Abstract
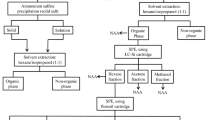
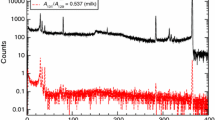
The absolute concentrations of iodine, bromine and chlorine in milk, have been determined by epithermal ‘neutron activation’ followed by high resolution gamma-ray spectrometry. Two kinds of milk commonly consumed in Israel have been investigated. The concentration of iodine, bromine and chlorine were found to be 0.18–0.30 μg/ml, 2.02–2.85 μg/ml and 0.65 mg/ml, respectively. The method is fast, selective, accurate and highly sensitive.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. STELLA, N. GENOVA, M. DI CASA, Radiochem. Radioanal. Lett., 30 (1977) 65
D. BEHNE, F. DIEL, in Nuclear Activation Techniques in the Life Sciences, IAEA-SM-157, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1972, p. 41.
D. BEHNE, H. JURGENSEN, J. Radioanal. Chem., 42 (1978) 447.
W. LEONHARDT, Kernenergie, 4 (1961) 395.
M. SKLAVENITIS, D. COMAR, Nuclear Activation Techniques in the Life Sciences, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1963, p. 445.
G. GUZZI, R. PIETRA, E. SABIONI, EUR 5282e, 1974.
N. M. SPYROU, M. E. FIRCKER, R. ROBERTSON, W. B. GILBOY, in Symp. on Nuclear Techniques in Comparative Studies of Food and Environmental Contamination, IAEA-SM-175, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1973.
S. K. NYARKU, A. CHATT, J. Radioanal. Chem., 71(1982) 129.
R. MALVONO, G. BUZZIGOLI, M. SCARLATINI, Anal. Chim. Acta, 61 (1972) 201.
H. L. ROOK, J. Radioanal. Chem., 39 (1977) 351.
L. GVARDJANCIC, L. KOSTA, M. DERMELY, J. Radioanal. Chem., 58 (1980) 359.
D. COMAR, L'Analyse par Radioactivation et les Applications aux Sciences Biologiques, Presses Univ. France, Paris, 1964, p. 307.
R. MALVANO, P. GROSSO, J. Nucl. Biol. Med., 12 (1968) 86.
T. SATO, M. KATO, J. Radioanal. Chem., 68 (1982) 175.
A. R. BRYNE, L. KOSTA, M. DERMELY, M. TUSEK-ZNIDARIC, in Trace Elements, Analytical Chemistry in Medicine and Biology, P. BRATTER, P. SCHRAMEL (Eds), Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, 1983, p. 21.
Handbook on Nuclear Activation Cross-Sections, Technical Report No. 156, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1974.
D. CHULTEM, Dz. GANZORIG, T. GUN-AUJAV, J. Radioanal. Chem., 50 (1979) 195.
D. BRUNE, P. O. WESTER, Anal. Chim. Acta, 52 (1970) 372.
Z. B. ALFASSI, N. LAVI, Radiochem. Radioanal. Lett., 53 (1982) 173.
Z. B. ALFASSI, N. LAVI, Anal. Chem., 55 (1983) 796.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alfassi, Z.B., Lavi, N. Rapid determination of halogens in milk by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Articles 90, 395–400 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02060796
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02060796