Summary
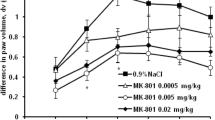
Intracerebroventricularly (icv) administered met-enkephalin, leuenkephalin, and morphine induced dose-related attenuation of carrageenin-induced acute paw oedema in rats. Naloxone (10 μ, icv) antagonized the anti-inflammatory effects of the enkephalins (20 μg) and morphine (20 μg), but itself induced an anti-inflammatory effect at a higher dose (50 μg, icv). The anti-inflammatory effects of the enkephalins, morphine, and the high dose of naloxone were significantly inhibited by metyrapone, an inhibitor of endogenous corticoid synthesis. The icv-administered doses of the enkephalins and morphine induced insignificant inflammation-attenuating effects when administered i.p. Results suggest that the anti-inflammatory effects of the enkephalins and morphine are exerted through central opiate receptors. Furthermore, the inflammation-attenuating effects of these drugs and the higher dose of naloxone appear to be dependent upon endogenous corticoids, suggesting that activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis may be involved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrigo-Reina R, Ferri S (1980) The opioid peptidergic system may be involved in the control of inflammatory reactions. Adv Pharmacol Res Pract 5:223–226
Basbaum AI, Fields HL (1984) Endogenous pain control systems: brain stem spinal pathways and endorphin circuitary. Annu Rev Neurosci 7:309–338
Bhattacharya SK, Dasgupta G (1988) Central modulation of peripheral inflammation. Indian J Exp Biol 26:77–84
Bhattacharya SK, Das Neeta, Sarkar MK (1987) Inhibition of carrageenin-induced pedal oedma in rats by immobilization stress. Res Exp Med 187:303–313
Bonta IL (1978) Endogenous modulators of the inflammatory response. In: Vane JR, Ferreira SH (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology (vol 50/I). Springer. Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 523–567
Domenjoz R (1966) Synthetic anti-inflammatory drugs: concepts of their mode of action. Adv Pharmacol 4:143–217
Feldberg W, Lotti VJ (1967) Temperature responses to monoamines and an inhibitor of MAO injected into the cerebral ventricles of rats. Br J Pharmacol 31:152–161
Ferri S, Arrigo-Reina R, Scoto G, Spadaro C, Spampinato S (1980) The role of peptidergic system in body reactivity. In: Costa E, Trabucchi M (eds) Neural peptides and neuronal communications. Raven Press, New York. pp 347–351
Furst S, Gyires K (1989) Central and peripheral analgesic actions of morphine compared with various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Adv Biosci 75:491–494
Guillemin R, Vargo T, Bossier J, Minick S, Ling N, Rivier C, Vale W, Bloom F (1977) β-Endorphin and adrenocorticotropin are secreted simultaneously by the pituitary gland. Science 197:1367–1369.
Gyires K, Torma Z (1984) The use of the writhing test in mice for screening different types of analgesics. Arch In Pharmacodyn 167:131–140
Horrobin DF (1977) Schizophrenia as a prostaglandin deficiency disease. Lancet I:936–937
Jesova D, Vigas M, Jurcovicova J (1982) ACTH and corticosterone response to naloxone and morphine in normal, hypophysectomized and dexamethasone-treated rats. Life Sci 31:307–314
Kow LM, Pfaff DW (1988) Neuromodulatory actions of peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 28:163–188
Temple TE, Liddle CW (1970) Inhibitors of adrenal steroid biosynthesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 10:199–218
Volovka J, Cho D, Mallya A, Benman J (1979) Naloxone increases ACTH and cortisol levels in man. N Engl J Med 300:1056–1057
Winter CA, Risley EA, Nuss GW (1962) Carrageenin-induced edema in hind paw of rats as an assay for anti-inflammatory drugs. Proc Soc Exp Biol 111:544–547
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, S.K., Saraswati, M. & Sen, A.P. Effect of centrally administered enkephalins on carrageenin-induced paw oedema in rats. Res. Exp. Med. 192, 443–449 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02576302
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02576302