Abstract
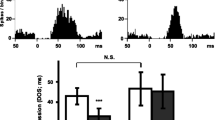
This study assessed the effects of acute as well as long-term administration of fluoxetine, a selective serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibitor with anti-depressant properties, on hippocampal (HIP) seizures elicited by electrical stimulation in rats. The fluoxetine effect on HIP seizures was also assessed following long-term treatment with gepirone, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist. Acute single administration of fluoxetine (1, 10 mg/kg; IP) was found to produce no significant effect on HIP seizure activity. Following daily IP administration of fluoxetine (10 mg/kg per day) or gepirone (10 mg/kg per day) for 21 days, animals were given a 7-day drug-free period and then challenged with an acute dose of 10 mg/kg fluoxetine. These treatment regimens resulted in a significantly increased afterdischarge threshold of HIP seizures in response to acute fluoxetine administration. The inhibitory effect of fluoxetine, however, was not present 4 weeks after long-term treatment with either fluoxetine or gepirone. The present results indicate that long-term treatment with these compounds enhances the antiepileptic effect of subsequent fluoxetine administration on the generation of HIP seizures. This effect is possibly related to the well-demonstrated evidence that fluoxetine and gepirone, on long-term treatment, facilitate net 5-HT neurotransmission through desensitization of presynaptic 5-HT autoreceptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bel N, Artigas F (1993) Chronic treatment with fluvoxamine increases extracellular serotonin in frontal cortex but not in raphe nuclei. Synapse 15:243–245
Blier P, de Montigny C (1983) Electrophysiological investigations on the effect of repeated zimelidine administration on serotonergic transmission in the rat. J Neurosci 3:1270–1278
Blier P, de Montigny C (1987) Modification of 5-HT neuron properties by sustained administration of the 5-HT1A agonist gepirone:electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Synapse 1:470–480
Blier P, de Montigny C (1990) Differential effect of gepirone on pre- and postsynaptic serotonin receptors:single cell recording studies. J Clin Psychopharmacol 10 [suppl]:13S-20S
Blier P, de Montigny C, Tardif D (1984) Effects of the two antidepressant drugs mianserin and indalpine on the serotonergic system:single cell studies in the rat. Psychopharmacology 84:242–249
Burdette LJ, Dyer RS (1987) Differential effects of caffeine, picrotoxin, and pentylenetetrazol on hippocampal afterdischarge activity and wet dog shakes. Exp Neurol 96:381–392
Caccia S, Cappi M, Fracasso C, Garattini S (1990) Influence of dose and route of administration on the kinetics of fluoxetine and its metabolite norfluoxetine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 100:509–524
Cavalheiro EA, Elisabetsky E, Campos CJR (1981) Effect of brain serotonin level on induced hippocampal paroxysmal activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:363–366
Chaput Y, de Montigny C, Blier P (1986) Effect of a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, citalopram, on the sensitivity of 5-HT autoreceptors:electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 333:342–348
Charney DS, Heninger GR (1986) Receptor sensitivity hypothesis of antidepressant action. Annu Meet Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacology, 49
Cott JM, Kurtz NM, Robinson DS, Lancaster SP, Copp JE (1988) A 5-HT1A ligand with both antidepressant and anxiolytic properties. Psychopharmacol Bull 24:164–167
Csanalosi I, Schweizer E, Case WG, Rickels K (1987) Gepirone in anxiety:a pilot study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 7:31–33
Dailey JW, Yan QS, Mishra PK, Burger RL, Jobe PC (1992) Effects of fluoxetine on convulsions and on brain serotonin as detected by microdialysis in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:533–540
de Montigny C, Blier P, Chaput Y (1984) Electrophysiologically-identified serotonin receptors in the rat NS. Neuropharmacology 23:1511–1520
de Montigny C, Blier P, Chaput Y (1990) Modification of serotonergic neuron properties by long-term treatment with serotonin reuptake blockers. J Clin Psychiatry 51 [12, suppl B]:4–8
Dragunow M, Goddard GV, Laverty R (1987) Proconvulsant effects of theophylline on hippocampal afterdischarges. Exp Neurol 96:732–735
Edwards JG (1985) Antidepressants and seizures:epidemiological and clinical aspects. In: Trimble MR (ed) The psychopharmacology of epilepsy. Wiley, Chichester, pp 119–139
Engel G, Gothert M, Hoyer D, Schlicker E, Hillenbrand K (1986) Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:1–7
