Abstract
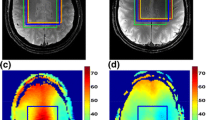
MR spectroscopy of the posterior fossa is pitted with numerous technical difficulties. It is, however, of great clinical interest in the study of the degenerative diseases and tumors of this area. We have developed a method to perform 2D CSI of this area, by using a sagittal slice and a careful positioning of outer volume saturation. We performed this acquisition in 30 healthy volunteers to determine the normal metabolic ratios in five voxels of this area (mesencephalon. pons. medulla oblongata, vermis, cerebellar white matter). The main technical difficulty was magnetic field inhomogeneity in the lower brainstem generated by dental alloys. However, 88% of the voxels were of sufficient quality to be analyzed. The statistically significant regional variations were a higher NAA/Cr ratio in the pons than in the medulla oblongata, higher Cho/Cr in the pons than in the mesencephalon and higher Cho/ Cr in the cerebellar white matter than in the vermis. We conclude that 2D CSI of the brainstem, although technically delicate can be performed in most patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mareci TH, Brooker HR. High-resolution magnetic resonance spectra from a sensitive region defined with pulsed field gradients. J Magn Reson 1984;57:157–63.
Mareci TH, Brooker HR. Essential considerations for spectral localization using indirect gradient encoding of spatial information. J Magn Reson 1991:92:229–46.
Brooker HR, Mareci TH, Mao J. Selective Fourier transformation localization. Magn Reson Med 1987:5:417–33.
Hugg JW, Maudsley AA, Weiner MW, Matson GB. Comparison of k-space sampling for multidimensional MR spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 1996;36:469–73.
Le Fur Y, von Kienlin M. Acquisition weighted chemical shift imaging of the isolated rat heart at 11.7 Tesla. SMRM (third scientific meeting) and ESMRMB (twelfth annual meeting). Nice, France. 19–25 August, 1995.
Hetherington HP, Limey DJE, Vaughan LJ, Pan JW, Ponder SL, Tscendcl O, et al. 3D31P spectroscopic image at 4.1 T. Magn Reson. Med 1995:33:427–31.
Pohmann R, von Kienlin MV. Acquisition-weighted 31P-CSIof the human heart. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 7th Meeting. Philadelphia 22–28 May, 1999.
Köchenberger W, Heidenreich M, Chandrakumar N. Bowtell R. Kimmich R. Dynamic studyof the movement of 31C labelled sucrose in castor bean seedlings by MRI with cyclic J cross polarized transfer (CYCLCROP). Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med 6th, Sydney, 1998.
Weidensteiner C, Lanz T, Horn M, Neubauer S, Haase A. Von Kienlin M. Three-dimensional13C-spectroscopic imaging in the isolated infarct rat heart. J Magn Reson 2000;143:17–23.
Von Kienlin M. Ziegler A, Le Fur Y, Rubin C, Decorps MRC. 2D-Spatial/2D-spectral spectroscopic imaging of intracerebral gliomas in rat brain. Magn Reson Med 2000;43:211–9.
Tkac I, Starcuk Z, Choi IY, Gruetter R. In vivo HNMR spectroscopy of rat brain at 1 ms echo time. Magn Reson Med 1999;41:649–56.
Matson G. An integrated program for amplitude-modulated RF pulse generation and re-mapping with shaped gradients. Magn Reson Imag 1994;12:1205–25.
Pijnapel WWF, Van den Boogart A, De Beer R, Van Ordmond D. SVD-based quantification of magnetic resonance signal. J Magn Reson 1992;97:122–134.
Vanhamme L, Fierro RD, Van Huffel S, De Beer R. Fast removal of residual water in proton spectra. J Magn Reson 1998;132:197–203.
Vanhamme L, Van den Boogart A, Von Huffel S. Improved method for accurate and efficient quantification of MRS data with use of prior knowledge. J Magn Reson 1997:129:35–43.
Detre JA, Wang ZY. Bogdan AR, Gusnard DA, Bay CA, Bingham PM, et al. Regional variation in brain lactate in Leigh’s syndrome by localized1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Ann Neurol 1991;29:218–21.
Pioro EP. MR spectroscopy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis motor neuron disease. J Neurol Sci 1997;152(Suppl l):S49–53.
Tedeschi G, Litvan I, Bonavita S, Bertolino A, Lundbom N, Patronas NJ, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in progressive supranuclear palsy, Parkinson’s disease and corticobasal degeneration. Brain 1997; 120;1541–52.
Haley RW, Marshall WW, McDonald GG. Daugherty MA, Petty F, Fleckenstein JL. Brain abnormalities in Gulf War syndrome: evaluation with1H MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2000;215:807–17.
Mascalchi M, Tosetti M, Plasmati R, Bianchi MC, Tessa C, Salvi F, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in an Italian family with spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Ann Neurol 1998;43:244–52.
Davie CA, Barker GJ, Webb S, Tofts PS, Thompson AJ. Harding AE, et al. Persistent functional deficit in multiple sclerosis and autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia is associated with axon loss [published erratum appears in Brain 1996; Aug:119(Pt 4):1415]. Brain 1995;118:1583–92.
Martin PR, Gibbs SJ. Nimmerrichter AA, Riddle WR, Welch LW, Willcott MR. Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in recently abstinent alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1995;19:1078–82.
Tedeschi G, Bertolino A, Massaquoi SG, Campbell G, Patronas NJ, Bonavita S, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in patients with cerebellar degeneration. Ann Neurol 1996;39:71–8.
Cwik VA, Hanstock CC, Allen PS, Martin WR. Estimation of brainstem neuronal loss in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurology 1998;50:72–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galanaud, D., Le Fur, Y., Nicoli, F. et al. Regional metabolite levels of the normal posterior fossa studied by proton chemical shift imaging. MAGMA 13, 127–133 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02668161
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02668161