Abstract
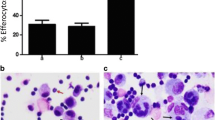
A role for eosinophils in the immune reaction has not been yet established. Considering that these leukocytes accumulate in lymphoid organs under glucocorticoid stimulation, we explored the possibility that they participate in the depression of immune reactions induced by these hormones and that they degranulate to exert this action. In this context, we investigated the dose effect of three estrogens on the number and degranulation of spleen red pulp eosinophils and on the percentage of spleen cross sectional area comprising white pulp. Estradiol-17β or 4(OH)estradiol-17β increased red pulp eosinophils at low doses; 2(OH)estradiol-17β increased them at a very high dose. The three estrogens degranulated the spleen eosinophils and decreased the lymphocyte containing spleen white pulp. We propose that the decrease in white pulp is a response mediated by agents released from degranulating eosinophils under the action of estrogen. Consequently, both estrogen-induced eosinophil degranulation and estrogen-induced increase in red pulp eosinophil numbers are conditions contributing to a decrease in white pulp volume. All above evidence supports the hypothesis that eosinophils are involved in immunoregulation by diminishing the number of lymphocytes contained in lymphoid organs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Duic, D. N. Croizier, M. J. Lynch and P. D. McClure,Swiss agammaglobulinemia with hypoglycemia, osseous changes and eosinophilia. Can. Med. Assoc. J.103, 64–68 (1970).
R. A. Gatti, H. D. Allen, H. J. Meuwissen, R. Hong and R. A. Good,Immunological reconstitution of sex-linked lymphopenic immunological deficiency. Lancet2, 1366–1369 (1968).
W. H. Hitzig, R. Landolt, G. Muller and P. Bodmer,Heterogeneity of phenotypic expression in family with swiss-type agammaglobulinemia: observations on the acquisition of agammaglobulinemia. J. Pediat.78, 968–980 (1971).
R. Hong, M. D. Cooper, M. J. G. Allan, H. E. M. Kay, H. Meuwissen and Meuwissen and R. A. Good,Immunological restitution in lymphopenic immunological deficiency syndrome. Lancet1, 503–506 (1968).
Y. Kikkawa, K. Kamimura, K. Hamajima, T. Sekiguchi, T. Kawai, M. Takenaka and T. Tada,Thymic alymphoplasia with hyper-IgE-globulinemia. Pediatrics51, 690–696 (1973).
G. J. Lawlor Jr., A. J. Ammann, W. C. Wright Jr., S. H. Lafranchi, D. Bilstrom and E. R. Stiehm,The syndrome of cellular immunodeficiency with immunoglobulins. J. Pediatr.84, 183–192 (1974).
M. E. Miller and K. Hummeler,Thymic dysplasia (“Swiss agammaglobulinemia”). II. Morphologic and functional observations. J. Pediatr.70, 737–744 (1967).
M. E. Miller and R. M. Schieken,Thymic dysplasia. A separable entity from “Swiss agammaglobulinemia”. Am. J. Med. Sci.253, 741–750
L. A. Kater, R. J. Goetzl and K. F. Austen,Isolation of human eosinophil phospholipase D. J. Clin. Invest.57, 1173–1180 (1976).
R. P. Orange, R. C. Murphy and K. R. Austen,Inactivation of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) by arylsulfatase. J. Immunol.113, 316–322 (1974).
S. I. Wasserman, E. J. Goetzl and K. F. Austen,Inactivation of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis by human eosinophil arylsulfatase. J. Immunol.114, 645–649 (1975).
W. R. Henderson, A. Jörg and S. J. Klebanoff,Eosinophil peroxidase-mediated inactivation of leukotrienes B 4, C4, and D4. J. Immunol.128, 2609–2613 (1982).
G. J. Gleich,The eosinophil. New aspects of structure and function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.60, 73–82 (1977).
K. S. Ramesh, S. H. Pincus and R. E. Rocklin,Human lymphocyte-eosinophil interactions. I. Modulation of phytohemagglutinin-induced lymphocyte proliferation by eosinophils. Cell. Immunol.92, 366–375 (1985).
