Abstract
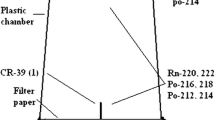
The concentration of radon (222Rn) was measured in the soil near the ground surface, using CR/39 solid state nuclear track detectors. The measurements were carried out in PVC tubes at 0.25 m intervals up to 1.25 m. The detectors were etched in 7N NaOH solutions at 80°C. The α-tracks from radon's decay were counted using a microscope. A microscope-camera-computer system developed for automatic counting was also used. The results provide evidence for the non-diffusive transport of radon in soils. A transport length of (46.9±3.2) cm was estimated for radon transport near ground surface. Also the variation of soil's radon concentration was correlate to humidity and atmospheric pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A. Durrani, R.K. Bull. Solid state nuclear track detection- Principles, Methods and Applications, Pergamon Press, 1987.
K. Ioannides, Unpublished.
K. Kristiansson L. Malmqvist, Geophysics, 47, 110 (1982) 1444.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ioannides, K.G., Papachristodoulou, C., Karamanis, D.T. et al. Measurements of222Rn migration in soil. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Articles 208, 541–547 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02040071
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02040071