Abstract
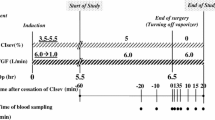
Sevoflurane, a new inhalational anesthetic, is metabolically broken down into several decomposition products in the presence of CO2 absorbents. One of the products, CF2=C (CF3) OCH2F (compound A), which appears to be the most toxic, was quantitated in 20 surgical patients subjected to more than 3 h of anesthesia using a low-flow anesthesia circuit. To minimize the variables in the reaction velocity between sevoflurane and the CO2 absorbents, we maintained the sevoflurane concentration at 2%. Wakolime-A, one type of soda lime, resulted in the highest increase in compound A concentration. The peak concentration was 27.1±3.1 ppm, less than one-tenth of the LC50 (50% lethal concentration) of compound A, which was previously reported as 420 or 400 ppm in rats. We also measured the temperature in CO2 absorbents, which had been reported to influence compound A production. The elevation in the temperature was 27.9±1.3°C in Wakolime-A, 29.4±8.4°C in Baralyme, and 31.0±5.0°C in Sodasorb II. Further studies are needed to assess the safety and efficacy of sevoflurane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holaday DA, Smith FR (1981) Clinical characteristics and biotransformation of sevoflurane in healthy human volunteers. Anesthesiology 54:100–106
Wallin RF, Regan BM, Napoli MD, Stern IJ (1975) Sevoflurane: A new inhalational anesthetic agent. Anesth Analg 54:758–765
Mazze RI (1992) The safety of sevoflurane in humans. Anesthesiology 77:1062–1063
Hanaki C, Fujii K, Morio M, Tashima T (1987) Decomposition of sevoflurane by sodalime. Hiroshima. J Med Sci 36:61–67
Morio M, Fujii K, Satoh N, Imai M, Kawakami U, Mizuno T, Kawai Y, Ogasawara Y, Tamura T, Negishi A, Kumagai Y, Kawai T (1992) Reaction of sevoflurane and its degradation products with soda lime. Toxicity of the byproducts. Anesthesiology 77:1155–1164
Liu J, Laster MJ, Eger EII, Taheri S (1991) Absorption and degradation of sevoflurane and isoflurnae in a conventional anesthetic circuit. Anesth Analg 72:785–789
Frink EJ, Malan TP, Morgan SE, Brown EA, Malcomson M, Brown BR (1992) Quantification of the degradation products of sevoflurane in two CO2 absorbents during low-flow anesthesia in surgical patients. Anesthesiology 77:1064–1069
Kudo M, Kudo T, Matsuki A (1990) Reaction products of sevovlurane with new Sodalime-A under various conditions. Masui 39:626–631
Kudo M, Kudo T, Oyama T, Matsuki A (1990) Reaction products of sevoflurane with components of sodalime under various conditions. Masui 39:39–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Osawa, M., Shinomura, T., Murakawa, M. et al. Compound A concentration and the temperature of CO2 absorbents during low-flow sevoflurane anesthesia in surgical patients. J Anesth 9, 1–5 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482025
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482025