Summary
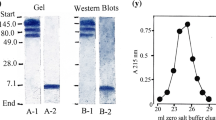
Insulin binding to human placenta membranes treated at pH 7.6 or 8.5 in the presence or absence of 2.0mm DTT for 5 min, followed by the simultaneous removal of the DTT and pH adjustment to pH 7.6, displayed curvilinear (heterogeneous) insulin binding plots when analyzed by the method of Scatchard. However, Triton X-100 solubilization followed by Bio-Gel A-1.5m gel filtration chromatography of the placenta membranes previously treated with DTT at pH 8.5 generated a nearly straight line (homogeneous) Scatchard plot.125I-insulin affinity crosslinking studies coupled with Bio-Gel A-1.5m gel filtration chromatography demonstrated that the alkaline pH and DTT treatment of placenta membranes followed by detergent solubilization generated an αβ heterodimeric insulin receptor complex from the α2β2 heterotetrameric disulfide-linked state. The ability of alkaline pH and DTT to produce a functional αβ heterodimeric insulin receptor complex was found to be time dependent with maximal formation and preservation of tracer insulin binding occurring at 5 min. These data demonstrate that (i) a combination of alkaline pH and DTT treatment of placenta membranes can result in the formation of a functional αβ heterodimeric insulin receptor complex. (ii) the αβ heterodimeric complex displays homogeneous insulin binding. (iii) the insulin receptor membrane environment maintains the α2β2 association state, which displays heterogeneous insulin binding, despite reduction of the critical domains that are responsible for the covalent interaction between the αβ heterodimers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
adenosine 5′-triphosphate
- DTT:
-
dithiothreitol
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
- DSS:
-
disuccinimidyl suberate
- NEM:
-
N-ethylmaleimide
- IGF-I:
-
insulin-like growth factor-I
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- HEPES:
-
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine-ethanesulfonic acid
References
Avruch, J., Nemenoff, R.A., Blackshear, P.J., Pierce, M.W., Osathanondh, R. 1982. Insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in detergent extracts of human placental membranes.J. Biol. Chem. 257:15162–15166
Boni-Schnetzler, M., Rubin, J.B., Pilch, P.F. 1986. Structural requirements for the transmembrane activation of the insulin receptor kinase.J. Biol. Chem. 261:15281–15287
Boni-Schnetzler, M., Scott, W., Waugh, S.M., Dibella, E., Pilch, P.F. 1987. The insulin receptor.J. Biol. Chem. 262:8395–8401
Boyle, T.R., Campana, J., Sweet, L.J., Pessin, J.E. 1985. Subunit structure of the purified human placental insulin receptor.J. Biol. Chem. 260:8593–8600
Czech, M.P. 1985. The nature and regulation of the insulin receptor: Structure and function.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 47: 357–381
Deger, A., Kramer, H., Rapp, R., Koch, R., Weber, U. 1986. The nonclassical insulin binding of insulin receptors from rat liver is due to the presence of two interacting α-subunits in the receptor complex.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 135:458–464
Ebina, Y., Ellis, L., Jarnagin, K., Edery, M., Graf, L., Clauser, E., Ou, J.-H., Masiarz, F., Kan, Y.W., Goldfine, I.D., Roth, R.A., Rutter, W.J. 1985. The human insulin receptor cDNA: The structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signaling.Cell 40:747–758
Grunfeld, C., Shigenaga, J.K., Ramachandran, J. 1985. Urea treatment allows dithiothreitol to release the binding subunit of the insulin receptor from the cell membrane: Implications for the structural organization of the insulin receptor.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 133:389–396
Harrison, L.C., Itin, A. 1980. Purification of the insulin receptor from human placenta by chromatography on immobilized wheat germ lectin and receptor antibody.J. Biol. Chem. 255:12066–12072
Hedo, J.A., Collier, E., Watkinson, A. 1987. Myristyl and palmityl acylation of the insulin receptor.J. Biol. Chem. 262:954–957
Jacobs, S., Cuatrecasas, P. 1980. Disulfide reduction converts the insulin receptor of human placenta to a low affinity form.J. Clin. Invest. 66:1424–1427
Jacobs, S., Cuatrecasas, P. 1983. Insulin receptors.Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 23:461–479
Jacobs, S., Hazum, E., Shechter, Y., Cuatrecasas, P. 1979. Insulin receptor: Covalent labeling and identification of subunits.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:4918–4921
Kahn, C.R. 1985. The molecular mechanism of insulin action.Annu. Rev. Med. 36:429–451
Kasuga, M., Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y., Blithe, D.L., Kahn, C.R. 1983. Tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity is associated with the purified insulin receptor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:2137–2141
Kasuga, M., Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y., Blithe, D.L., White, M.F., Kahn, C.R. 1983. Characterization of the insulin receptor kinase purified from human placental membranes.J. Biol. Chem. 258:10973–10980
Kasuga, M., Karlsson, F.A., Kahn, C.R. 1982. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-Dalton subunit of its own receptor.Science 215:185–187
Kasuga, M., Zick, Y., Blith, D.L., Karlsson, F.A., Haring, H.U., Kahn, C.R. 1982. Insulin stimulation of phosphorylation of the β subunit of the insulin receptor.J. Biol. Chem. 257:9891–9894
