Abstract
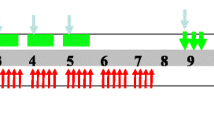
A pilot study was performed to assess the feasibility of combining 5-fluorouracil, recombinant alpha-2b-interferon, external radiation therapy and intraluminal high dose rate brachytherapy with surgery in patients with locally advanced esophageal carcinoma. 5-fluorouracil, 750 mg m−2, was administered via continuous 5-day infusion beginning day 1 and weekly thereafter; interferon, 10 mu subcutaneously, was administered three times per week beginning day 1 and sargramostin, 5µg kg−1, was administered on days without 5-fluorouracil. External radiation began on day one using 1.5 daily fractions to 55.5 Gy. Intraluminal brachytherapy was delivered concomitantly once each week for 5 fractions of 4 Gy. None of the first eight patients went to surgery. The external radiation was changed to 1.5 Gy BID to 45 Gy followed by BID intraluminal radiation to 15 Gy. Of the last four patients, there was one case of radiation myelitis. It was found that successful surgery was not possible and excessive toxicities, including radiation myelitis, occurred with this aggressive regimen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Earlam, R. and Cunha-Melo, J.R. (1980) Oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma:II. A critical review of radiotherapy.Brit. J. Surg. 67, 457.
Earlam, R. and Cunha-Melo, J.R. (1980) Oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma:I. A Critical Review of Surgery.Brit. J. Surg. 67, 381.
Herskovic, A., Martz, K., Al-Sarraf, M., Leichman, L., Brindle, J., Vaitkevicius, V., Cooper, J., Byhardt, R., Davis, L. and Emami, B. (1992) Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in patients with cancer of the esophagus.N. Engl. J. Med. 326, 1593.
Wadler, S., Wersto, R. and Weinberg, V. (1990) Interaction of fluorouracil and interferon in human colon cancer cell lines: cytotoxic and cytokinetic effects.Cancer Res. 50, 5735.
Wadler, S., Fell, S., Haynes, H., Katz, H.J., Rozenblit, A., Kaleya, R. and Wiernik, P.H. (1993) Treatment of Carcinoma of the Esophagus with 5-Fluorouracil and recombinant alfa-2a-Interferon.Cancer 71, 1726.
Kelsen, D., Lovett, D., Wong, J., Saltz, L., Buckley, M., Murray, P., Heelan, R. and Lightdale, C. (1992) Interferon alfa-2a and Fluorouracil in the Treatment of Patients with Esophageal Cancer.J. Clin. Oncol. 10, 269.
Ajani, J.A. (1994) Contributions of Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Carcinoma of the Esophagus: Results and Commentary.Sem. Oncol. 21, 474.
Iizuka, T. (1969) Treatment of Esophageal Cancer.Jpn. J. Cancer Clin. 15, 297.
Hareyama, M., Nishio, M., Kagami, Y., Narimatsu, N., Saito, A. and Sakurai, T. (1992) Intracavitary Brachytherapy combined with external-beam irradiation for squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 24, 235.
Hishikawa, Y., Kurisu, K., Taniguchi, M., Kamikonya, N. and Miura, T. (1991) High-dose-rate intraluminal brachytherapy for esophageal cancer.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 21, 1133.
National-Cancer-Institute. (1988) Guidelines for reporting of adverse drug reactions. Bethesda, MD: Division of Cancer Treatment, National Cancer Institute.
Schultheiss, T.E., Stephens, L.C., Jiang, G-L., Ang, K.K. and Peters, L.J. (1990) Radiation myelopathy in primates treated with conventional fractionation.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 19, 935.
Marcus, R.B. and Millin, R.R. (1990) The incidence of myelitis after irradiation of the cervical spinal cord.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 19, 3.
McCunniff, A.J. and Liang, M.J. (1989) Radiation Tolerance of the Cervical Spinal Cord.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 16, 675.
Hall, E.J. (1988) Cell-Survival Curves. In E.J. Hall (ed.)Radiobiology for the Radiologist, 3rd edn, p. 17. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott.
Tucker, S.L. and Thames, H.D. (1983) Flexure Dose: The low-dose limit of effective fractionation.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 9, 1373.
van-der-Kogel, A.J. (1979)Late effects of radiation on the spinal cord: dose-effect relationships and pathogenesis. University of Amsterdam, Radiobiological Institute TNO, Rijswijk, the Netherlands.
White, A. and Hornsey, S. (1978) Radiation damage to the rat spinal cord: the effects of single and fractionated doses of x ray.Brit. J. Radiol. 51, 515.
Masuda, K., Reid, B.O. and Withers, H.R. (1977) Dose effect relationship for epilation and late effects on spina cord in rats exposed to gamma rays.Radiology 122, 239.
Ang, K.K., Jiang, G.L., Guttenberger, R., Thames, H.D., Stephens, L.C., Smith, C.D. and Feng, Y. (1992) Impact of spinal cord repair kinetics on the practice of altered fractionation schedules.Radiother. Oncol. 25, 287.
van-den-Bogaert, W., van-der-Schueren, E., Horiot, J.C., Chaplain, G., Devilhena, M., Raposo, S., Leonor, J., Schraub, S.et al. (1986) Early Results of the EORTC randomized clinical trial of multiple fractions per day (MFD) and misonidazole in advanced head and neck cancer.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 12, 587.
Dische, S. and Saunders, M.I. (1989) Continuous, hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy (CHART): An interim report upon late morbidity.Radiother. Oncol. 16, 67.
Dische, S. (1991) Accelerated treatment and radiation myelitis.Radiother. Oncol. 20, 1.
Wong, C.S., Van-Dyk, J. and Simpson, W.J. (1991) Myelopathy following hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy for anaplastic thyroid cancer.Radiother. Oncol. 20, 3.
Fu, K.K. (1979) Normal Tissue Effects of Combined Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer.Front. Radiat. Ther. Onc. 13, 113.
Holsti, L.R., Mattson, K., Niiranen, A., Standertskiold-Nordenstam, C., Stenman, S., Sovijarvi, A. and Cantell, K. (1987) Enhancement of Radiation Effects by Alpha Interferon in the treatment of small cell carcinoma of the lung.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 13, 1161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beitler, J.J., Wadler, S., Haynes, H. et al. Phase II trial of chemotherapy, external and intraluminal radiation plus surgery for oesophageal cancer. Med Oncol 12, 115–120 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01676712
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01676712