Summary
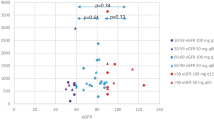
In an open randomised crossover study the antibacterial activity of pefloxacin and norfloxacin was assessed in the urine after a single 800-mg oral dose in 14 healthy female volunteers. Pefloxacin demonstrated lower peak concentrations in the urine than norfloxacin (mean, 217.2 mg/l versus 492.9 mg/l as determined by the microbiological assay) but pefloxacin was present over a longer period of time in sufficient concentrations than norfloxacin. Mean urine levels of at least 2 mg/l were present for 7 days after pefloxacin administration and 2 days after norfloxacin administration as determined by the microbiological assay. Overall, the urinary recovery of pefloxacin and norfloxacin amounted to 49.3% and 25.1%, respectively, of the total administered dose. The average urine bactericidal activity against the five test organisms was as follows: against reference strainEscherichia coli ATCC 25922 susceptible to nalidixic acid (Nal-S) for 5 days with pefloxacin and 2 days with norfloxacin; against three clinical isolates, one strain each ofE. coli resistant to nalidixic acid (Nal-R),Klebsiella pneumoniae Nal-R, andStaphylococcus saprophyticus, for 3 days with pefloxacin and 24 h with norfloxacin; and against a clinical isolate ofEnterococcus faecalis for 2 days with pefloxacin and 12 h with norfloxacin. In conclusion, pefloxacin as a single dose proved to have sufficiently high and long-lasting urine bactericidal activity against urinary pathogens. These findings support the results of a meta-analysis of seven clinical trials in patients with uncomplicated lower UTI, demonstrating a single oral dose of 800 mg pefloxacin to be as effective as a conventional treatment with comparative drugs [21].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naber, K. G. Uncomplicated urinary tract infections — is single dose therapy effective? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 4 (Suppl. 2) (1984) S39-S45.
Norrby, S. R. Short-term treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in women. Rev. Infect. Dis. 12 (1990) 458–467.
Leibovici, L., Wysenbeck, A. Single-dose treatment for symptomatic infections in women: meta-analysis of randomised trials. Q. J. Med. New Series 78 (1991) 43–57.
Gonzalez, J. P., Henwood, J. M. Pefloxacin, a review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 37 (1989) 628–668.
Montay, G., Goueffon, Y., Roquet, F. Absorption, distribution, metabolic fate and elimination of pefloxacin mesylate in mice, rats, dogs, monkeys, and humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 25 (1984) 463–472.
Guibert, J., Kitzis, M. D., Brumpt, I., Acar, J. F. Antibacterial activity of pefloxacin in the urine during seven days after a single 800 mg oral dose. (In French). Path. Biol. 37 (1989) 406–410.
Ratcliffe, M. T., Smith, J. T. The mechanism of reduced activity of 4-quinolone agents in urine. FAC Fortschr. Antimicrob. Antineoplast. Chemother. 3–5 (1984) 563–569.
Machka, C., Braveny, I. Inhibitorische Wirkung verschiedener Faktoren auf die Aktivität von Norfloxacin. FAC Fortschr. Antimicrob. Antineoplast. Chemother. 3–5 (1984) 557–562.
Ozaki, K., Uchida, H., Irikura, T. Studies on the metabolism of AM-715 in humans by high performance liquid chromatography. Chemotherapy (Tokyo) 29 (Suppl. 4) (1981) 128–135.
Sutherland, R., Rolinson, G. N. Methods of antibiotic assay. In:Reeves, D. S., Phillips, I., Williams, J. D., Wise, R. (eds.): Laboratory methods in antimicrobial chemotherapy. Churchill Livingstone, London, New York 1978, pp. 171–175.
National Committee of Clinical and Laboratory Standards (NCCLS): Methods for determining bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents. Tentative guideline. September 1992. NCCLS document M26-T Vol. 12, No. 19.
Eandi, M., Viano, I., Di Nola, F., Leone, L., Genazzani, E. Pharmacokinetics of norfloxacin in healthy volunteers and patients with renal and hepatic damage. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2 (1983) 253–259.
Swanson, B. N., Boppana, V. K., Vlasses, P. H., Rotmensch, H. H., Ferguson, R. K. Norfloxacin disposition after sequentially increasing doses. Antimicrob. Chemother. 23 (1983) 284–288.
Bauernfeind, A., Petermüller, C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and nalidixic acid. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2 (1983) 111–115.
Hohl, E. B., Felber, A. M. Effect of method, medium, pH, and inoculum on thein vitro antibacterial activities of fleroxacin and norfloxacin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 22 (Suppl. D) (1988) 71–80.
Zhanel, G. G., Karlowsky, J. A., Davidson, R. J., Hoban, D. J. Influence of human urine on thein vitro activity and postantibiotic effect of ciprofloxacin againstEscherichia coli. Chemotherapy 37 (1991) 218–223.
Auckenthaler, R., Michéa-Hamzehpour, M., Pechère, J. C. In vitro activity of newer quinolones against aerobic bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 17 (Suppl. B) (1986) 29–39.
Lebel, M., Paradis, D., Vallee, F.: Norfloxacin 800 mg single dose: urinary bactericidal activity and pharmacokinetics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., Special Issue (1991) 516–517.
Saginur, R., Nicolle, L. E. Single-dose compared with 3-day norfloxacin treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. Arch. Intern. Med. 152 (1992) 1233–1237.
van Balen, F. A. M., Touw-Otten, F. W. M., de Melker, R. A. Single-dose pefloxacin versus five-day treatment with norfloxacin in uncomplicated cystitis in women. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 26 (Suppl. B) (1990) 153–160.
Naber, K. G., Baurecht, W., Fischer, M., Kresken, M. Pefloxacin single-dose in the treatment of acute uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in women: a meta-analysis of seven clinical trials. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 4 (1994) 197–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofbauer, H., Naber, K.G., Kinzig-Schippers, M. et al. Urine bactericidal activity of pefloxacin versus norfloxacin in healthy female volunteers after a single 800-mg oral dose. Infection 25, 121–126 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02113592
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02113592