Abstract
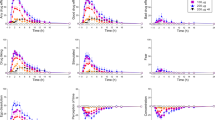
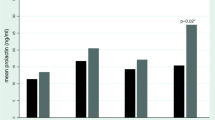
Six female and six male healthy volunteers received 100 mg remoxipride, 200 mg sulpiride and placebo as single oral doses in a double blind trial with a randomized crossover design. The main objective was to compare the effect of the two drugs on serum prolactin levels, but effects on other hormones were also investigated. Remoxipride and sulpiride increased the serum levels of prolactin to similar peak levels. This effect was larger in female than in male subjects. Sulpiride increased prolactin levels at much lower plasma concentrations than remoxipride, and sulpiride's effect on prolactin lasted for considerably longer than remoxipride's. No consistent effects on serum levels of LH, FSH, GH, oestradiol, progesterone, testosterone or cortisol could be detected after remoxipride and sulpiride compared to placebo. No drug-related effects on plasma homovanillic acid (HVA) were found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfredsson G, Bjerkenstedt L, Edman G, Härnryd C, Oxenstierna G, Sedvall G, Wiesel G-A (1984) Relationships between drug concentrations in serum and CSF, clinical effects and monoaminergic variables in schizophrenic patients treated with sulpiride or chlorpromazine. Acta Psychiatr Scand 69:49–74
von Bahr C, Movin G, Yisak W-A, Jostell K-G, Widman M (1990) Clinical pharmacokinetics of remoxipride. Acta Psychiatr Scand 82 [Suppl. 358]:41–44
Beumont PJV, Bergen J (1982) Neuroendocrine effects of neuroleptics. In: Beumont PJV, Burrows GD (eds) Handbook of psychiatry and endocrinology. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam New York Oxford pp 157–181
Braude WM, Barnes TRE, Gore SM (1983) Clinical characteristics of akathisia. A systematic investigation of acute psychiatric of inpatient admissions. Br J Psychiatry 143:139–150
Crosignani PG, Ferrari C (1987) Research review: synthesis, release and biological actions of human prolactin. Res Reprod 19:2–3
Dannies PS (1982) Prolactin: multiple intracellular processing routes plus several potential mechanisms for regulation. Biochem Pharmacol 31:2845–2849
Davis JRE, Selby C, Jeffcoate WJ (1984) Oral contraceptive agents do not affect serum prolactin in normal women. Clin Endocrinol 20:427–434
Farde L, Grind M, Nilsson MI, Ogenstad S, Sedvall G (1988) Remoxipride — a new potential antipsychotic drug. Pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics following repeated oral administration in male volunteers. Psychopharmacology 95:157–161
Franz AG (1974) Prolactin secretion in physiologic and pathologic human conditions measured by bioassay and immuno-radioassay. In: Josimovich et al. (eds) Lactogenic hormones, fetal nutrition and lactation. John Wiley & Sons, New York London Sydney Toronto pp 379–412
Franz AG (1978) Prolactin. N Engl J Med 298:201–207
Grind M, Nilsson M-J, Nilsson L, Oxenstierna G, Sedwall G, Wahlén A (1989) Remoxipride — a new potential antipsychotic compound. Tolerability and pharmacokinetics after single oral and intravenous administration in healthy male volunteers. Psychopharmacology 98:304–309
Hall H, Farde L, Sedwall G (1988) Human dopamine receptor subtypes — in vitro binding analysis using3H-SCH/23390 and3H-raclopride. J Neural Transm 73:7–21
Holford NHG, Sheiner LB (1981) Understanding the dose-effect relationship: Clinical application of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models. Clin Pharmacokinet 6:429–453
Härnryd C, Bjerkenstedt L, Gullberg B, Oxenstierna G, Sedvall G, Wiesel F-A (1984) Time course for effects of sulpiride and chlorpromazine on monoamine metabolite and prolactin levels in cerebrospinal fluid from schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand, Suppl 311:75–92
Labrie F, Drouin J, Ferland L, Lagacé L, Beaulieu M, DeLéan A, Kelly PA, Caron MG, Raymond V (1978) Mechanism of action of hypothalamic hormones in the anterior pituitary gland and specific modulation of their activity by sex steroids and thyroid hormones. In: Greep ro (ed.) Recent progress in hormone research, Vol. 34. Academic, Press, New York San Francisco London pp 25–93
Lapierre et al. (1990) A controlled dose-ranging study of remoxipride and haloperidol in schizophrenia — a Canadian multicentre trial. Acta Psychiatr Scand 82 [Suppl. 358]:72–76
Lindkvist SO (1987) Determination of free HVA in plasma by liquid chromatography and dual electrochemical detection. Astra Method 805-00 AFB-08
McMurdo MET, Howie PW, Lewis M, Marnic M, McEwen J, McNeilly S (1987) Prolactin response to low dose sulpiride. Br J Clin Pharmacol 24:133–137
Müller EE, Stefanini E, Camanni F, Locatelli V, Massara F, Spano PF, Cocchi I (1979) Prolactin releasing effect of sulpiride isomers in rats and man. J Neural Transm 46:205–214
Müller EE, Fregnan GB, Chieli T, Cocchi D, Frigerio C, Locatelli V (1980) Effects of neuroleptics on neuroendocrine mechanims for gonadotropin secretion. In: Cattabeni et al. (eds) Long-term effects of neuroleptics. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol vol. 24. Raven Press, New York, pp 387–397
Müller EE, Locatelli V, Cella S, Penalva A, Novelli A, Cocchi D (1983) Prolactin-lowering and -releasing drugs. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications. Drugs 25:399–432
Nilsson LB (1990) Determination of remoxipride in plasma and urine by reversed-phase column liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 526:139–150
Nilsson L (1987) Determination of sulpiride in plasma by reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Astra Method 805-17 AFB-09
Raymond V, Beaulieu M, Labrie F, Boissier J (1978) Potent antidopaminergic activity of estradiol at the pituitary level on prolactin release. Science 200:1173–1175
Schaeffer JM, Hsueh JW (1979) 2-hydroxyestradiol interaction with dopamine receptor binding in rat anterior pituitary. J Biol Chem 254:5606–5608
Sugnaux FR, Benakis A, Fonzo D, Di Carlo R (1983) Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of sulpiride and sulpiride-induced prolactin secretion in man. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 8:189–200
Tuomisto J, Männistö P (1985) Neurotransmittor regulation of anterior pituitary hormones. Pharmacol Rev 37:249–332
Wiesel F-A, Alfredsson G, Ehrnebo N, Sedwall G (1980) The pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral sulpiride on healthy human subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17:385–389
Wiesel F-A, Alfredsson G, Ehrnebo M, Sedvall G (1982) Prolactin response following intravenous and oral sulpiride in healthy human subjects in relation to sulpiride concentrations. Psychopharmacology 76:44–47
Wiesel F-A, Alfredsson G, Jonsson E (1989) Dose finding and serum concentrations of neuroleptics in the treatment of schizophrenic patients. In: Dahl SG, Gram LF, Montgomery SA (eds) Proc. 5th Int. Meeting of Clinical Pharmacology in Psychiatry. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York (in press)
Ögren SO, Hall H, Köhler C, Magnusson D, Lindbom L-O, Angeby K, Florvall L (1984) Remoxipride, a new potential antipsychotic compound with selective antidopaminergic actions in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 102:459–474
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Bahr, C., Wiesel, FA., Movin, G. et al. Neuroendocrine responses to single oral doses of remoxipride and sulpiride in healthy female and male volunteers. Psychopharmacology 103, 443–448 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244242
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244242