Abstract
Background
HER2/neu encodes a receptor related to breast cancer pathogenesis and topoisomerase IIα is an enzyme involved in response to anthracycline chemotherapy. The aim of this study is to analyse HER2/neu and topoisomerase IIα in a homogenous series of 49 patients with locally-advanced breast cancer (LABC) to determine their status and predictive value with respect to response to treatment.
Material and methods
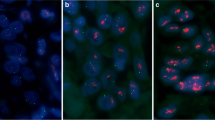
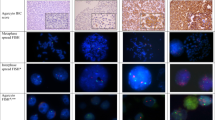
Paraffin-embedded tissues samples from patients with LABC (prior to their neoadjuvant chemotherapy programme) were analysed using the FISH technique.
Results
HER2 amplification was noted in 29% of cases of which 77% presented amplification in the topoisomerase IIα gene, 15% had deletion and 8% did not show any aberration in topoisomerase IIα status.
Conclusions
These preliminary analyses show a correlation between HER2 amplification and topoisomerase IIα status (92%), and suggest that patients with non-amplified HER2/neu or topoisomerase IIα have better response and have and increase (albeit not statistically significant) in disease-free survival (DFS). However, the limited numbers of patients in the study preclude definitive conclusion regards the value of these genes in predicting patient response to anthracycline-based chemotherapy.
Resumen
Introducción
HER2/neu codifica para un receptor implicado en la patogénesis del cáncer de mama y topoisomerase IIα es una enzima que se ha relacionado con la respuesta a antraciclinas. El objetivo del estudio es analizar HER2/neu y topoisomerasa IIα en una serie homogénea de 49 pacientes diagnosticadas de cáncer de mama localmente avanzado (CMLA) para determinar la correlación entre ambos genes así como evaluar su valor predictivo.
Material y métodos
Se estudiaron por FISH muestras en parafina previas al tratamiento neoadyuvante con antraciclinas.
Resultados
El 29% de los casos presentó amplificación de HER2/neu, de los cuales el 77% mostraba amplificación de topoisomerasa IIα, el 15% deleción y el 8% no tenía alteraciones en elstatus de este gen.
Conclusiones
Existe una correlación de un 92% entre la amplificación de HER2/neu y la alteración delstatus de topoisomerasa IIα. Nuestros resultados sugieren que pacientes sin amplificación de estos genes muestran una tendencia a una mejor tasa de respuestas globales y una mejor supevvivencia libre de enfermedad (SLE) que los pacientes con coamplificación, pero el limitado número de pacientes impide establecer una conclusión definitiva sobre el valor predictivo de estos genes en respuesta a antraciclinas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolff AC, Davidson NE. Primary systemic therapy in operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2000;18:1558–69.
Makris A, Powles TJ, Dowsett M, et al. Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in primary breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 1997;3:593–600.
Baselga J, Tripathy D, Mendelsohn J, et al. Phase II study of weekly intravenous recombinant humanized anti-p185HER2 monoclonal antibody in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastasic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 1996;14:737–44.
Cobleigh MA, Vogel CL, Tripathy D, et al. Multinational study of efficacy and safety of humanized anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody in women who have HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer that progressed after chemotherapy for metastatic disease. J Clin Oncol 1999;17:2639–48.
MacGrogan G, Mauriac L, Durand M, et al. Primary chemotherapy in breast invasive carcinoma: Predictive value of the immunohistochemical detection of hormonal receptors, p53, c-erb B2, MiB1, p52 and GSTpi. Br J Cancer 1996;74:1458–65.
Yamuchi H, Stearns V, Hayes DF. When is a tumour marker ready for prime time? A case study of c-erbB2 as a predictive factor in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:2334–56.
Jarvinen TA, Tanner M, Rantanen V, et al. Amplification and deletion of topoisomerase II associate with ErbB2 amplification and effect sensitivity to topoisomerase II inhibitor doxorubicin in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 2000;156:839–47.
