenic function in tumorigenesis. Many experimental and clinical data indicated that c-fos expression plays a role in the progression of several types of carcinomas. However, some recent studies challenge this view as they indicate that c-fos has tumor suppressor activity. In the present study, we assessed c-fos protein expression in 625 consecutive gastric cancers immunohistochemically, and analyzed its relationship with clinicopathologic factors and survival. We found that a loss of c-fos expression is correlated with a more advanced stage, lymph node metastasis, lymphatic invasion and shorter survival, indicating that c-fos expression in gastric cancer cells is lost during progression and that this loss is associated with a poor prognosis. The above findings suggest that loss of c-fos expression has tumor suppressor activity in gastric cancer and we suspect that this suppressor activity might be related to the pro-apoptotic function of c-fos.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halazonetis TD, Georgopoulos K, Greenberg ME, Leder P: c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell 55: 917–924, 1988
Schutte J, Viallet J, Nau M, Segal S, Fedorko J, Minna J: jun-B inhibits and c-fos stimulates the transforming and trans-activating activities of c-jun. Cell 59: 987–997, 1989
Bakin AV, Curran T: Role of DNA 5-methylcytosine transferase in cell transformation by fos. Science 283: 387–390, 1999
Grigoriadis AE, Schellander K, Wang ZQ, Wagner EF: Osteoblasts are target cells for transformation in c-fos transgenic mice. J Cell Biol 122: 685–701, 1993
Hu E, Mueller E, Oliviero S, Papaioannou VE, Johnson R, Spiegelman BM: Targeted disruption of the c-fos gene demonstrates c-fos dependent and independent pathways for gene expression stimulated by growth factors or oncogenes. EMBO J 13: 3094–3103, 1994
Fialka I, Schwarz H, Reichmann E, Oft M, Busslinger M, Beug H: The estrogen-dependent c-JunER protein causes a reversible loss of mammary epithelial cell polarity involving a destabilization of adherens junctions. J Cell Biol 132: 1115–1132, 1996
Franchi A, Calzolari A, Zampi G: Immunohistochemical detection of c-fos and c-jun expression in osseous and cartilaginous tumours of the skeleton. Virchows Arch 432: 515–519, 1998
Papachristou DJ, Batistatou A, Sykiotis GP, Varakis I, Papavassiliou AG: Activation of the JNK-AP-1 signal transduction pathway is associated with pathogenesis and progression of human osteosarcomas. Bone 32: 364–371, 2003
Gamberi G, Benassi MS, Bohling T, Ragazzini P, Molendini L, Sollazzo MR, Pompetti F, Merli M, Magagnoli G, Balladelli A, Picci P: C-myc and c-fos in human osteosarcoma: prognostic value of mRNA and protein expression. Oncology 55: 556–563, 1998
Bamberger AM, Milde-Langosch K, Rossing E, Goemann C, Loning T: Expression pattern of the AP-1 family in endometrial cancer: correlations with cell cycle regulators. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 127: 545–550, 2001
Prusty BK, Das BC: Constitutive activation of transcription factor AP-1 in cervical cancer and suppression of human papillomavirus (HPV) transcription and AP-1 activity in HeLa cells by curcumin. Int J Cancer 113: 951–960, 2005
Yuen MF, Wu PC, Lai VC, Lau JY, Lai CL: Expression of c-Myc, c-Fos and c-Jun in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 91: 106–112, 2001
Wakita K, Ohyanagi H, Yamamoto K, Tokuhisa T, Saitoh Y: Overexpression of c-Ki-ras and c-fos in human pancreatic carcinomas. Int J Pancreatol 11: 43–47, 1992
Bland KI, Konstadoulakis MM, Vezeridis MP, Wanebo HJ: Oncogene protein co-expression. Value of Ha-ras, c-myc, c-fos, and p53 as prognostic discriminants for breast carcinoma. Ann Surg 221: 706–718, 1995
Mikula M, Gotzmann J, Fischer AN, Wolschek MF, Thallinger C, Schulte-Hermann R, Beug H, Mikulits W: The proto-oncoprotein c-Fos negatively regulates hepatocellular tumorigenesis. Oncogene 22: 6725–6738, 2003
American Joint Committee on Cancer: AJCC cancer staging manual 6th ed. Springer-Verlag, New York, 2002
