Abstract
The fluctuating populations of the field vole (Microtus agrestis), the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus) and the yellow-necked field mouse (Apodemus flavicollis) were observed in the years from 1980 through 1985 in wooded areas in Bavaria. Every spring and autumn rodents were trapped with snap traps in test plots, then frozen and dissected in the lab.
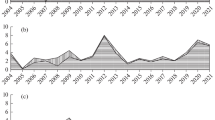
In the flat regions of Bavaria the density of the three species fluctuated synchronously in two-year cycles. In the alpine region irregular fluctuations dependent upon seed crop of forest trees were observed. The parameters of fertility of the yellow-necked field mouse, i. e. the weight of gonads of both sexes and the percentage of the pregnant females, were inversely correlated to the density of that species. The fertility of the bank vole and field vole rose during the progradation period but declined suddenly at high density levels. The following decline of density of all three species was simultaneous and a consequence of reduced reproduction.
The fluctuation of abundance was correlated to changes of fertility in the rodents and high density produced an adverse effect upon fertility. The detection of causative agents which can affect the reproduction of rodents, i. e. pheromones, hormones, secretions, other chemical compounds, sounds, visual, tactile or other signals, are of great importance for applied zoology, such as for the forecast and for the control of outbreaks of harmful rodents.
Zusammenfassung
Die Populationsentwicklung der Erdmaus, der Rötelmaus und der Gelbhalsmaus verlief in den Flachlandgebieten Bayerns synchron in einem regelmäßigen zweijährigen Zyklus. Im Alpenraum wurde bisher nur nach einem guten Waldsamenjahr eine starke Zunahme und nachfolgend eine starke Reduktion der Mäusedichte beobachtet. In allen Gebieten wurde ein sehr enger Zusammenhang zwischen der Dichte und der Fruchtbarkeit der Tiere beobachtet. Eine hohe Mäusedichte hatte stets einen negativen Effekt auf die Fertilität. Dabei spielten möglicherweise soziale Interaktionen bzw. Duftstoffe (Pheromone) oder Sekrete der Tiere eine wichtige Rolle.
Die Forschung steht hier erst ganz am Anfang. Sofern es gelingt, die entscheidenden Hemmfaktoren der Fertilität bei Mäusen aufzudecken und zu manipulieren, könnte die Schadnagerbekämpfung in vielen Bereichen auf eine völlig neue Basis gestellt werden, nälich weg von der problematischen Vergiftung der Tiere mit Rodentiziden hin zu einer natürlichen, spezifischen und umweltschonenden Kontrolle der Fruchtbarkeit der Tiere.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literaturverzeichnis
Bäumler, W., 1973: Über einen Zusammenbruch der Gelbhalsmauspopulation im Nationalpark Bayerischer Wald. Anz. Schädlingskde., Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz46, 161–168.
Bäumler, W., 1975: Wachstum und Vermehrung der Erdmaus (Microtus agrestis L.) in Forstkulturen. Anz. Schädlingskde., Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz48, 65–77.
Bäumler, W., 1980: Die Sommerkrise der Erdmaus (Microtus agrestis L.), Teil II: Aufzucht in der Gefangenschaft. Anz. Schädlingskde., Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz53, 177–181.
Bäumler, W., 1982: Ein Beitrag zur Prognose der Populationsentwicklung von Mäusen in Forstkulturen. Anz. Schädlingskde., Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz55, 40–44.
Bäumler, W., 1985: Feldrattenbekämpfung in Ägypten. Bekämpfungsmöglichkeiten der Hausmaus (Mus musculus) in den “new reclaimed areas”. GTZ-Bericht 81.2083.9-01.100, 48 S.
Bäumler, W.;Hohenadl, W., 1980: Über den Einfluß alpiner Kleinsäuger auf die Verjüngung in einem Bergmischwald der Chiemgauer Alpen. Forstwiss. Centralblatt99, 207–221.
Braumandl, A., 1983: Einfluß der Nahrung auf die Populationsdynamik von Mäusen in Forstkulturen. Diplomarbeit Univ. München, Forstw. Fak. 75 S.
Clarke, J. R., 1977: Long and short term changes in gonadal activity of field voles and bank voles. Oikos29, 457–468.
Drickamer, L., 1981: Pheromones, social influences and population regulation in rodents. In:Gilmore, D. &Cook, B. (ed.): Environmental factors in mammal reproduction. Macmillan publ. Ltd., London, pp. 100–112.
Kalela, O., 1962: On the fluctuations in the numbers of arctic and boreal small rodents as a problem of production biology. Ann. Sci. fenn. (AIV)66, 1–38.
Klemm, M., 1964: Beitrag zur Kenntnis des Auftretens der Feldmaus (Microtus arvalis Pall.) in Deutschland in den Jahren 1928–1941. Z. angew. Zool.51, 419–499.
Krampitz, H. E.;Bäumler, W., 1979: Vorkommen, Saisondynamik und Wirtskreis von Babesien in einheimischen Nagetieren. Zeitschr. f. Parasitenkde.58, 15–33.
Krebs, C.;Myers, J., 1974: Population cycles in small mammals. Adv. Ecol. Res.8, 267–399.
Lidicker, W., 1978: Regulations of numbers in small mammal populations — historical reflections and a synthesis. In:Snyder, D. P. (ed.): Populations of small mammals under natural conditions. Pymatuning Lab. Ecol. Special. Publ. No. 5, 122–141.
Maercks, H., 1954: Über den Einfluß der Witterung auf den Massenwechsel der Feldmaus (Microtus arvalis) in der Wesermarsch. Nachrbl. Deutsch. Pflanzenschutzd. (Braunschweig)6, 101–108.
Niemeyer, H., 1979: Beobachtungen zum Massenwechsel der Erdmaus (Microtus agrestis) und der Rötelmaus (Clethrionomys glareolus) in Niedersachsen und zur Möglichkeit einer Prognose. Aus dem Walde31, 233.
Wendland, V., 1975: Dreijähriger Rhythmus im bestandeswechsel der Gelbhalsmaus. Oecologia20, 301–310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 4 Abbildungen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bäumler, W. Populationsdynamik von Mäusen in verschiedenen Waldgebieten Bayerns. Anz. Schadlingskde., Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz 59, 112–117 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01903220
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01903220