Summary
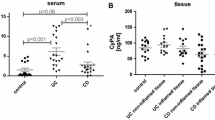
In order to study the clinical significance and change of interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 concentration in intestinal mucosal tissues in various stage of ulcerative colitis (UC), IL-1β and IL10 levels were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). Our results showed that IL-β level caused by spontaneous secretion in the intestinal mucous tissues in active stage of ulcerative colitis was significantly higher than that in normal controls and in remission stage of ulcerative colitis (P <0. 01,P<0. 001). IL-10 level in various stage of UC was relatively lower in controls, but there was no significantly difference between the two groups. Our study suggested that higher IL-1β level in active might play an important role in pathogenesis of UC, and IL-10, as an anti-inflammatory cytokine, was low in active UC, suggesting that it may be a important factor contributing to the development of higher IL-1β level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herfarth H H, Bocher U, Janardhanam Ret al. Subtherapeutic corticostevoids potentiate the ability of interleukin 10 to prevent chronic inflammation in rates. Gastroenterology, 1998, 115:856
Strong S A, Pizarro T T, Klein J Set al. Proinflammatory cytokines differentially modulate their own expression in human intestinal mucosal mesenchymal cells. Gastroenterology, 1998, 114:1244
Nikolaus S, Bauditz J, Giouchettii Pet al. Increased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytkines by circulating Polymorphnuclear neutrophils and regulation by interleukin 10 during intestinal inflammation. Gut, 1998, 42:470
1994,2(1)57
Mahida Y R, Wu K, Jewell D P. Enhanced production of interlukin-1β in mononuclear cells isolated from mucosa with active ulcerative colitis and crohn’s disease. Gut, 1989, 30:835
Fiorentino D F, Zlotnik A, Vieira Pet al. IL-10 acts on the antigen presenting cell to inhibit cytokine production by Th1 cells. J Immunol, 1991, 146(10):3444
Nielsen O H, Koppen T, Rudiger Net al. Involvement of interleukin 4 and interleukin 10 in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci, 1996, 41(9)1786
Schreiber S, Heinig T, Thieve H Get al. Immunoregulatory role of interleukin 10 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology, 1995, 108(5): 1434
Steidler L, Hans W. Treatment of murine colitis by Iactococcus Iactis secreting interleukin-10. Science, 2000, 289:352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was supported by the grant of the Scientific Research Fund of the Ministry of Health (No. 98-2-387).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaifang, Z., Shi, L., Xiaoping, X. et al. Clinical significance and assessment of cytokines in various stages of ulcerative colitis. Current Medical Science 21, 308–309 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02886564
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02886564