Abstract
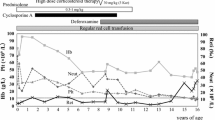
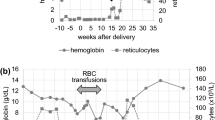
Five patients between 3 to 54 months of age presented with normocytic anemia with erythroblastopenia. All of them had normal milestones without any developmental delay or physical anomalies. Inheritance appeared to be autosomal recessive in one case. Of the four patients treated, two responded to corticosteroids, of which one developed late resistance. One patient responded to oxymetholone and the other was refractory to both cortico-steroids and androgen therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaznelson P: Zur Entstehung der Blutplattchen.Ver Dtsch Ges Int Med 34: 557, 1922
Diamond LK, Blackfan KD: Hypoplastic anemia.Am J Dis Child 36: 464, 1938
Alter BP, Rappaport JM, Parkman R: The bone marrow failure syndromes. In:Hematology of infancy and childhood. Nathan DG and Oski FA (eds.) WD Saunder Company, Philadelphia, 1981 p 168
Falter ML, Robinson MG: Autosomal dominant inheritance and aminoaciduria in Blackfan-Diamond anemia.J Med Genet 9: 64, 1972
Khatua SP: Congenital hypoplastic anemia (pure red cell type).Indian Pediatr 1: 278, 1964
Tada K, Kudo Tet al: Anemia congonitale hypoplastique.Arch Franc Pediatr 15: 183, 1958
Van Wed Sipman, Van De Kamp JJP, Koning Jde: A female patient with “Aase-Syndrome”.J Pediatr 91: 753, 1977
Giblett ER, Varela JE, Finch CA: Damage of bone marrow due to Rh antibody.Pediatrics 17: 37, 1956
Ortega JA, Shore NA, Duke PP, Hammond D: Congenital hypoplastic anemia: inhibition of erythropoiesis by sera from patients with congenital hypoplastic anemia.Blood 45: 83, 1975
Hoffman R, Zanjani ED, Zalusky JVR, Lutton JD, Wasserman LR: Diamond Blackfan syndrome, Lymphocyte mediated suppression of erythropoiesis.Science 193: 899, 1976
Diamond LK, Wang WC, Alter BP: Congenitalhy poplastic anemia.Adv Pediatr 22: 349, 1976
Freedman MH, Amato D, Saunders EF: Heme synthesis in the Diamond-Blackfan syndrome.Br J Hematol 31: 515, 1975
Nathan DG, Clarke BJ, Hillman DG, Alter BP, Houseman D: Erythroid precursors in congenital hypoplastic (Diamond Blackfan) anemia.J Clin Invest 61: 489, 1978
Freedman MH, Saunders EF: Diamond Blackfan syndrome: Evidence against cell mediated erythropoitic suppression.Blood 51: 1125, 1975
Steinberg MH, Coleman MF: Diamond Blackfan syndrome: Evidence for T cell mediated suppression of erythroid development and a serum blocking factor associated with remission.Br J Hematol 41: 57, 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, R.K., Moudgil, A., Pati, H. et al. Congenital pure red cell aplasia in northern India. Indian J Pediatr 52, 97–102 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02754728
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02754728