Abstract
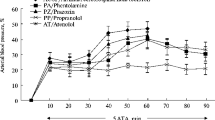
Chlorpromazine (75 mg daily) or placebo was administered, during a week, to 10 healthy students, 23–27 years old, on a double-blind cross-over basis. Minute ventilation and alveolar ventilation increased significantly under Chlorpromazine (p<0, 05) when a hypoxic gas mixture was inspired (simulating an altitude of 3000 m above sea level). The chlorpromazine induced (hypoxia related) hyperventilation decreased the arterial PCO2 (0, 1>p>0, 05) and increased the arterial PO2 (p<0, 0025), without any change of P-50. We conclude that low oral doses of chlorpromazine had no influence on the alveolar-capillary O2-carriage. The drug taken in the chosen dosis, however, seems to stimulate the aortic and carotid chemoreceptor activity, possibly by a local blockade of the cytochrome P-450.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ader, R., Clink, D. W.: Effects of chlorpromazine on the acquisition and extinction of an avoidance response in the rat. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther.121, 144 (1957)
Baum, G. L., Schotz, A., Gumpel, R. C., Osgood, C.: The role of chlorpromazine in the treatment of bronchial asthma and chronic pulmonary emphysema. Dis. Chest32, 574 (1957)
Bickel, M. H.: Binding of phenothiazines and related compounds to tissues and cell constituents. In: Phenothiazines and structurally related drugs, p. 163. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company 1974
Bunney, B. S., Walters, J. R., Roth, R. H.: Dopaminergic effect of antipsychotic drugs and amphetamine on single cell activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.185, 560 (1973)
Burns, B., Gurtner, G. H.: A specific carrier for oxygen and carbon monoxide in the lung and placenta. Amer. Soc. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.1, 374 (1973)
Comroe, J. H.: The peripheral chemoreceptors. In: Handbook of Physiology, Section 3: Respiration I, Vol. I, p. 557. (Fenn, W. O., Rahn, H., ed.) Washington D. C.: Amer. Physiol. Soc. 1964
Courvoisier, S., Fournel, J., Ducrot, R., Kolsky, M., Koetschet, P.: Propriétés pharmodynamiques du chlorhydrate de chloro-3(dimethyl-amino-3′ propyl)-10 phénothiazine. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Thér.92, 305 (1953)
De Burgh Daly, M., Lambertsen, C. J., Schweitzer, A.: Observations on the volume of blood flow and oxygen utilisation of the carotid body in the cat. J. Physiol. (London)125, 67 (1954)
Gurtner, G. H., Burns, B.: Possible facilitated transport of O2 across the placenta. Nature240, 473 (1972)
Jarvik, M. E.: Drugs used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders. In: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics 5. Ed. p. 157 (Goodman, L. S., Gilman, A., ed.) London-Toronto: MacMillan 1975
Joels, N., Neil, E.: The action of high tensions of carbon monoxide on the carotid chemoreceptors. Arch. Int. Pharmacydyn.139 528 (1962)
Kähler, H. J.: Störwirkungen von Psychopharmaka und Analgetika. Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft 1967
Key, B. J., Bradley, P. B.: The effects of drugs on conditioning and habituation to arousal stimuli in animals. Psychopharmacologia1, 450 (1960)
Killam, K. F., Killam, E. K.: Drug action on pathways involving the reticular formation. In: Reticular formation of the brain. (Jasper, H. H., Proctor, L. D., Knighton, S. S., Noshay, W. C., Costell, R. T., ed.) Boston: Little, Brown & Co. 1958
Kintzel, H. W.: Die Atemtätigkeit Frühgeborener unter Chlorpromazinemedikation. Z. Kinderheilk.105, 334 (1969)
Laborit, H.: Le phénomène de potentialisation des anésthésiques généraux. Nouv. Presse Méd.58, 416 (1950)
Lambertsen, C. J., Wendel, H., Longenhagen, J. B.: The separate and combined respiratory effects of chlorpromazine and meperidine in normal men controlled at 46 mm Hg alveolar pCO2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.131, 381 (1961)
Longmuir, I. S., Sun, S.: A hypothetical tissue oxygen carrier. Sixth Europ. Conf. Microcirculation, Aalborg 1970. Basel: Karger 1971
Mills, E., McIvor, W., Edwards, J. R.: Stimulation of aortic and carotid chemoreceptors during carbon monoxide inhalation. J. Appl. Physiol.25, 494 (1968)
Neil, E., Joels, N.: The carotid glomus sensory mechanism. In: The regulation of human respiration, p. 163. (Cunningham, D. J. C., Lloyd, B. B., ed.) Oxford: Blackwell 1963
Pantal, A. S.: Mechanism of stimulation of aortic chemoreceptors by natural stimuli and chemical substances. J. Physiol. (London)189, 63 (1967)
Remmer, H.: The role of the liver in drug metabolism. Amer. J. Med.49, 617 (1970)
Renzetti, A. D., Padget, W. R.: The acute respiratory effects of chlorpromazine in man. J. Lab. Clin Med.50, 400 (1957)
Rosenstein, R.: Respiratory effects of chlorpromazine in unanesthesized decerebrated cats. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn.196, 164 (1972)
Sakalis, G., Curry, S. H., Mould, G. P.: Physiologic effects and clinical effects of chlorpromazine and their relationship to plasma level. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.13, 931 (1972)
Scherrer, M., Hadorn, W.: Krankheiten des Respirationstraktes. In: Lehrbuch der Therapie. (Hadorn, W., Stucki, P., ed.) Bern-Stuttgart-Wien: H. Huber 1976
Tauberger, G.: Die Hemmung der zentralnervösen vaguserregenden Nicotinwirkung durch Chlorpromazin, Fluphenazin und Imipramin. Drug Res.21, 535 (1971)
Ulrich, W. D., Maess, M., Wirth, J.: Respiratorischer Stoffwechsel und Körpertemperatur bei Behaglichkeitstemperatur nach Gabe von Chlorpromazin. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn.167, 80 (1967)
Ulrich, W. D., Wirth, J., Maess, M.: Die Temperaturregulation unter Chlorpromazin. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn.167, 90 (1967)
Von Hollmann, W., Schmücker, B., Heck, H., Stolte, A., Liesen, H., Fotescu, M. D., Mathur, D. N.: Über das Verhalten spiroergo-metrischer Meßgrößen bei Radrennfahrern auf dem Laufband und auf dem Fahrradergometer. Sportarzt und Sportmedizin7, 153 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The study was supported by grants from the Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boll, J., Emch, F. & Scherrer, M. Stimulation of the aortic and carotid chemoreceptor drive by low doses of chlorpromazine. Pneumologie 153, 301–310 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02095370
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02095370