Abstract
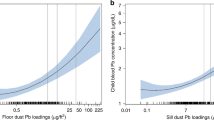
Data from the Edinburgh Lead Study are used to estimate the respective contributions of water and dust lead to blood lead in 6–9 year old children. Both sources are significantly related to blood lead. An exposure of 100 μg/l in kitchen cold water is estimated to be equivalent to 2700 μg/g of lead in dust. In this population water is a more important source of lead than dust for the bulk of the population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, R.J. & Russell, P.F. 1981.Environ. Tech. Lett. 2, 57–66.
Duggan, M.J. 1983.Environ. Health Perspect. 50, 371–81.
Duggan, M.J. & Inskip, M.J. 1985.Public Hlth. Rev. 13, 1–54.
Elwood, P.C., Gallacher, J.E.J., Phillips, K.M. 1984.Nature 310, 138–40.
Elwood, P.C. 1986.Sci. Total Environ. 52, 1–23.
Fulton, M., Raab, G.M., Thomson, G.O.B., Laxen, D.P.H., Hunter, R., Hepburn, W. 1987.The Lancet 1, 1221–26.
Hausman, J.A. & Wise, D.A. 1982.In Structural Analysis of Discrete Data with Econometric Applications, C. Manski and D. McFadden etc., pp. 365–391, Cambridge, Mass, MIT Press.
Lacey, R.F., Moore, M.R., Richards, W.N. 1985.Science of the Total Environ. 41, 235–257.
Laxen, D.P.H. 1983. Proc. Int. Conf. “Heavy Metals in the Environment”, Heidelberg, CEP Consultants, Edinburgh. Vol. 1, pp. 290–293.
Laxen, D.P.H., Lindsay, F., Raab, G.M., Hunter, R., Fell, G.S., Fulton, M. 1987. The Variability of lead in dusts within the homes of young children. Proceedings of the ConferenceLead in the Home Environment. In press.
Pocock, S.J. 1980.Arch. Environ, Hlth. 35, 45–51.
Pocock, S.J., Shaper, A.G., Walker, M., Wale, C.J., Clayton, B., Delves, T., Lacey, R.F., Packam, R.F., Powell, P. 1983.J. Epidem. Comm. Hlth. 37, 1–7.
Raab, G.M., Fulton, M., Laxen, D.P.H. & Thomson, G.O.B. 1985.Statistician 34, 45–57.
SASPAK user manual, Release 3. 1983. Local Authority Management Services and Computer Committee.
Sherlock, J.C., Ashby, D., Delves, H.T., Forbes, G.I., Moore, M.R., Patterson, W.J., Pocock, S.J., Quinn, M.J., Richards, W.N., Wilson, T.S. 1984.Human Toxicol. 3, 383–92.
Worth, D., Matranga, A., Lieberman, M., DeVos, E., Karelekas, P., Ryan, C., Grain, G. 1981.In Environmental Lead, D.R. Lynam and L.G. Pantanida (Eds.) Academic Press, N.Y. pp. 199–225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is also being published in Proceedings of the Conference on “Lead in the Home Environment” and is one of several selected from SEGH sponsored conferences for simultaneous publication in this journal.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raab, G.M., Laxen, D.P.H. & Fulton, M. Lead from dust and water as exposure sources for children. Environ Geochem Health 9, 80–85 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02057280
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02057280