Koch, R., Deger, A., Jack, H.M., Klotz, K.N., Schnezle, D., Kramer, H., Kelm, S., Muller, G., Rapp, R., Weber, U. 1986. Characterization of solubilized insulin receptors from rat liver microsomes: Existence of two receptor species with different binding properties.Eur. J. Biochem. 154:281–287
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature (London) 227:680–685
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275
Marshall, R.N., Underwood, L.E., Voina, S.J., Foushee, D.B., Van Wyk, J.J. 1974. Characterization of the insulin and somatomedin-C receptors in human placental cell membranes.J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 39:283–292
Massague, J., Czech, M.P. 1982. Role of disulfides in the subunit structure of the insulin receptor.J. Biol. Chem. 257:6729–6738
Morrison, B.D., Swanson, M.L., Sweet, L.J., Pessin, J.E. 1988. Insulin-dependent covalent reassociation of isolated αβ heterodimeric insulin receptors into an α2β2-heterotetrameric disulfide-linked complex.J. Biol. Chem. 263:7806–7813
Munson, P.J., Rodbard, D. 1980. Ligand: A versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems.Anal. Biochem. 107:220–239
Pessin, J.E., Mottola, C., Yu, K.-T., Czech, M.P. 1985. Subunit structure and regulation of the insulin-receptor complex.In: Molecular Basis of Insulin Action M.P. Czech, editor. pp. 3–29. Plenum, New York
Petruzzelli, L.M., Ganguly, S., Smith, C.J., Cobb, M.H., Rubin, C.S., Rosen, O.M. 1982. Insulin activates a tyrosine-specific protein kinase in extracts of 3T3-L1 adipocytes and human placenta.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:6792–6796
Petruzzelli, L., Herrera, R., Rosen, O.M. 1984. Insulin receptor is an insulin-dependent tyrosine protein kinase: Copurification of insulin-binding activity and protein kinase activity to homogeneity from human placenta.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:3327–3331
Pilch, P.F., Czech, M.P. 1980. Hormone binding alters the conformation of the insulin receptor.Science 210:1152–1153
Pilch, P.F., Czech, M.P. 1980. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor.J. Biol. Chem. 255:1722–1731
Pilch, P.F., O'Hare, T., Rubin, J., Boni-Schnetzler, M. 1986. The ligand binding subunit of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor has properties of a peripheral membrane protein.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 136:45–50
Roth, R.A., Cassell, D.J. 1983. Insulin receptor: Evidence that it is a protein kinase.Science 219:299–301
Scatchard, G. 1949. The attractions of proteins for small molecules and ions.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 51:660–672
Schweitzer, J.B., Smith, R.M., Jarett, L. 1980. Differences in organizational structure of insulin receptor on rat adipocyte and liver plasma membranes: Role of disulfide bonds.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:4692–4696
Shia, M.A., Pilch, P.F. 1983. The β subunit of the insulin receptor is an insulin-activated protein kinase.Biochemistry 22:717–721
Swanson, M.L., Dudley, D.T., Boyle, T.R., Walker, P.S., Pessin, J.E. 1988. Functional differences in insulin receptors in rat adipocyte and human placental membranes.Endocrinology 122:967–975
Sweet, L.J., Morrison, B.D., Pessin, J.E. 1987. Isolation of functional αβ heterodimers from the purified human placental α2β2 heterotetrameric insulin receptor complex.J. Biol. Chem. 262:6939–6942
Sweet, L.J., Wilden, P.A., Pessin, J.E. 1986. Dithiothreitol activation of the insulin receptor/kinase does not involve subunit dissociation of the native α2β2 insulin receptor subunit complex.Biochemistry 25:7068–7074
Tamura, S., Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y., Larner, J. 1983. Insulin-like effect of trypsin on the phosphorylation of rat adipocyte insulin receptor.J. Biol. Chem. 258:14749–14752
Ullrich, A., Bell, J.R., Chen, E.Y., Herrera, R., Petruzzelli, L.M., Dull, T.J., Gray, A., Coussens, L., Liao, Y.-C., Tsubokawa, M., Mason, A., Seeburg, P.H., Grunfeld, C., Rosen, O.M., Ramachandran, J. 1985. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes.Nature (London) 313:756–761
Van Obberghen, E., Rossi, B., Kowalski, A., Gazzano, H., Ponzio, G. 1983. Receptor-mediated phosphorylation of the hepatic insulin receptor: Evidence that theM r 95,000 receptor subunit is its own kinase.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:945–949
Wang, C.-C., Hedo, J.A., Kahn, C.R., Saunders, D.T., Thamm, P., Brandenburg, D. 1982. Photoreactive insulin derivatives: Comparison of biologic activity and labeling properties of three analogues in isolated rat adipocytes.Diabetes 31:1068–1076
Yip, C.C., Yeung, C.W.T., Moule, M.L. 1978. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor of rat adiopocyte plasma membrane.J. Biol. Chem. 253:1743–1745
Yip, C.C., Yeung, C.W.T., Moule, M.L. 1980. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor proteins of liver plasma membrane preparations.Biochemistry 19:70–76
Zick, Y., Kasuga, M., Kahn, C.R., Roth, J. 1983. Characterization of insulin-mediated phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system.J. Biol. Chem. 258:75–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swanson, M.L., Pessin, J.E. High affinity insulin binding in the human placenta insulin receptor requires αβ heterodimeric subunit interactions. J. Membrain Biol. 108, 217–225 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871736
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871736