Abstract
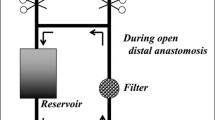
Objective: We reviewed the surgical management of acute type A aortic dissection between 1989 and 1998.Methods: Subjects were 28 consecutive patients (mean age: 61.8±10.7 years) with acute type A aortic dissection were studied. The mean duration between aortic dissection onset and surgery was 17.5±17.0 hours. In surgery, aortic pathology and flow patterns in dissected aortic channels were evaluated using transesophageal and epiaortic echo. Simple, safe combination of profound hypothermic circulatory arrest with retrograde cerebral perfusion and open aortic anastomosis was used for brain protection. Hypothermic circulatory arrest was 46.9±24.8 minutes. Aortic repair consisted in ascending aortic replacement in 5 patients, with hemiarch repair in 17, and total arch repair in 6. Intimal tears were resected in all but 2 patients. Concomitantly resuspension of the aortic valve was done in 9 and aortic root replacement in 2.Results: No operative (30-day) deaths occurred, although 2 died from unrelated hepatic failure during hospitalization or late-stage pancreatic cancer in the late stage. In cerebral sequellae, 1 patient suffered a stroke and 2 patients developed temporary neurologic dysfunction.Conclusion: Our experience demonstrated that the simplified conjunction of hypothermic circulatory arrest with retrograde cerebral perfusion and open aortic anastomosis, associated with real-time assessment by transesophageal and epiaortic echo, is safe and useful during emergency aortic repair for acute type A aortic dissection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crawford ES, Svensson LG, Coselli JS, Safi HJ, Kenneth RH. Aortic dissection and dissecting aortic aneurysms. Ann Surg 1988; 208: 254–73.
Crawford ES, Kirklin JW, Naftal DC, Svensson LG, Coselli JS, Safi HJ. Surgery for acute dissection of ascending aorta. Should the arch be included? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1992; 104: 46–59.
Bachet J, Goudot B, Dreyfus GD, Brodaty D, Dubois C, Delentdecker P, et al. Surgery for acute type A aortic dissection: the Hospital Foch experience (1977–1998). Ann Thorac Surg 1999; 67: 2006–9.
Griepp RB, Stinson EB, Hollingsworth JF, Buehler D. Prosthetic replacement of the aortic arch. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1975; 70: 1051–63.
Ueda Y, Miki S, Kusuhara K, Okita Y, Tahata T, Ogino H, et al. Protective effect of continuous retrograde cerebral perfusion on the brain during deep hypothermic systemic circulatory arrest. J Cardiac Surg 1994; 9: 584–59.
Livesay JJ, Cooley DA, Duncan JM, Ott DA, Walker WE, Reul GJ. Open aortic anastomosis: improved results in treatment of aneurysms of the aortic arch. Circulation 1982; 6 (Suppl II):.
Ogino H, Ueda Y, Sugita T, Morioka K, Sakakibara Y, Matsubayashi K, et al. Monitoring of regional cerebral oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy during continuous retrograde cerebral perfusion for aortic arch surgery. Euro J Cardio-Thorac Surgery 1998; 14: 415–8.
Safi HJ, Miller III CC, Reardon MJ, Iliopoulos DC, Letson GV, Espada R, et al. Operation for acute and chronic aortic dissection: recent outcome with regard to neurologic deficit and early death. Ann Thorac Surg 1998; 66: 402–11.
Takamoto S, Omoto R. Visualization of thoracic dissecting aneurysm by transesophageal Doppler color flow mapping. Herz 1987; 12: 187–93.
Orihashi K, Matsuura Y, Sueda T, Watari M, Okada K. Reversible visceral ischemia detected by transesophageal echocardiography and near infrared spectroscopy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000; 119: 384–6.
Kazui T, Washiyama N, Bashar AHM, Terada H, Yamashita K, Takinami M, et al. Extended total arch replacement for acute type A aortic dissection: experience with seventy patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000; 119: 558–65.
Rokkas CK, Kouchoukos NT. Single-stage extensive replacement of the thoracic aorta, the arch-first technique. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999; 117: 99–105.
Ando M, Takamoto S, Okita Y, Morota T, Matsukawa R, Kitamura S. Elephant trunk procedure for surgical treatment of aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg 1998; 66: 82–7.
Bachet JE, Termignon JL, Dreyfus G, Goudot B, Martinelli L, Piquois A, et al. Aortic dissection: prevalence, cause, and results of late reoperations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1994; 108: 199–206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Real at the 18th World Congress of the International Union of Angiology, Tokyo, September 17, 1998.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogino, H., Ueda, Y., Sugita, T. et al. Surgery for acute type a aortic dissection using retrograde cerebral perfusion. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 49, 337–342 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02913146
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02913146