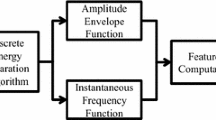
Abstract
This work is part of a project to develop an expert system for automated classification of the sleep/waking states in human infants; i.e. active or rapid-eye-movement sleep (REM), quiet or non-REM sleep (NREM), including its four stages, indeterminate sleep (IS) and wakefulness (WA). A model to identify these states, introducing an objective formalisation in terms of the state variables characterising the recorded patterns, is presented. The following digitally recorded physiological events are taken into account to classify the sleep/waking states: predominant background activity and the existence of sleep spindles in the electro-encephalogram; existence of rapid eye movements in the electro-oculogram; and chin muscle tone in the electromyogram. Methods to detect several of these parameters are described. An expert system based on artificial ganglionar lattices is used to classify the sleep/waking states, on an off-line minute-by-minute basis. Algorithms to detect patterns automatically and an expert system to recognise sleep/waking states are introduced, and several adjustments and tests using various real patients are carried out. Results show an overall performance of 96.4% agreement with the expert on validation data without artefacts, and 84.9% agreement on validation data with artefacts. Moreover, results show a significant improvement in the classification agreement due to the application of the expert system, and a discussion is carried out to justify the difficulties of matching the expert's criteria for the interpretation of characterising patterns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders, T., Emde, R., andParmelee, A. H. (1971): ‘A manual of standardized terminology, techniques criteria for scoring of states of sleep and wakefulness in newborn infants’ (UCLA, Brain Research Institute/Brain Information Service, Los Angeles, USA)
Bankman, I. N., Sigillito, V. G., Wise, R. A., andSmith, P. L. (1992): ‘Feature-based detection of the K-complex wave in the human electroencephalogram using neural networks’,IEEE Trans.,BME-39, (12), pp. 1305–1310
Bes, F., Fagioli, I., Peirano, P., Schulz, H., andSalzarulo, P. (1994): ‘Trends in EEG synchronization across non REM sleep in infants’,Sleep,17, pp. 323–328
Besset, A. (1998): ‘L'analyse automatique du sommeil’,in Billiard, M. (Ed.), ‘Le sommeil normal et pathologique, 2nd edn’ (Masson, Paris, France) pp. 126–133
Carskadon, M. A., andDement, W. C. (1989): ‘Normal human sleep: an overview’,in Kryger, M. H., Roth, T., andDement, W. C. (Eds.): ‘Principles and practice of sleep medicine’ (W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, USA) pp. 3–13
Collura, T. F., Jacobs, E. C., Braun, D. S., andBurgess, R. C. (1993): ‘EVIEW— a workstation-based viewer for intensive clinical electroencephalography’,IEEE Trans.,BME-40, (8), pp. 736–744
Crowell, D., Brooks, L. J., Colton, T., Corwin, M. J., Hoppenbrouwers, T., Hunt, C. E., Kapuniai, L. E., Lister, G., Neuman, M. R., Peucker, M., Davidson Ward, S. L., Weese-Mayer, D. E., Willinger, M. and The Collaborative Home Infant Monitoring Evaluation (CHIME) Steering Commitee (1997): ‘Infant polysomnography: reliability’,Sleep,20, pp. 553–560
Curzi-Dascalova, L., Peirano, P., andMorel Kahn, F. (1988): ‘Development of sleep states in normal premature and full term newborns’,Develop. Psychobiol.,21, pp. 431–444
Curzi-Dascalova, L., andMirmiran, M. (1996): ‘Manual of methods of recording and analyzing sleep-wakefulness states in premature and full-term infants’ (INSERM publ., Paris, France)
Curzi-Dascalova, L., andChallamel, M. J. (in press): ‘Neurophysiological basis of sleep development’,in Loughlin, G. M. (Ed.): ‘Sleep and breathing in pediatrics’ (Marcel Dekker, New York, USA)
Durbin, R., andRumelhart, D. E. (1989): ‘Product units: a computationally powerful and biologically plausible extension to back-propagation networks’,Neural Comput.,1, pp. 133–142