Finch DM, Feld RE, Babb TL (1978) Effects of mesencephalic and pontine electrical stimulation on hippocampal neuronal activity in drug-free cat. Exp Neurol 61:318–336
Gardier AM, Lepoul E, Trouvin JH, Chanut E, Dessalles MC, Jacquot C (1994) Changes in dopamine metabolism in rat forebrain regions after cessation of long-term fluoxetine treatment:relationship with brain concentrations of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine. Life Sci 54:PL51–56
Kalichman MW (1982) Neurochemical correlates of the kindling model of epilepsy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 6:165–181
Köhler C (1984) The distribution of serotonin binding sites in the hippocampal region of the rat brain:an autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 13:667–680
Leander JD (1992) Fluoxetine, a selective serotonin-uptake inhibitor, enhances the anticonvulsant effects of phenytoin, carbamazepine, and ameltolide (LY201116). Epilepsia 33:573–576
Meltzer HY, Lowy MT (1987) The serotonin hypothesis of depression. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology:The third generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 513–526
Middlemiss DN (1984) Stereoselective blockade at [3H]5-HT binding sites at the 5-HT autoreceptor by propranolol. Eur J Pharmacol 101:289–293
Nishi H, Watanabe S, Ueki S (1980) Effect of median raphe stimulation on hippocampal seizure discharge induced by carbacol in the rabbit. Jpn J Pharmacol 30:759–762
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Peroutka SJ (1988) 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes:molecular, biochemical and physiological characterization.Trends Neurosci 11:496–500
Post RM, Uhde TW (1984) Carbamazepine in the treatment of mood and anxiety disorders:implications for limbic system mechanisms. In: Trimble MR, Zarifian E (eds) Psychopharmacology of the limbic system. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 134–147
Rickels K, Schweizer E (1990) Clinical overview of serotonin reuptake inhibitors. J Clin Psychiatry 51 [12, suppl B]:9–12
Rigdon GC, Wang CM (1987) Serotonin reuptake blockers inhibit the firing rate of serotonergic neurons of the dorsal raphe in vitro. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:1648
Robertson MM (1985) Depression in patients with epilepsy:an overview and clinical study. In:Trimble MR (ed) The psychopharmacology of epilepsy. Wiley, Chichester, pp 65–82
Segal M (1975) Physiological and pharmacological evidence for a serotonergic projection to the hippocampus. Brain Res 94:115–131
Sotelo C, Cholley B, Mestikawy SE, Gozlan H, Hamon M (1990) Direct immunohistochemical evidence of the existence of 5-HT1A autoreceptors on serotoninergic neurons in the midbrain raphe nuclei. Eur J Neurosci 12:1144–1154
Sparks DL, Buckholtz NS (1985) Combined inhibition of serotonin reuptake and oxidative deamination attenuates audiogenic seizures in DBA/2J mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:753–757
Trimble M (1978) Non-monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants and epilepsy:a review. Epilepsia 19:241–250
Wada Y, Hasegawa H, Nakamura M, Yamaguchi N (1991) Suppressive effect ofl-5-hydroxytrytophan in a feline model of photosensitive epilepsy. Brain Res 552:8–12
Wada Y, Nakamura M, Hasegawa H, Yamaguchi N (1992) Role of serotonin receptor subtype in seizures kindled from the feline hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 141:21–24
Wada Y, Nakamura M, Hasegawa H, Yamaguchi N (1993a) Intrahippocampal injection of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) inhibits partial and generalized seizures induced by kindling stimulation in cats. Neurosci Lett 159:179–182
Wada Y, Nakamura M, Hasegawa H, Yamaguchi N (1993b) Effect of serotonin reuptake inhibiting antidepressants on hippocampal kindled seizures in cats. Neurosci Res Commun 12:119–124
Welner SA, de Montigny C, Desroches J, Desjardins P, Suranyicadotte BE (1989) Autoradiographic quantification of serotonin1A receptors in rat brain following antidepressant drug treatment. Synapse 4:347–352
Yan QS, Jobe PC, Dailey JW (1994) Evidence that a serotonergic mechanism is involved in the anticonvulsant effect of fluoxetine in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Eur J Pharmacol 252:105–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wada, Y., Shiraishi, J., Nakamura, M. et al. Prolonged but not acute fluoxetine administration produces its inhibitory effect on hippocampal seizures in rats. Psychopharmacology 118, 305–309 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245959
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245959