Moulder SL, Yakes FM, Muthuswamy SK, Bianco R, Simpson JF, Arteaga CL. Epidermial growth factor receptor (HER1) tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa) inhibits HER2/neu (erbB2)-overexpressing breast cancer cellsin vitro andin vivo. Cancer Res 2001;61:8887–95.
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, et al. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER2/neu oncogene. Science 1987;235: 177–235.
Borg A, Tandon AK, Sigurdsson H, et al. HER2/neu amplification predicts poor survival in node-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res 1990;50:4332–7.
Pegram MD, Lipton A, Hayes DF, et al. Phase II study of receptor-enhanced chemosensitivity using recombinant humanized antip 185 HER2/neu monoclonal antibody plus cisplatin in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer refractory to chemotherapy treatment. J Clin Oncol 1998;23:1141–50.
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, et al. Studies of the HER2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1989;244:707–12.
Tanner M, Jarvinen P, Isola J. Amplification of Her2/neu and topoisomerase II in primary and metastasisc breast cancer. Cancer Res 2001;61:5345–8.
Di Leo A, Gancberg D, Larsimont D, et al. HER2 amplification and topoisomerase IIα gene aberration as predictive markers in node positive breast cancer patients randomly treated either with anthracycline-based therapy or with cyclophosphamide, methrotexane and 5-fluorouracil. Clin Cancer Res 2002;8:1107–16.
Jarvinen T, Liu ED. HER2/neu and topoisomerase IIα in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2003;78:299–311.
Coon JS, Marcus E, Gupta-Burt S, et al. Amplification and overexpression of topoisomerase IIα predict response to anthracycline-based therapy in locally advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2002;8:1061–7.
Salido M, Solé F, Tusquets I, et al. A comparative study of HER2/neu amplification and overexpression using fluorescencein situ hybridization (FISH) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) in 101 breast cancer patients. Rev Oncol 2002;4:255–9.
Cianciulli AM, Botti C, Coletta AM, et al. Contribution of fluorescencein situ hybridisation to immunohistochemistry for the evaluation of HER2 in breast cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2002;133:66–71.
Rudolph P, MacGrogan G, Bonichon F, et al. Prognostic significance of Ki-67 and topoisomerase IIα expression in infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1999;55:61–71.
Depowski P, Rosental SI, Brien TP, et al. Topoisomerase IIα expression in breast cancer: correlation with outcome variables. Mod Pathol 2000;13:542–7.
Smith K, Houlbrook S, Greenall M, et al. Topoisomerase II alpha co-amplification with erbB2 in human primary breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines: relation to m-AMSA and mitoxantrone sensitivity. Oncogene 1993;8: 933–8.
Keith WN, Douglas F, Wishart GC, et al. Co-amplification of erbB2, topoisomerase II alpha and retinoic acid receptor alpha genes in breast cancer and allelic loss at topoisomerase I on chromosome 20. Eur J Cancer 1993; 29:1469–75.
Takano H, Ise T, Nomoto M, et al. Structural and functional analysis of the control region of human DNA topoisomerase II alpha gene in drug-resistant cells. Anticancer Drug Des 1999;14:87–92.
Takano H, Khono K, Matsuo T, et al. DNA topoisomerase-targeting antitumor agents and drug resistance. Anticancer Drugs 1992;3:323–30.
Harris LN, Yang L, Liotcheva V, et al. Induction of topoisomerase II activity after erbB2 activation associated with a differential response to breast cancer chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2001;7:1497–504.
Di Leo A, Isola J. Topoisomerase IIα as a marker predicting the efficacy anthracyclines in breast cancer: are we at the end of the beginning? Clin Breast Cancer 2003;4: 179–86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Contero, C.C., Trias de Bes, I.T., Galeote, M.S. et al. Characterization of HER2/neu and topoisomerase IIα status by FISH in locally advanced breast cancer. Rev Oncol 6, 289–294 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02711836
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02711836