Summary
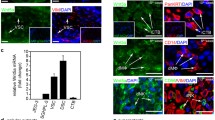
Using five trophoblast cell lines of different differentiation status, we have shown that trophoblasts could constitutively release the transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGFβ1), but not TGFβ2. Treatment of the human tumorigenic, TL, and BeWo cells with a differentiating agent and a potent protein kinase C activator—the tumor-promoting agent—or the JEG-3 cells with cholera toxin—a potent cyclic adenosine 3′:5′ monophosphate (cAMP) inducer—or its analogue 8-bromo-cAMP, potentiates TGFβ production, but the two signaling pathways appear to be mutually exclusive. Surprisingly, the JAR cell line failed to respond to either type of TGFβ activator. Based on reverse transcriptase (RT)-polymerase chain reaction (PCR), it was found that only the JAR cell line expressed messenger ribonucleic acid for decorin, a natural inhibitor of TGFβ, and none of the cell lines had detectable protein expression as determined by immunocytochemical studies. The cell number in cultures with decorin was invariably lesser than in those without decorin under serum-free conditions for all the cell lines tested. These results suggest that TGFβ may act as an autocrine-survival factor for transformed trophoblasts by allowing the cells to survive longer under a microenvironment which is not favorable for growth. Lastly, our results indicate that decorin, acting in a paracrine manner, may also play an important negative regulatory role in the development of transformed trophoblasts by sequestering TGFβ, thereby preventing its action.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altomonte, M.; Montagner, R.; Fonsatti, E., et al. Expression and structural features of endoglin (CD105), a transforming growth factor β1 and β3 binding protein, in human melanoma. Br. J. Cancer 74:1586–1591 1996.
Asundi, V. K.; Dreher, K. L. Molecular characterization of vascular smooth muscle decorin: deduced core protein structure and regulation of gene expression. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 59:314–321; 1992.
Böl, G. F.; Gros, C.; Hülster, A., et al. Phorbol ester-induced sensitisation of adenylyl cyclase type II is related to phosphorylation of threonine 1057. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 237:251–256; 1997.
Burnside, J.; Nagelberg, S. B.; Lippman, S. S., et al. Differential regulation of hCGα and β subunit in RNAs in JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells by 8-bromo-cAMP. J. Biol. Chem. 260:12,705–12,709; 1985.
Caniggia, I.; Taylor, C. V.; Ritchie, J. W. K., et al. Endoglin regulates trophoblast differentiation along the invasive pathway in human placental villous explants. Endocrinology 138:4977–4988; 1997.
Chantry, D.; Turne, M.; Abney, E., et al. Modulation of cytokine production by transforming growth factor-β1. J. Immunol. 142:4295–4300; 1989.
Chou, J. Y. Effects of adenosine cyclic nucleotides on the synthesis of human chorionic gonadotropin in transformed human placental cells. Cancer Res. 40:4025–4030; 1980.
Dyne, K. M.; Valli, M.; Forlino, A., et al. Deficient expression of the small proteoglycan decorin in a case of severe/lethal osteogenesis imperfecta. Am. J. Med. Genet. 63:161–166; 1996.
Ganguly, N. K.; Kaur, T. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin & other toxins. Indian J. Med. Res. 104:28–37; 1996.
Graham, C. H.; Connelly, I.; MacDougall, J. R., et al. Resistance of malignant trophoblast cells to both the anti-proliferative and anti-invasive effects of transforming growth factor-β. Exp. Cell Res. 214:93–99; 1994.
Graham, C. H.; Lala, P. K. Mechanisms of placental invasion of the uterus and their control. Biochem. Cell Biol. 70:867–874; 1992.
Graham, C. H.; Lysiak, J. J.; McCrae, K. R., et al. Localization of transforming growth factor-β at the human fetal-maternal interface: role in trophoblast growth and differentiation. Biol. Reprod. 46:561–572; 1992
Grande, J. P. Role of transforming growth factor-beta in tissue injury and repair. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 214:27–40; 1997.
Ho, C. K.; Chiang, H.; Li, S. Y., et al. Establishment and characterization of a tumorigenic trophoblast-like cell line from a human placenta. Cancer Res. 47:3220–3224; 1987.
Ho, C. K.; Wang, C. C.; Li, S. Y., et al. Characterization of a human tumorigenic poorly differentiated trophoblast cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 30A:415–417; 1994.
