Summary
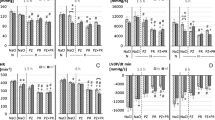
The role of histamine in acute hypoxic pulmonary hypertension was studied in dogs, and the correlation between the effect of histamine and the characteristics of hypoxic pulmonary response was examined. Acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstrictive response was not blocked by H1-receptor antagonist, but was potentiated by H2-receptor antagonist. Combined H1- and H2-receptor blockade failed to modify the hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. It seems that H1-receptor antagonist could abolish the potentiating effect of H2-receptor antagonist. Exogenous histamine dilated lung vessels when pulmonary vascular tone was increased. This is in contrast to its vasoconstrictive effect when pulmonary vascular tone was normal. The vasodilating effect of histamine was blocked by H2-receptor antagonist. It is deduced that histamine probably plays the role of a modulator in hypoxic pulmonary vascular response. The dominant effect of H2-receptor caused by increasing pulmonary vascular tone might be implicated in the modulating effect. Infusion of histamine not only suppressed the pulmonary response to hypoxia, but also attenuated the progressive increase in pulmonary vascular resistance in repeated hypoxia. The reduction of the modulating effect of histamine probably contributes to the progressive increase in pulmonary vascular response to repeated hypoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergofsky EA, et al. Mechanism underlying vascular motor regulation of regional pulmonary blood flow in normal and diseased status. Am J Med 1974; 7:378–94.
Fishman AP. Vasomotor regulation of the pulmonary circulation. Ann Rev Physiol 1980; 42:211–20.
Fishman AP. Hypoxia on the pulmonary circulation; How and where it acts. Circ Res 1976; 38:221–31.
Giordano J, et al. Effect of H1 and H2 histamine antagonists on the pulmonary pressor response to alveolar hypoxia. J Surg Res 1977; 22:392–99.
Hauge A, et al. Role of histamine in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in the rats: I. Blockade or potentiation of endogenous amine kinin and ATP. Circ Res 1968; 23:371–83.
Howand P, et al. Factors causing and reversing vasoconstriction in unventilated lung. Respir Physiol 1975; 24:325–45.
Hoffman EA, et al. Histamine H1 and H2 receptors in the cat and their roles during alveolar hypoxia. Respir Physiol 1977; 29:255–64.
Levasseur JE, et al. Circulatory effects of prolonged hypoxia before and during antihistamine. J Appl Physiol 1976; 40: 549–58.
Miller MA, et al. Stability of alveolar hypoxic vasoconstriction with intermittent hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 1980; 49:846–50.
Newman JH, et al. Postnatal change in response of canine neonatal pulmonary artery to histamine. Am J Physiol 1979; 237:H76-H82.
Susmano A, et al. Effects of antihistamine drugs on hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Cardiol 1973; 31:718–23.
Susmano A, et al. Prevention of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by chlorpheniramine. J Appl Physiol 1971; 31:531–35.
Tucker A, et al. Failure of histamine antagonists to prevent hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in dogs. J Appl Physiol 1976; 40:496–500.
Tucker A, et al. Histamine H1- and H2- receptors in the pulmonary and systemic vessels of the dogs. Am J Physiol 1975; 229:1008–13.
Unger M, et al. Potentiation of pulmonary vasoconstrictor response with repeated intermittent hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 1977; 43:662–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ai-ping, Z., Di-xun, W., Chang-jian, F. et al. The role of histamine in acute hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in dogs. Acta Academiae Medicinae Wuhan 4, 50–55 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856951
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856951