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): World Health Organization Classification of Tumors; pathology and genetics of tumors of the digestive system. IARC Press, Lyon, 2000
Lee HS, Lee HK, Kim HS, Yang HK, Kim YI, Kim WH: MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6 expressions in gastric carcinomas: their roles as prognostic indicators. Cancer 92: 1427–1434, 2001
Nevine S, Darwish, Kim MA, Chang MS, Lee HS, Lee BL, Kim YI, Kim WH: Prognostic significance of CD24 expression in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res Treat 36: 298–302, 2004
Kustikova O, Kramerov D, Grigorian M, Berezin V, Bock E, Lukanidin E, Tulchinsky E: Fra-1 induces morphological transformation and increases in vitro invasiveness and mobility of epithelioid adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 18: 7095–7105, 1998
Levin WJ, Press MF, Gaynor RB, Sukhatme VP, Boone TC, Reissmann PT, Figlin RA, Holmes EC, Souza LM, Slamon DJ: Expression patterns of immediate early transcription factors in human non-small cell lung cancer. The Lung Cancer Study Group. Oncogene 11: 1261–1269, 1995
Liu G, Takano T, Matsuzuka F, Higashiyama T, Kuma K, Amino N: Screening of specific changes in mRNAs in thyroid tumors by sequence specific differential display: decreased expression of c-fos mRNA in papillary carcinoma. Endocr J 46: 459–466, 1999
Fleischmann A, Jochum W, Eferl R, Witowsky J, Wagner EF: Rhabdomyosarcoma development in mice lacking Trp53 and Fos: tumor suppression by the Fos protooncogene. Cancer Cell 4: 477–482, 2003
Grimm C, Wenzel A, Behrens A, Hafezi F, Wagner EF, Reme CE: AP-1 mediated retinal photoreceptor apoptosis is independent of N-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun. Cell Death Differ 8:859–867, 2001
Kalra N, Kumar V: c-Fos is a mediator of the c-myc-induced apoptotic signaling in serum-deprived hepatoma cells via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 279: 25313–25319, 2004
Silvers AL, Bachelor MA, Bowden GT: The role of JNK and p38 MAPK activities in UVA-induced signaling pathways leading to AP-1 activation and c-Fos expression. Neoplasia 5: 319–329, 2003
Siegmund D, Mauri D, Peters N, Juo P, Thome M, Reichwein M, Blenis J, Scheurich P, Tschopp J, Wajant H: Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD) and caspase-8 mediate up-regulation of c-Fos by Fas ligand and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) via a FLICE inhibitory protein (FLIP)-regulated pathway. J Biol Chem 276: 32585–32590, 2001
Willaime S, Vanhoutte P, Caboche J, Lemaigre-Dubreuil Y, Mariani J, Brugg B: Ceramide-induced apoptosis in cortical neurons is mediated by an increase in p38 phosphorylation and not by the decrease in ERK phosphorylation. Eur J Neurosci 13: 2037–2046, 2001
Kondo T, Sharp FR, Honkaniemi J, Mikawa S, Epstein CJ, Chan PH: DNA fragmentation and prolonged expression of c-fos, c-jun, and hsp70 in kainic acid-induced neuronal cell death in transgenic mice overexpressing human CuZn-superoxide dismutase. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17: 241–256, 1997
Hasegawa K, Litt L, Espanol MT, Sharp FR, Chan PH: Expression of c-fos and hsp70 mRNA in neonatal rat cerebrocortical slices during NMDA-induced necrosis and apoptosis. Brain Res 785: 262–278, 1998
Meyer-ter-Vehn T, Covacci A, Kist M, Pahl HL: Helicobacter pylori activates mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades and induces expression of the proto-oncogenes c-fos and c-jun. J Biol Chem 275: 16064–16072, 2000
Myllykangas S, Monni O, Nagy B, Rautelin H, Knuutila S: Helicobacter pylori infection activates FOS and stress-response genes and alters expression of genes in gastric cancer-specific loci. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 40: 334–341, 2004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, S.P., Kim, J.H., Kim, M.A. et al. Prognostic significance of loss of c-fos protein in gastric carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 13, 284–289 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02940306
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02940306