Abstract
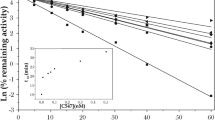
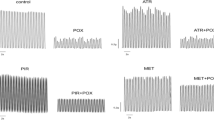
Isolated rat diaphragm preparations treated with soman or with the irreversible and oxime resistant cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitor S27 (see Compounds) showed a considerable recovery of neuromuscular transmission (NMT) during incubation with the (bis)pyridinium oximes HI-6, HGG-12, P2S and obidoxime. In the soman-treated preparations this NMT recovery was predominantly caused by reactivation of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) but in the S27-treated preparations it was caused by a direct (pharmacological) effect unrelated to enzyme reactivation. Atropinized rats were artificially ventilated after injection with 3×LD50 soman for 3 h and then treated with HI-6, i.e. at a time when oxime reactivation of soman inhibited ChE is no longer possible. Nevertheless, these rats started to breathe spontaneously and 50−60% survived more than 24 h, whereas all control animals (saline instead of HI-6) died within 10 min after artificial ventilation was terminated. In such animals no significant reactivation of ChE activity at various time intervals following HI-6 treatment was found, either in the diaphragms or in the brains. There was a significant amount of NMT (50%) in vitro in diaphragms obtained from these animals. This NMT did not improve in vitro in the presence of HI-6 and was not inhibited by soman administered to the medium. It is concluded that in this case the NMT found was based on synaptic adaptation to the continued inhibition of ChE and that the survival of the animals might be due to a combination of this synaptic adaptation and central direct effects of HI-6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharoni AH, O'Brien RD (1968) The inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by anionic organophosphorus compounds. Biochemistry 7: 1538–1543
Alkondon M, Ras KS, Albuquerque EX (1988) Acetylcholinesterase reactivators modify the functional properties of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ion channel. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245: 534–556
Clement JG (1979) Pharmacological action of HS-6, an oxime, on the neuromuscular junction. Eur J Pharmacol 53: 135–141
Clement JG (1981) Toxicology and pharmacology of bispyridinium oximes — insight into the mechanisms of action versus soman poisoning in vivo. Fundam Appl Toxicol 1: 193–202
De Jong LPA, Wolring GZ (1984) Stereospecific reactivation by some Hagedorn oximes of acetylcholinesterases from various species including man, inhibited by soman. Biochem Pharmacol 33: 1119–1125
De Jong LPA, Benschop HP (1970) Organophosphorus compounds. Part X. Anticholinesterase-properties of O-2-trimethylammoniethyl methylphosphonefluoridothioate iodide and of S-2-di-n-propylaminoethyl methylphosphonofluoridothioate. Becueil des Traveaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas 89: 1038–1042
Ellman GI, Coutney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7: 88–95
Gordon JJ, Leadbeater L, Maidment MP (1978) The protection of animals against organophosphate poisoning by pretreatment with a carbamate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 43: 207–216
Hamilton MG, Lundy PM (1989) HI-6 therapy of soman and tabun poisoning in primates and rodents. Arch Toxicol 63: 144–149
Hauser W, Weger N (1979) Therapeutic effects of the bispyridinium salts HGG-12, HGG-42, and atropine and benactizine in organophosphate poisoning in dogs. Arch Toxicol Suppl 2: 393–396
Heilbronn E, Tolagen B (1965) Toxogonin in sarin, soman and tabun poisoning. Biochem Pharmacol 14: 73–78
Heilbronn-Wikström (1965) Phosphorylated cholinesterases: their formation, reactions and induced hydrolysis. Svensk Kem Tidskr 77: 3–35
Hobbiger F, Vojvodic V (1967) The reactivation by pyridinium aldoximes of phosphylated acetylcholinesterase in the central nervous system. Biochemistry 38: 439–445
Kirsch DM, Weger N (1981) Effects of the bispyridinium compounds HGG-12, HGG-42 and obidoxime on synaptic transmission and NAD(P)H fluorescence in the superior cervical ganglion of the rat in vitro. Arch Toxicol 47: 217–232
Kloog Y, Gabron R, Balderman D, Sokolovsky M (1985) Reversible and irreversible inhibition of rat brain muscarinic receptors is related to different substitutions on bisquaternary pyridinium oximes. Arch Toxicol 58: 37–39
Kuhnen-Clausen P, Hagedorn I, Gross G, Bayer H, Hucho F (1983) Interactions of bisquaternary pyridine salts (H-oximes) with cholinergic receptors. Arch Toxicol 54: 171–177
Ligtenstein DA, Kossen SP (1983) Kinetic profile in blood and brain of the cholinesterase reactivating oxime HI-6 after intravenous administration to the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 71: 177–183
Loomis TA, Salafsky B (1963) Antidotal action of pyridinium oximes in anticholinesterase poisoning, comparative effects of soman, sarin, and neostigmine on neuromuscular function. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 5: 685–690
Massoulié J, Bon S (1982) The molecular forms of cholinesterase and AChE in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci 5: 57–106
Meeter E, Wolthuis OL (1968) The spontaneous recovery of respiration and neuromuscular transmission in the rat after anticholinesterase poisoning. Eur J Pharmacol 2: 377–386
Melone MAR, Longo A, Taddei C, Augusti-Tocco G (1987) Acetylcholinesterase in neuroblastoma and neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells: cellular cocalization and molecular forms. Int J Dev Neurosci 5: 417–428
Oldiges H, Schoene K (1970) Pyridinium und Imidazolinium-Salze als Antidote gegen Soman-und Paraoxonvergiftungen bei Mause. Arch Toxicol 26: 293–299
Schoene K, Steinhanses J, Oldiges H (1976) Protective activity of pyridinium salts against soman poisoning in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol 25: 1955–1965
Silver A (1974) The biology of cholinesterases. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 1–596
Simons KJ, Briggs CJ (1985) Disposition of HI-6 oxime in rats after intravenous and intramuscular administration. J Pharm Pharmacol 37: 367–369
Smith AP, Muir AW (1977) Antidotal action of the oxime HS-6 at the soman neuromuscular junction of the rat and the guinea-pig. J Pharm Pharmacol 29: 762–764
Valdes JJ, Shih T, Whalley C (1985) Competitive binding of the oximes HI-6 and 2-PAM with regional brain muscarinic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 34: 2815–2818
Van Dongen CJ, Elskamp RM, De Jong LPA (1987) Influence of atropine upon reactivation and aging of rat and human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase inhibited by soman. Biochem Pharmacol 36: 1167–1169
Van Helden HPM, Van der Wiel HJ, Wolthuis OL (1983) Therapy of organophosphate poisoning; the marmoset as a model for man. Br J Pharmacol 78: 579–589
Van Helden HPM, Berends F, Wolthuis OL (1984) On the existence of a soman depot. In: Brzin M, Barnard EA, Sket D (eds) Cholinesterases, fundamental and applied aspects, Walter de Gruijter and Co., Berlin, NY, pp 375–388
Van Helden HPM, Van der Wiel HJ, Wolthuis OL (1986) The prophylactic efficacy of various simulators against intoxication with the organophosphate soman; structure-activity studies. J Pharm Pharmacol 38: 439–445
Wolthuis OL, Vanwersch RAP, Van der Wiel HJ (1981) The efficacy of some bis-pyridinium oximes as antidotes to soman in isolated muscles of several species including man. Eur J Pharmacol 70: 355–369
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Helden, H.P.M., de Lange, J., Busker, R.W. et al. Therapy of organophosphate poisoning in the rat by direct effects of oximes unrelated to ChE reactivation. Arch Toxicol 65, 586–593 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973721
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973721