C. G. B. Peterson, V. Skoog and P. Venge,Human eosinophil cationic proteins (ECP and EPX) and their suppressive effects on lymphocyte proliferation. Immunobiol.171, 1–13 (1986).
N. Sabag, M. A. Castrillón and A. Tchernitchin,Cortisol-induced migration of eosinophil leukocytes to lymphoid organs. Experientia34, 666–667 (1978).
T. F. Dougherty,Effect of hormones of lymphatic tissue. Physiol. Rev.32, 379–401 (1952).
W. Niederer,Immunoendokrinologie. Schweiz. Med. Wschr.104, 841–847 (1974).
H. N. Claman,How corticosteroids work. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.55, 145–151 (1975).
G. R. Crabtree, S. Gillis, K. A. Smith and A. Munck,Glucocorticoids and immune responses. Arthritis Rheum22, 1246–1256 (1979).
T. R. Cupps and A. S. Fauci,Corticosteroid-mediated immunoregulation in man. Immunol. Rev.65, 133–155 (1982).
F. R. Weller, H. H. Weller, C. G. M. Kallenberg, T. H. The and N. G. M. Orie,Sensitivity to hydrocortisone is a relevant factor in the immunoendocrine relationship. I. The cell-mediated immune response in relation to blood levels and in vitro immunosuppressive effects of hydrocortisone in patients with asthma and healthy control subjects. J. Allergy clin. Immunol.78, 423–430 (1986).
A. Tchernitchin,The role of eosinophil receptors in the nongenomic response to oestrogens in the uterus. J. Steroid Biochem.11, 417–424 (1979).
T. Rytomäa,Organ distribution and histochemical properties of eosinophil granulocytes in rat. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand50 (suppl. 140), 1–118 (1960).
E. G. Bassett,Infiltration of eosinphils into the modified connective tissue of oestrus and pregnant animals. Nature140, 1259–1261 (1962).
L. Bjersing and N. E. Borglin,Effect of hormones on incidence of uterine eosinophilia in rats. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand.60, 27–35 (1964).
A. Tchernitchin, J. Roorijck, X. Tchernitchin, J. Vandenhende and P. Galand,Dramatic early increase in uterine eosinophils after oestrogen administration.Nature 248, 142–143 (1974).
A. Tchernitchin, X. Tchernitchin and P. Galand,Correlation of estrogen-induced uterine eosinophilia with other parameters of estrogen stimulation, produced with estradiol-17β and estriol. Experientia31, 993–994 (1975).
A. N. Tchernitchin and P. Galand,Oestrogen levels in the blood, not in the uterus, determine uterine eosinophilia and oedema. J. Endocrinol.99, 123–130 (1983).
A. N. Tchernitchin,Eosinophil-mediated non-genomic parameters of estrogen stimulation: A separate group of responses mediated by an independent mechanism. J. Steroid Biochem.19, 95–100 (1983).
A. N. Tchernitchin, M. A. Mena, A. Rodríguez and M. Maturana,Radioautographic localization of estrogen receptors in the rat uterus: a tool for the study of classical and nontraditional mechanisms of hormone action. InExperimental Systems. Localization of putative steroid receptors, vol. 1. (Eds. L. P. Pertschuk and S. H. Lee) pp. 5–37. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida 1985.
G. Grunert, M. Porcia and A. N. Tchernitchin,Differential potency of oestradiol-17β and diethylstilboestrol on separate groups of responses in the rat uterus. J. Endocrinol.110, 103–114 (1986).
A. N. Tchernitchin, M. A. Mena, J. Soto and C. Unda,The role of eosinophils in the action of estrogens and other hormones. Med. Sci. Res.17, 5–10 (1989).
J. Zipper, G. Ferrando, G. Sáez and A. Tchernitchin,Intrauterine grafting in uterus of autologous and homologous rat skin. Am J. Obstet. Gynecol.94, 1056–1061 (1966).