Hurley, J. H. Structure, mechanism, and regulation of mammalian adenyl cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 274:7599–7602; 1999.
Iozzo, R. V. The biology of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 274:18,843–18,846; 1999.
Iozzo, R. V.; Moscatello, D. K.; McQuillan, D. J., et al Decorin is a biological ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 274:4489–4492; 1999.
Koli, K.; Keski-Oja, J. Transforming growth factor-beta system and its regulation by members of the steroid-thyroid hormone superfamily. Adv. Cancer Res. 70:63–94; 1996.
Krusius, T.; Ruoslahti, E. Primary structure of an extracellular matrix proteoglycan core protein deduced from cloned cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:768307687; 1986.
Laiho, M.; Keski-Oja, J. Growth factors in the regulation of pericellular proteolysis: a review. Cancer Res. 49:2533–2553; 1989.
Lang, A. K.; Searle, R. F. The immunomodulatory activity of human amniotic fluid can be correlated with transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) and β2 activity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 97:158–163; 1994.
Lastres, P.; Letamendia, A.; Zhang, H., et al. Endoglin modulates cellular responses to TGF-β1. J. Cell Biol. 133:1109–1121; 1996.
Leof, E. B.; Porper, J. A.; Goustin, A. S., et al. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor-β: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:2453–2457; 1986.
Lin, H. Y.; Moustakas, A. TGF-beta receptors: structure and function. Cell. Mol. Biol. 40:337–349; 1994.
Loke, Y. W. Experimenting with human extravillous trophoblast: a personal view. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 24:22–28; 1990.
Lysiak, J. J.; Hunt, J.; Pringle, G. A., et al. Localization of transforming growth factor β and its natural inhibitor decorin in the human placenta and decidua throughout gestation. Placenta 16:221–231; 1995.
Massague, J. TGFβ signaling: receptors, transducers, and Mad proteins. Cell 85:947–950; 1996.
McCartney-Francis, N. L.; Wahl, S. M. Transforming growth factor beta: a matter of life and death. J. Leukoc. Biol. 55:401–409; 1994.
Mitchell, E. J.; Fitz-Gibbon, L.; O'Connor-McCourt M. D. Subtypes of betaglycan and of type I and type II transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) receptors with different affinities for TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 are exhibited by human placental trophoblast cells. J. Cell Physiol. 150:334–343; 1992.
Morrish, D. W.; Dakour, J.; Li, H. Functional regulation of human trophoblast differentiation. J. Reprod. Immunol. 39:179–195; 1998.
Mossman, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assay. J. Immunol. Methods 65:55; 1983.
Nash, M. A.; Loercher, A. E.; Freedman, R. S. In vitro growth inhibition of ovarian cancer cells by decorin: synergism of action between decorin and carboplatin. Cancer Res. 59:6192–6196; 1999.
Ritvos, O.; ErÄmaa, M. Adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate and phorbol ester induce transforming growth factor-β1 messenger ribonucleic acid levels in choriocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology 129:2240–2245; 1991.
Roberts, A. B.; Anzano, M. A.; Wakefield, L. M., et al. Type β transforming growth factor: a bifunctional regulator of cellular growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:119–123; 1985.
Roberts, A. B.; Sporn, M. B. Physiological actions and clinical applications of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). Growth Factors 8:1–9; 1993.
Santra, M.; Skoroski, T.; Calabretta, B., et al. De novo decorin gene expression suppresses the malignant phenotype in human colon cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:7016–7020; 1995.
Shibamoto, S.; Hayakawa, M.; Hori, T. et al. Hepatocyte growth factor and transforming factor-β stimulate both cell growth and migration of human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Struct. Funct. 17:185–190; 1992
Ständer, M.; Naumann, U.; Wick, W., et al. Transforming growth factor-β and p-21: multiple molecular targets of decorin-mediated suppression of neoplastic growth. Cell Tissue Res. 296:221–227; 1999.
Yamaguchi, Y.; Mann, D. M.; Ruoslahti, E. Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-β by the proteoglycan decorin. Nature 346:281–284; 1990.
Yamashita, H.; Ichijo, H.; Grimsby, S., et al. Endoglin forms a heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors for transforming growth factor-β. J. Biol. Chem. 269:1995–2001; 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, CK., Au, LC., Peng, HJ. et al. Transforming growth factor beta may act as an autocrine-survival-promoting factor for transformed trophoblasts. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 37, 245–250 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577537
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577537