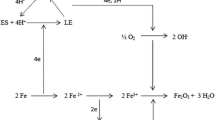
Abstract
The objective of this work was to evaluate the performance of calcium tripolyphosphate in anticorrosive paints. Its anticorrosive properties were studied in pigment suspensions and in solventborne paints with 10% and 30% of the pigment by volume and a pigment volume concentration/critical pigment volume concentration (PVC/CPVC) equal to 0.8. The behavior of paints formulated with epoxy and alkyd resins was assessed by accelerated (salt spray cabinet and humidity chamber) and electrochemical tests (corrosion potential, ionic resistance, and polarization resistance).
Calcium tripolyphosphate was proven to inhibit steel corrosion when incorporated in a paint film. Good protection was achieved employing only 10% by volume of the pigment, instead of 30%, as was suggested in the case of phosphates. The anticorrosion protection afforded by alkyd paints was impaired when the pigment content was increased. Epoxy paints seemed to be less sensitive to the pigment content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romagnoli, R. and Vetere, V.F., “Non-Pollutant Corrosion Inhibitive Pigments: Zinc Phosphate: A Review,”Corr. Rev., 13, No. 1, 45 (1995).
del Amo, B., Romagnoli, R., and Vetere, V.F., “Study of the Anticorrosive Properties of Zinc Phosphate and Zinc Molybdophosphate in Alkyd Paints,”Corr. Rev., 14 (1–2), 121 (1996).
Chromy, L. and Kaminska, E., “Non-Toxic Anticorrosive Pigments,”Prog. Org. Coat., 18, 319 (1990).
Bittner, A. and Ruf, J., “Testing of Phosphates in Anticorrosive Primers,”Polym. Paint Color J., October, 22 (1997).
Schauer, T., Liu, W.M., and Dulog, L., “Corrosion Protective Pigments: Their Efficiency in Organic and Waterborne Primers,”Eur. Coat. J., 3, 233 (1997).
Nishihara, M., Nakano, G., Kobayashi, M., Nagita, M., and Murakami, M., “Studies on Anticorrosive Properties of Aluminum Triphosphate Pigments,”Polym. Paint Color J., August 22, 590 (1984).
Noguchi, T., Nakano, J., Kobayashi, M., Nagita, M., Kinugasa, M., and Murakami, M., “Studies on Anticorrosive Properties of Aluminum Triphosphate Pigments,”Polym. Paint Color J., December, No. 12/26, 888 (1984).
Krieg, S., “Lead and Chromate Free Anticorrosive Pigments Based on Phosphates,”Pitture Vernici, 72, No. 12, 18 (1996).
Vetere, V.F. and Romagnoli, R., “The Role of Calcium Acid Phosphate as Corrosion Inhibitive Pigment,”Bri. Corros. J., 29, No. 2, 115 (1994).
del Amo, B., Romagnoli, R., and Vetere, V.F., “Steel Corrosion Protection by Means of Alkyd Paints Pigmented with Calcium Acid Phosphate,”Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 38, 2310 (1999).
ASM International Handbook Committee. ASM Handbook, Vol. 13:Corrosion, Control of Environmental Variables in Water-Recirculating Systems, 487 (1987).
Amirudin, A., Barreau, C., Hellouin, R., and Thierry, D., “Evaluation of Anti-Corrosive Pigments by Pigment Extract Studies, Atmospheric Exposure and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy,”Prog. Org. Coat., 25, 339 (1995).
Takahashi, M., “Characteristics and Applications of Aluminum Triphosphate as a Special Chemical,”Polym. Paint Color J., April 18, 281 (1984).
Kamiya, K., Okuda, M., and Okajima, M., “Combination Effect of K-White and Chromate Pigments in Coil Coatings Systems,”Polym. Paint Color J., December, No. 14, 178, 974 (1988).
Ironakano, J., Murakami, M., and Okuda, M., “Aluminum Triphosphate Salt Spray Studies,”Polym. Paint Color J., September, No. 16, 177, 4199, 642 (1987)
Brauer, G.,Química Inorgánica Preparativa, 346, 1958.
Bailar, J.C., Emeléus, H.J., Nyholm, R., and Trotman-Dickenson, A.F. (Eds.),Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry, Chapter 20: “Phosphorous,” 514–519, 1975.
Giudice, C.A., Benitez, J.C., and Rascio, V.J., “Study of Variables Which Affect Dispersion of Antifouling Paints in Ball Mills,”J. Oil Chem. Assoc., 63, No. 4, 153 (1980).
Blustein, G., del Amo, B., and Romagnoli, R., “The Influence of the Solubility of Zinc Phosphate Pigments on Their Anticorrosive Behavior,” to be published inPigment & Resin Technology.
Romagnoli, R. and Vetere, V.F., “Heterogeneous Reaction Between Steel and Zinc Phosphate,”Corrosion, 51, No. 2, 116 (1995).
Pryor, M. J. and Cohen, M., “The Inhibition of the Corrosion of Iron by Some Anodic Inhibitors,”J. Electrochem. Soc., 100, No. 5, 203 (1953).
Cohen, M., “The Breakdown and Repair of Inhibitive Films in Neutral Solutions,”Corrosion, 32, No. 12 (1976).
Deyá, M., Vetere, V.F., Romagnoli, R., and del Amo, B., “Aluminum Triphosphate Pigments for Anticorrosive Paints,” submitted for publication.
Szauer, T. “Electrical and Electrochemical Resistances for the Evaluation of Protective Nonmetallic Coatings,”Prog. Org. Coat., 10, 171 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología de Pinturas (CIC-CONICET), Calle 52 e/121 y 122. (1900) La Plata. Argentina. Fax: 54.221.427. 1537. email: cidepint@ba.net
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vetere, V.F., Deyá, M.C., Romagnoli, R. et al. Calcium tripolyphosphate: An anticorrosive pigment for paint. Journal of Coatings Technology 73, 57–63 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698398
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698398