Summary
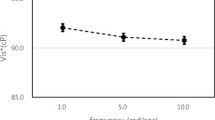
This study demonstrates the importance of defining normal reference population ranges for P- and S-viscosity with respect to posture. The normal ranges determined for P-viscosity are not acceptable as a reference range for a hospitalized population that is predominantly in a supine position. Mean percentage changes of P-and S-viscosity in the recumbent posture as compared to the same population in the upright posture were 7.51 and 5.88, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage P.: Statistica medica. Feltrinelli, Milano, 1975; p. 142.
Böhme A.: Über die Schwankungen der Serumkonzentration beim gesunden Menschen —Dtsch. Arch. klin. Med.103, 522, 1911.
Dintenfass L., Kammer S.: Plasma viscosity in 615 subjects. Effects of fibrinogen globulin and cholesterol in normals, peripheral vascular disease, retinopathy and melanoma—Biorheology14, 247, 1977.
Dt Perri T.: Aspetti fisiopatologici e clinici delle sindromi da iperviscosità emance—Lab Ricerca Clin. Lab11, (Suppl. 1), 73 1981
Dixon M., Paterson C. R.: Posture and composition of plasma—Clin. Chem.24, 824, 1978
Fawcett H. K., Wynn V.: Effects of posture on plasma volume and some blood constituents. —J. clin. Path.13, 304, 1960.
Felding P., Tryding N., Hyltoft Petersen P., Hörder M.: Effects of posture on concentrations of blood constituents in healthy adults: practical application of blood specimen collection procedures recommended by the Scandinavian Committee on Reference Values—Scand J. clin. Lab. Invest.40, 615, 1980.
Forconi S., Guerrini M., Pieracalli D., Acciavatti A.: Viscosimetria ematica. Approccio metodologico—La Ricerca Clin. Lab.11, (Suppl. 1), 135, 1981.
Harkness J.: The viscosity of human blood plasma; its measurement in health and disease —Biorheology8, 171, 1971.
Harkness J.: Measurement of plasma viscosity. In:Lowe G. D. O., Barbenel J. C., Forbes C. D. (Eds.): Clinical aspects of blood viscosity and cell deformability. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, New York, 1981; p. 78.
Hess E. L., Cobure A.: The intrinsic viscosity of mixed protein systems, including studies of plasma and serum—J. gen Physiol.33 511, 1950.
Humphrey K. R., Gruemer H., Lott J. A.: Impact of posture on the ‘Reference Range’ for serum proteins and calcium—Clin. Chem.23, 1343, 1977.
Hyltoft Petersen P., Felding P., Hörder M., Tryding N.: Effects of posture on concentrations of serum proteins in healthy adults. Dependence on the molecular size of proteins— Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.40, 623, 1980.
Parving H. H., Rossing N., Nielsen S. L., Lassen N. A.: Increased transcapillary escape rate of albumin, IgG and IgM after plasma volume expansion—Amer. J. Physiol.227, 245, 1974.
Seaman G. V. F., Corry W. D., Blume P., Jackson L.: Theoretical bases for the role of erythrocyte sedimentation rate, plasma viscosity and zeta sedimentation ratio measurements in clinical medicine—Clin. Hemorheol.1, 87, 1981.
Somer T.: Hyperviscosity syndrome in plasma cell dyscrasias—Advanc. Microcirc.6, 1, 1975.
Statland B. E., Bokelund H., Winkel P.: Factors contributing to intra-individual variation of serum constituents. 4. Effects of posture and tourniquet application on variation of serum constituents in healthy subjects—Clin. Chem.20, 1513, 1974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lippi, U., Dell’Anna, L. & Cappelletti, P. Effects of posture on plasma and serum viscosity. La Ricerca Clin. Lab. 14, 47–52 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02905040
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02905040