Abstract
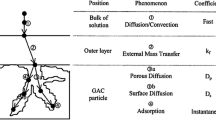
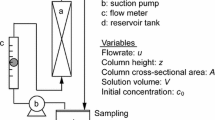
A fixed bed is gradually exhausted from top to bottom without backwashing; however, backwashing can rearrange the concentration gradient in the bed. After backwashing, saturated particles which are located at the top of the bed are homogeneously distributed in the bed. The used model to predict adsorption and backwashing effect of organic component is the plug flow pore surface diffusion model (PFPSDM). A sensitivity analysis was performed to determine which parameters have the greatest impact on the model results for components which can represent various organics. In addition, the effects of backwashing were examined by rearranging concentration gradient. For single component sensitivity analysis, the molecular weight was an important parameter. The breakthrough of the smaller molecular weight component was impacted more by backwashing. The SPDFR showed a significant impact on the breakthrough pattern. When surface diffusion was the dominant mechanism, high SPDFR, the breakthrough profile was sharper than when pore diffusion was dominant, low SPDFR. The adsorbability was an important parameter in determining the breakthrough pattern. As expected, the strongly adsorbable component showed the later breakthrough. Backwashing yielded earlier breakthrough for all single components and multi-components examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman, G.,Mathematical modeling of multicomponent adsorption in batch and fixed-bed reactors, MS Thesis, Michigan Technological Univ. Ann Arbor, Michigan. US (1984).
Hong, S., “The role of pH and initial concentration on GAC adsorption for removal of natural organic matter,”J. of Environ. Eng. Res.,3, 183(1998).
Kim, S. H., Kim, T. W., Cho, D. L., Lee, D. H., Kim, J. C. and Moon, H., “Application of characterization procedure in water and waste-water treatment by adsorption,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 895 (2002).
Radke, C. J. and Prausnitz, J. M., “Adsorption of organic solutes from dilute aqueous solution on activated carbon,”Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund.,11, 445(1972).
Randtke, S. J. and Snoeyink, V. L., “Evaluating GAC adsorptive capacity,”J. of AWWA,75, 406 (1983).
Shim, W. G., Chaudhary, D. S., Vigneswaran, S., Ngo, H.-H., Lee, J. W. and Moon, H., “Mathematical modeling of granular activated carbon (GAC) biofiltration system,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,21, 212 (2004).
Sontheimer, H., Crittenden, J. C. and Summers, R.,Activated carbon for water treatment, DVGW Forschungsstelle, Karlsruhe, Germany (1988).
Vaith, K.,Predicting the removal of organic carbon with fixed bed adsorbers, M.S., Thesis, Michigan Technological Univ. Houghton, MI (1988).
Vaith, K., Crittenden, J. C., Hand, D., Wallace, D. E., Aieta, E. M. and Tate, C.,Design of fixed-bed adsorbers to remove natural organic matter, Proceedings, AWWA Annual Conference, Orlando, FL, June 19–23 (1988).
Yuasa, A.,A kinetic study of activated carbon adsorption processes, Ph.D Diss., Hokkaido Univ., Sapporo, Japan (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, S., Summers, R.S. Effect of backwashing on activated carbon adsorption using plug flow pore surface diffusion model. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 23, 57–62 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705692
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705692