M. López, M. A. Castrillón and A. N. Tchernitchin,Colloidal carbon blocks oestrogen-induced migration of eosinophils to the uterus and the uterine water imbibition response. J. Endocrinol.109, 89–95 (1986).
G. Neumann, G. Grunert and A. N. Tchernitchin,Effect of various estrogens on spleen eosinophilia. Med. Sci. Res.15, 97–98 (1987).
P. Galand, N. Tchernitchin and A. N. Tchernitchin,Dissociation of uterine eosinophilia and water imbibition from other estrogen-induced responses by nafoxidine pretratment. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.42, 227–233 (1985).
J. Steinsapir, A. M. Rojas, A. Tchernitchin and R. PachecoEosinopenic hormones. IRCS Med. Sci.6, 513 (1978).
A. N. Tchernitchin, J. Barrera, P. Arroyo, M. A. Mena, K. Vilches and G. Grunert,Degranulatory action of estradiol on blood eosinophil leukocytes in vivo and in vitro. Agents and Actions17, 60–66 (1985).
L. Daniel, G. Souweine, J. C. Monier and S. Saez,Specific estrogen binding sites in human lymphoid cells and thymic cells. J. Steroid Biochem.18, 559–563 (1983).
N. B. West, D. J. Anderson, L. L. Stunz and E. J. Hoch,A specific estrongen receptor in the mouse spleen. Characterization and evidence of physiological regulation. J. Steroid Biochem.16, 557–562 (1982).
J. H. M. Cohen, L. Danel, G. Cordier, S. Saez and J. P. Revillard,Sex steroid receptors in peripheral T cells: absence of androgen receptors and restriction of estrogen receptors to OKT8-positive cells. J. Immunol.131, 2767–2771 (1983).
C. J. Grossman, L. J. Sholiton and P. Nathan,Rat thymic estrogen receptor-I. Preparation, location and physiocochemical properties. J. Steroid Biochem.11, 1233–1240 (1979).
C. J. Grossman, L. J. Sholiton, G. C. Blaha and P. Nathan,Rat thymic estrogen receptor-II physiological properties. J. Steroid Biochem.11, 1241–1246 (1979).
N. J. McLusky, E. R. Barnea, C. R. Clark and F. Naftolin,Catechol estrogens and estrogen receptors. InCatechol Estrogens. (Eds G. R. Merriam and M. B. Lipsett) pp. 151–165 Raven Press, New York 1983.
M. V. Vásquez, M. Silva, C. Unda, R. Arriagada and A. N. Tchernitchin,Adenohypophysisimplants under the renal capsula increase spontaneous and estrogen-induced eosinophil leukocyte degranulation in the blood. Med. Sci. Res.15, 149–150 (1987).
G. Grunert, M. Porcia, G. Neumann, S. Sepúlveda and A. N. Tchernitchin,Progesterone interaction with eosinophils and with responses already induced by oestrogen in the uterus. J. Endocrinol.102, 295–303 (1984).
E. R. Decombre,Peroxidase: a marker for estrogen expression. InBiochemical Actions of Hormones, vol. 11. (Ed G. Litwack) pp. 309–345, Academic Press, Orlando 1987.
S. L. Sepúlveda, G. Grunert and A. N. Tchernitchin,Estrogen-induced eosinophilia in the rat uterine cervix. IRCS Med. Sci.14, 7–8 (1986).
M. A. Castrillón, G. Grunert, M. López and A. N. Tchernitchin,Effect of progesterone on spleen eosinophilia. IRCS Med. Sci.10, 955–956 (1982).
M. V. Berridge and E. G. Bassett,The effects of antieosinophil serum on haemopoietic cells of normal and parasite infected mice. New Zealand Med. J.98, 763 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tchernitchin, A.N., Carter, W., Soto, J. et al. Effect of eosinophil-degranulating estrogens on spleen eosinophils and white pulp/red pulp ratio. Agents and Actions 31, 249–256 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01997616
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01997616