Fagioli, I., Bes, F., Peirano, P., andSalzarulo, P. (1995): ‘Dynamics of EEG background activity within quiet sleep in successive cycles in infants’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,94, pp. 6–11
Ferber, R., andKryger, M. (1995): ‘Principles and practice of sleep medicine in the child’ (Saunders, Philadelphia, USA)
Guilleminault, C., andSouquet, M. (1979): ‘Sleep states and related pathology’,in Korobkin, R., andGuilleminault, C. (Eds.): ‘Advances in perinatal neurology, vol. 1’ (Spectrum, New York, USA)
Guilleminault, C. (1998): ‘Le sommeil normal de l'homme’,in Billiard, M. (Ed.): ‘Le sommeil normal et pathologique 2nd ed’. (Masson, Paris, France) pp. 3–11
Harper, R. M., Schechtman, V. L., andKluge, K. A. (1987): ‘Machine classification of infant sleep state using cardiorespiratory measures’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,67, pp. 379–387
Holzmann, C., Pérez, C., andRosselot, E. (1988): ‘A fuzzy model for medical diagnosis’,Med. Prog. Through Technol.,13, pp. 171–178
Holzmann, C., Hasseldieck, U., Rosselot, E., Estévez, P., Andrade, A., andAcuña, G. (1990): ‘Interpretation module for screening normal ECG’,Med. Prog. Through Technol.,16, pp. 163–171
Holzmann, C. A., andAvaria, M. (1992): ‘Entropy aided diagnosis in genetics’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag.,11, (3), pp. 35–40
Holzmann, C., Ehijo, A., andPérez, C. (1996): ‘Methodology for a medical expert system on fuzzy analog ganglionar lattices’, Med. Prog. Through Technol.,21, pp. 147–158
Holzmann, C., andSan Martín, M. (1997): ‘Medical expert system on fuzzy analog ganglionar lattices: explication and prospection based on sensitivity’,Med. Prog. Through Technol.,21, pp. 195–203
Jansen, B. H., andDawant, B. M. (1989): ‘Knowledge-based approach to sleep EEG analysis— a feasibility study’,IEEE Trans.,BME-36, (5), pp. 510–518
Jouvet, M. (1994): ‘Paradoxical sleep mechanisms’,Sleep,17, pp. 577–583
Louis, J., Zhang, J. X., Revol, M., Debilly, G., andChallamel, M. J. (1992): ‘Ontogenesis of nocturnal organization of sleep spindles: a longitudinal study during the first 6 months of life’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,83, pp. 289–296
Park, S., Principe, J. C., Smith, J. R., andReid, S. A. (1990): ‘TDAT— time domain analysis tool for EEG analysis’,IEEE Trans. BME-37, (8), pp. 803–811.
Peirano, P., Fagioli, I., Singh, B. B., andSalzarulo, P. (1989): ‘Effect of early human malnutrition on waking and sleep organization’,Early Hum. Dev.,20, pp. 67–76
Peirano, P., Fagioli, I., Singh, B. B., andSalzarulo, P. (1990): ‘Quiet sleep and slow wave sleep in early human malnutrition’,Brain Dysfunct.,3, pp. 80–83
Peirano, P., Fagioli, I., Bes, F., andSalzarulo, P. (1993): ‘The role of slow wave sleep on quiet sleep duration in infants’,J. Sleep Res.,2, pp. 130–133
Rechtschaffen, A., andKales, A. (1968): ‘A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human dubjects’ (UCLA, Brain Research Institute/Brain Information Service, Los Angeles, USA)
Roncagliolo, M., andVivaldi, E. (1991): ‘Time course of rat sleep variables assessed by a microcomputer-generated data base’,Brain Res. Bull.,27, pp. 573–580
Smith, J. R. (1986): ‘Automated analysis of sleep EEG data’,in Lopes De Silva, F. H., Storm Van Leeuwen, W., andRémond, A. (Eds.): ‘Handbook of rlectroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology, vol. 2’ (Elsevier Publ.) pp. 131–147
Tafti, M. (1998): ‘Analyse numèrique du sommeil’,in Billiard, M. (Ed.): ‘Le sommeil normal et pathologique, 2nd edn’ (Masson, Paris, France)
Vivaldi, E. A., Pastel, R. H., Fernstrom, J., andHobson, J. A. (1984): ‘Long term stability of rat sleep quantified by microcomputer analysis’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,58, pp. 235–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holzmann, C.A., Pérez, C.A., Held, C.M. et al. Expert-system classification of sleep/waking states in infants. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 37, 466–476 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02513332
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02513332