Abstract
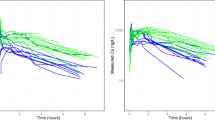
The volume of distribution (Vd) of theophylline and the relevant aminophylline loading dose (LD) are usually calculated on the basis of total body weight (TBW). In obese subjects it has been suggested that lean or ideal body weight (IBW) is the best predictor. In a sample of 40 acutely ill asthmatic patients (aged 22 to 78 yr, weighing 45 to 176 kg) we measured Vd and found that (1) it increases with TBW, (2) it cannot be accurately predicted from either TBW or IBW alone by a simple regression analysis. Power functions have been usefully applied in comparing the pharmacokinetics of animal species, including humans, with different body mass. In our sample, data were best fitted by the equation Vd = 1.29 TBW0.74, which seems to take care of lean as well as obese patients. Results were confirmed (r = 0.89 between predicted and measured values) in a second independent sample of patients (aged 26 to 77 yr, weighing 38 to 167 kg). This helps to minimize the error in obtaining the target serum concentration of theophylline when giving a LD calculated from a predicted Vd value.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen HD, Whitsett TL (1979) Measurement of xanthines and their metabolites by means of high pressure liquid chromatography. Chromat Sciences Series 10:507–535
Dedrick RL, Bischoff KB (1980) Species similarities in pharmacokinetics. Fed Proc 39:54–59
Draper N, Smith H (1981) Applied regression analysis, second edition. Wiley, New York
Gal P, Jusko WJ, Yurchak AM, Franklin BA (1978) Theophylline disposition in obesity. Clin Pharmacol Ther 23:438–444
Jewesson PJ, Ensom RJ (1985) Influence of body fat on the volume of distribution of theophylline. Ther Drug Monitor 7:197–201
Metropolitan Insurance Company (1982) Weight tables. New York
Ogilvie RI (1978) Clinical pharmacokinetics of theophylline. Clin Pharmacokinet 3:267–293
Rohrbaugh TM, Danish M, Ragni MC, Yaffe SJ (1982) The effect of obesity on apparent volume of distribution of theophylline. Pediatric Pharmacol 2:75–83
Samoszuk M, Kaplan E, Finkle HI (1983) Serum theophylline assay by rate nephelometric inhibitor immunoassay: a comparison with high performance liquid chromatography. Ther Drug Monitor 5:113–116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rizzo, A., Mirabella, A. & Bonanno, A. Effect of body weight on the volume of distribution of theophylline. Lung 166, 269–276 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02714057
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02714057