Abstract
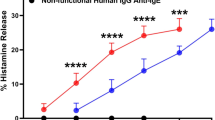
The histamine-releasing capability ofStaphylococcus aureus antigens was examined in human adenoidal and mesenteric mast cells obtained by enzymic dispersion of tissues from non-allergic patients. Both populations of mast cells released histamine after challenge with bacterial protein in concentrations between 5–500 μg/ml. The release was dependent on the dose, temperature and metabolic energy. The maximum release was observed at 15 min after challenge. The present results suggest thatStaphylococcus aureus antigens release histamine from human adenoidal and mesenteric mast cells via a non-cytotoxic, active secretory process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Norn, P. S. Skov, C. Jensen, J. O. Jarlov and F. Espersen,Histamine release induced by bacteria. A new mechanism in asthma? Agents and Actions20, 29–34 (1987).
M. K. Church, J.-K. Pao, S. T. Holgate and S. Norn,Histamine release from human mast cells induced by bacterial cell wall products, Annal. Allergy55, 272 (1985).
S. Norn, P. S. Skov, C. Jensen, F. Espersen, J. O. Jarlov and C. Koch,Bacteria and their products release histamine and potentiate mediator release: new aspects in airway diseases. Eur. J. Respir. Dis.69 (Suppl. 147), 230–234 (1986).
E. Brzezińska-Błaszczyk and M. Czuwaj,Isolation and sensitivity of human mesenteric mast cells to immunological and nonimmunological histamine releasers, Agents and Actions20, 226–228 (1987).
E. S. Schulman, A. Kagey-Sobotka, D. W. MacGlashan, N. F. Adkinson, S. P. Peters, R. P. Schleimer and L. M. Lichtenstein,Heterogeneity of human mast cells, J. Immunol.131, 1936–1941 (1983).
Ch. D. May, M. Lyman, R. Alberto and J. Cheng,Procedures for immunochemical study of histamine release from leukocytes with small volume of blood, J. Allergy46, 12–20 (1970).
R. R. Martin and A. White,The in vitro release of leukocyte histamine by staphylococcal antigens, J. Immunol.102, 437–441 (1969).
S. Norn, P. S. Skov, C. Jensen, C. Koch, H. Permin, T. C. Bog-Hansen, H. Lowenstein and N. Hoiby,Intrinsic asthma and bacterial histamine release via lectin effect, Agents and Actions13, 210–212 (1983).
C. Jensen, S. Norn, P. S. Skov, F. Espersen, C. Koch and H. Permin,Bacterial histamine release by immunological and nonimmunological lectin-mediated reactions, Allergy39, 371–377 (1984).
F. Espersen, J. O. Jarlov, C. Jensen, P. S. Skov and S. Norn,Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan induces histamine release from basophil human leukocytes in vitro. Infection and Immunity46, 710–714 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brzezińska-Błaszczyk, E., Czuwaj, M. & Wyczółkowska, J. Histamine release from human adenoidal and mesenteric mast cells induced by bacterial antigens. Agents and Actions 23, 230–232 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02142549
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02142549