Abstract
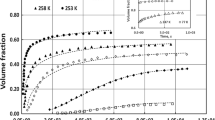
The development of the martensitic microstructure in a 1.86 wt pct C steel has been followed by quantitative metallographic measurements over the transformation range of 0.12 to 0.50 fraction transformed (f). The transformation kinetics are described by the equationf = 1 − exp [−0.008 (M s − Tq)] where Ms and Tq are the martensite start and the quenching temperatures respectively. Fullman’s analysis shows that the average volume per martensite plate decreases by almost an order of magnitude over the transformation range studied, but this decrease is less than that predicted by the Fisher analysis for partitioning of austenite by successive generations of martensite. Microcracking increases with increasingf up to 0.3, but does not increase forf above 0.3 where transformation proceeds by the nucleation of large numbers of small martensite plates. These observations indicate that a critical size of martensite plate is necessary to cause microcracking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Krauss and A. R. Marder:The Morphology of Martensite in Iron Alloys, Met. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2343–58.
D. P. Koistinen and R. E. Marburger:Acta Met, 1959, vol. 7, pp. 59–60.
C. L. Magee:Phase Transformation, ASM, 1970, pp. 115–56.
W. J. Harris and M. Cohen:AIME Trans., 1949, vol. 180, pp. 447–70.
D. G. McMurtrie and C. L. Magee:Met. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 3185–91.
J. C. Fisher, J. H. Hollomon, and D. Turnbull:AIME Trans., 1949, vol. 185, pp. 691–99.
R. Brook and A. R. Entwisle:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, vol. 203, pp. 905–12.
V. Raghavan:Acta Met., 1969, vol. 17, pp. 1299–1303.
V. Raghavan and A. R. Entwisle:Physical Properties of Martensite and Bainite, Special Report No. 93, pp. 30–37, Iron and Steel Inst., 1965.
S. R. Pati and M.Cohen:Acta Met, 1969, vol. 17, pp. 189–99.
A. R. Marder, A. O. Benscoter, and G. Krauss:Met. Trans., 1970, vol. l,pp. 1545–49.
R. L. Fullman:AIME Trans., 1953, vol. 197, pp. 447–52.
A. R. Marder and G. Krauss:Trans. ASM, 1967, vol. 60, pp. 651–60.
A. R. Krause: M.S. Thesis, Wayne State University, 1970.
R. Brook, A. R. Entwisle, and E. F. Ibrahim:J. Iron Steel Inst, 1960, vol. 195, pp. 292–98.
A. R. Entwisle:Met. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2395–2408.
E. S. Davenport, E. L. Roff, and E. C. Bain:Trans. ASM, 1934, vol. 22, pp. 289–310.
A. H. Rauch and W. R. Thurtle:Metals Progr., April 1956, vol. 69, pp. 73–76.
R. G. Davies and C. L. Magee:Met. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 307–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Postdoctoral Fellow at Lehigh University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendiratta, M.G., Krauss, G. The development of martensitic microstructure and microcracking in an Fe-1.86C alloy. Metall Trans 3, 1755–1760 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02642557
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02642557