Abstract
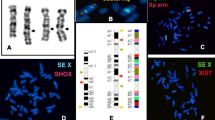
The X chromosome inactivation analysis of eight female relatives was performed to elucidate the X chromosome gene defect of six male hypogammaglobulinaemic individuals. The patients had diminished numbers of circulating B-cells and no relevant family history. The methylation status of three X-linked genes, phosphoglycerate kinase, hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase and DXS255, was determined on DNA from Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B-cell lines established from the female relatives. The methylation pattern of at least one gene was informative in all eight females examined. While both alleles were equally methylated in four of eight females, the remaining four female relatives of three hypogammaglobulinaemia patients exhibited a non-random methylation pattern in their B-cells, suggesting that these three patients represented sporadic cases of X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA). The clinical or immunological status of these three patients did not differ from the remaining two who had early onset hypogammaglobulinaemia and who were tentatively diagnosed as having common variable immunodeficiency. The sixth patient had recurrent infections after undergoing surgical removal of a brain tumour at 22 years of age, although his immunological features did not distinguish him from the other patients. X chromosome inactivation analysis can be useful in differentiating XLA from hypogammaglobulinaemia in male patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BLC:
-
B-lymphoblastoid cells
- CVID:
-
common variable immunodeficiency
- EBV:
-
Epstein-Barr virus
- HPRT:
-
hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase
- PBMC:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PGK:
-
phosphoglycerate kinase
- XLA:
-
X-linked agammaglobulinaemia
References
Conley ME, Puck JM (1988) Carrier detection in typical and atypical X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Pediatr 112:688–694
Conley ME, Sweinberg SK (1992) Females with a disorder phenotypically identical to X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Clin Immunol 12:139–143
Conley ME, Lavoie A, Briggs C, Brown P, Guerra C, Puck JM (1988) Nonrandom X chromosome inactivation in B cells from carriers of X chromosome-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:3090–3094
Fearon ER, Winkelstein JA, Civin CI, Pardoll DM, Vogelstein B (1987) Carrier detection in X-linked agammaglobulinemia by analysis of X-chromosome inactivation. N Engl J Med 316: 427–431
Fraser NJ, Boyd Y, Craig I (1989) Isolation and characterization of a human variable copy number tandem repeat at Xcen-p11.22. Genomics 5:144–148
Gilliland DG, Blanchard KL, Levy J, Perrin S, Bunn HF (1991) Clonality in myeloproliferative disorders: Analysis by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6848–6852
Hayakawa H, Iwata T, Yata J, Kobayashi N (1981) Primary immunodeficiency syndrome in Japan. I. Overview of a nationwide survey on primary immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Immunol 1:31–39
Hendriks RW, Schuurman RKB (1991) Genetics of human X-linked immunodeficiency diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 85: 182–192
Hendriks RW, De Weers M, Mensink RGJ, Kraakman MEM Mollee-Versteegde IFAM, Veerman AJP, Sandkuyl LA, Schuurmann RKB (1991) Diagnosis of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome by analysis of the X-chromosome inactivation patterns in maternal leukocyte populations using the hypervariable DXS255 locus. Clin Exp Immunol 84:219–222
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Matsuoka H, Okada J, Takahashi T, Mizuno T, Matsuoka M, Tsuge I, Torii S (1986) In vitro analysis of lymphocyte functions in common variable immunodeficiency: heterogeneity in B-cell defects. Eur J Pediatr 145:252–257
Tsuge I, Kojima S, Matsuoka H, Abe T, Kamachi Y, Torii S, Matsuyama T (1993) Clonal haematopoiesis in children with acquired aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol (in press)
Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Preisinger AC, Willard HF, Michelson AM, Riggs AD, Orkin SH (1987) Clonal analysis using recombinant DNA probes from X-chromosome. Cancer Res 47:4806–4813
World Health Organization (1992) Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of a WHO scientific group. Immunodefic Rev 3:195–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuge, I., Matsuoka, H., Abe, T. et al. X chromosome inactivation analysis to distinguish sporadic cases of X-linked agammaglobulinaemia from common variable immunodeficiency. Eur J Pediatr 152, 900–904 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957526
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957526