Abstract
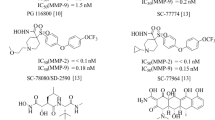
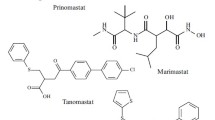
Prostromelysin, a member of the family of matrix metalloproteinases, is secreted as a zymogen which is activated after cleavage of the His81−Phe82 bond. The 82 amino acid propeptide that is removed during activation contains 12 amino acids, MRKPRC75GVPDVG, that are highly conserved in all MMPs. We evaluated a series of peptides that span this region for their ability to inhibit stromelysin. The hexapeptide, Ac-RCGVPD, and the pentapeptide, Ac-RCGVP had IC50 values of approx. 10 μM. The tetrapeptide, Ac-RCGV, was somewhat less potent with an IC50 of 60 μM. Smaller peptides, e. g. Ac-RCG, were significantly less potent as inhibitors. Substitutions of Cys75 with Ser resulted in a complete loss of inhibitory activity. The peptides in this series also inhibited human fibroblast collagenase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Nagase, J. J. Enghild and K. Suzuki,Stepwise activation mechanism of the precursor of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) by proteinases and (4-aminophenyl) mercuric acetate. Biochemistry290, 5783–5789 (1990).
S. E. Whitham, G. Murphy, P. Angel, H.-J. Rahmsdorf, B. J. Smith, A. Lyons, T. J. R. Harris, J. J. Reynolds, P. Herrlich and J. P. Docherty,Comparison of human stromelysin and collagenase by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem. J.240, 913–916 (1986).
E. B. Springman, E. L. Angleton, H. Birkedal-Hansen and H. E. Van Wart,Multiple modes of activation of latent human fibroblast collagenase: Evidence for the role of a Cys 73 activesite zinc complex in latency and “cysteine switch” mechanism for activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA87, 364–368 (1990).
W. G. Stetler-Stevenson, J.-A. Talano, M. E. Gallagher, H. C. Krutzsch and L. A. Liotta,Inhibition of human type IV collagenase by a highly conserved peptide sequence derived from its prosegment. Am. J. Med. Sci.302, 163–170 (1991).
T. E. Cawston, W. A. Galloway, E. Mercer, G. Murphy and J. J. Reynolds,Purification of rabbit bone inhibitor of collagenase. Biochem. J.195, 159–165 (1981).
S. Netzel-Arnett, S. K. Mallya, H. Nagase, H. Birkedal-Hansen and H. E. Van Wart,Continuously recording fluorescent assays optimized for five human matrix metalloproteinases. Anal. Biochem.195, 86–92 (1991).
G. Salvesen and H. Nagase,Inhibition of proteolytic enzymes. InProteolytic Enzymes, a Practical Approach. (Eds. R. J. Beyon and J. S. Bond), pp. 88–104, IRL Press at Oxford University Press, Oxford 1989.
A. J. Park, L. M. Matrisian, A. F. Kells, R. Pearson, Z. Yuan and M. Navre,Mutational analysis of the transin (rat stromelysin) autoinhibitor region demonstrates a role for residues surrounding the “cysteine switch”. J. Biol. Chem.266, 1584–1590 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanglow, A.C., Lugo, A., Walsky, R. et al. Peptides based on the conserved prodomain sequence of matrix metalloproteinases inhibit human stromelysin and collagenase. Agents and Actions 39 (Suppl 1), C148–C150 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972749
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972749