Summary
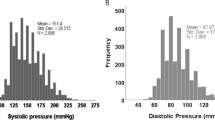
A study of the frequency distribution of plasma renin activity (PRA) in 123 patients with essential hypertension (EH) produced no evidence of a distinct subpopulation with low renin levels, whether the samples were taken from supine or upright patients. Applying an arbitraty classification criterion, however, low PRA levels were found in 30.1% of patients. There were no significant differences in mean blood pressure, 24-h sodium excretion, and age when groups with low, normal or high PRA levels were compared. The incidence of PRA hyporesponsiveness was similar in the three groups of patients, but increased with age. In the female there was a preponderance of low PRA levels. It is concluded that EH with low PRA levels is not a separate diagnostic entity and, when PRA is low in a hypertensive subject, the possible effects of age, blood pressure, and sex ought to be taken into account before other causes of low PRA are postulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beevers D. G., Nelson C. S., Padfield P. L., Barlow D. H., Duncan S., Greaves D. A., Hawthorne V. M., Morton J. J., Young G. A., Young J.: The prevalence of hypertension in an unselected population, and the frequency of abnormalities of potassium, angiotensin II and aldosterone in hypertensive subjects—Acta clin. belg.29, 276, 1974.
Brunner H. R., Sealey J. E., Laragh J. H.: Renin subgroups in essential hypertension further analysis of their pathophysiological and epidemiological characteristics—Circulat. Res.32 (Suppl. 1), 99, 1973.
Carey R. M., Douglas J. G., Schweikert J. R., Liddle G. W.: The syndrome of essential hypertension and suppressed plasma renin activity—Arch. intern. Med.130, 849, 1972.
Crane M. G., Harris J. J., Johns V. J.: Hyporeninemic hypertension—Amer. J. Med.52, 457, 1972.
Davies J. O.: The control of renin release—Amer. J. Med.55, 333, 1973.
Doyle A. E., Chua K. G., Duffy S., Louis W. J.: Plasma renin, urinary sodium excretion and vascular disease—Clin. Sci. molec. Med.48, 1275, 1975.
Doyle A. E., Jerums G.: Sodium balance, plasma renin and aldosterone in hypertension— Circulat. Res.36 (Suppl. 2), 267, 1970.
Dunn M. J., Young J.: Low renin hypertension—Kidney int.5, 317, 1974.
Friedman S. A., Raizner A. E., Rosen H., Solomon N. A., Sy W.: Functional defects in the aging kidney—Ann. intern. Med.76, 41, 1972.
Hollenberg N. K., Adams D. F., Solomon H. S., Rashid A., Abrams H. L., Merrill J. P.: Senescence and the renal vasculature in normal man—Circulat. Res.34, 309, 1974.
Lew E. A.: High blood pressure, other risk factors and longevity: the insurance viewpoint—Amer. J. Med.55, 281, 1973.
Mroczek W. J., Finnerty F. A., Catt K. J.: Lack of association between plasma tenin and history of heart attack or stroke in patients with essential hypertension—Lancetii, 464, 1973.
Padfield P. L., Allison M. E. M., Brown J. J., Lever A. F., Luke R. G., Robertson C. C., Robertson J. I. S., Tree M.: Effects of intravenous frusemide on plasma renin concentration: suppression of response in hypertension—Clin. Sci. molec. Med.49, 353, 1975.
Padfield P. L., Beevers D. G., Brown J. J., Davies D. L., Lever A. F., Robertson J. I. S., Schalekamp M. A. D. H., Tree M., Titterington M.: Is low-renin hypertension a stage in the development of essential hypertension, or a diagnostic entity?—Lanceti, 548, 1975.
Papper S., Vaamonde C. A.: Nephrosclerosis—In:Strauss M. B., Welt L. G. (Eds): Diseases of the kidney. Little, Brown and Co., Boston, 1971; p. 735.
Smith J. P.: Hyaline arteriosclerosis in the kidney—J. Path. Bact.69, 147, 1955.
Swales J. D.: Low-renin hypertension: nephrosclerosis?—Lanceti, 75, 1975.
Thomas G. W., Ledingham J. G. G., Beilin L. J., Stott A. N., Yeates K. M.: Reduced renin activity in essential hypertension: a reappraisal—Kidney int.13, 513, 1978.
Zucchelli P., Catizone L., Degli Esposti E., Fusaroli M., Ligabue A., Zuccala A.: Influence of ultrafiltration on the plasma renin activity and the adrenergic system. In: The 2nd Garda Meeting on new dialysis techniques and hemoperfusion. May 20, 1977. Opuscula medico-technica Lundensia, vol. 18.
Zucchelli P., Catizone L., Degli Esposti E., Fusaroli M., Ligable A., Zuccala A.: Influence of ultrafiltration on the plasma renin activity and the adrenergic system—Nephron21, 317, 1978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esposti, E.D., Chiarini, C., Gattiani, A. et al. Plasma renin activity in essential hypertension. La Ricerca Clin. Lab. 9, 147–153 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02904912
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02904912