Abstract
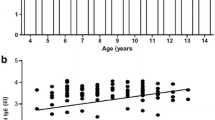
Objective : To study the serum Ig E levels in patients presenting with wheezing under the age of 24 months.Methods : The study was conducted on 38 cases and 35 controls. The children presenting with first attack of wheezing were clinically considered as bronchiolitis and those with recurrent attacks with positive history of atopy in the patient or in their first degree relatives were considered as bronchial asthma. The Ig E estimation was done by immune assay method.Results : The mean serum Ig E was significantly higher in asthma patients (p<0.001). It was also higher in bronchiolitis patients but the difference was not statistically significant. However, 26 per cent of these patients had values above 1 SD of the control mean. These patients were considered as potential cases of asthma.Conclusion : The determination of serum Ig E may be of value in identifying those children presenting with first wheezing attack, who may develop asthma in future. Only a long-term follow-up of these patients can give an answer to the postulation that raised Ig E level at the time of first viral lower respiratory tract infection is a potential marker for the development of recurrent wheezing in later life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar L, Newcomb RW, Ishizaka K, Middleton E, Hornbrook MM. Ig E levels in sera of children with asthma.Pediatrics 1971; 47: 848–856.
Najam FI, Giasuddin AS, Shembesh AH. Immunoglobulin isotypes in childhood asthma.Indian J Pediatr 1999; 66: 337–344.
Johansson SGO. Raised levels of a new immunoglbbulin class (Ig ND) in asthma.Lancet 1967; 2: 951–953.
Vazquez Nava F, Rodriguez Sanchez A, Beltran Guzman FJ. Clinical analysis of the serum 1evels of Ig E in pediatric asthmatic patients.Rev Alerg Mex 1998; 45: 3–6.
Sears MR, Burrows B, Flannery EM, Herbison GP, Hewitt CJ, Holdaway MD. Relationship between airway responsiveness and serum Ig E in children with asthma and in apparently normal children.N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 1067–1071.
Polmer SH, Robinson LD, Minnefor AB, Immunoglobulin E in bronchiolitis.Pediatrics 1972; 50: 279–285.
Wittig, HJ, Cranford NJ, Glaset J. The relationship between bronchiolitis and childhood asthma.J Allerg, 1959; 30: 19–23.
Eisen AH, Bacal HL. The relationship of acute bronchiolitis to bronchiolitis.Pediatrics 1963; 31: 859–861.
Martinez FD, Stem DA, Wright AL, Taussig LM, Halonen M. Differential immune responses to acute lowei respiratory illness in early life and subsequent development of persistent wheezing and asthma.J Allerg Clin Immunol 1998; 102: 915–920.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, B.K., Kumar, S., Panda, B.K. et al. Serum immunoglobulin E in early childhood wheezing. Indian J Pediatr 70, 213–215 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02725585
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02725585