Summary
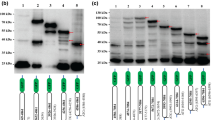
A 4.8 kilobase segment located at the left-terminal in the unique long (UL) region of infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) SA-2 strain contained three open reading frames (ORFs). The first of 421 amino acids (aa) was located at map units 0.065 to 0.07, and its predicted 48 kiloDaltons (kDa) protein product has significant homology to the immediate early regulatory protein ICP27 (UL54) of herpes simplex virus type-1 (HSV-1), to varicella-zoster virus (VZV) ORF4 and to equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) ORF5. The zinc finger conserved in the C-terminal of the proteins from HSV-1, VZV and EHV-1, is poorly conserved in ILTV homologue. The second ORF of 336 aa, located at map units 0.075 to 0.08, has a predicted molecular weight (MW) of 38 kDa with significant homology to glycoprotein K (gK) of HSV-1 (UL53), ORF5 of VZV and ORF6 of EHV-1. ILTV gK has features characteristic of a membrane-bound glycoprotein. The 3′ region of a third ORF was located at map units 0.08 to 0.095. Translation of the sequence revealed significant homology to the 3′-region of the DNA helicase-primase complex protein (UL52) of HSV-1, ORF6 of VZV and ORF 7 of EHV-1. Northern blot analyses were used to characterize the ILTV ICP27, gK and DNA helicase mRNAs. The data revealed that ILTV ICP27 is an immediate early gene that encodes a 1.6 kb mRNA, ILTV gK encodes a late transcript of 1.8 kb, while ILTV DNA helicase encodes a late transcript of 3.7 kb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann M, Braun DK, Perera L, Roizman B (1984) Characterization of herpes simplex virus 1 a proteins 0,4 and 27 with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol 52: 108–118
Berg JM (1986) Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science 232: 485–487
Berg JM (1988) Proposed structure for the zinc binding domains from transcription factor Illa and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 99–102
Beveridge WIB, Hart L (1985) Infectious laryngotrachetitis (ILT). In: Beveridge WIB, Hart L (eds) Animal health in Australia. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, vol 7, pp 38–42
Birnstiel ML, Bussinger M, Strub K (1985) Transcription termination and 3′ processing: the end is in site! Cell 41: 349–359
Crute JJ, Tsurumi T, Zhu L, Weller SK, Olivo PD, Challberg MD, Mocarski E, Lehman IR (1989) Herpes simplex virus helicase-primase: a complex of three herpes-encoded gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 2126–2189
Davison AJ, Scott JE (1986) The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol 67: 1759–1816
DebRoy C, Pederson N, Person S (1985) Nucleotide sequence of a herpes simplex virus type 1 gene that causes cell fusion. Virology 145: 36–48
Griffin AM (1989) Identification of 21 genes of infectious laryngotracheitis virus using random sequencing of genomic DNA. J Gen Virol 70: 3085–3089
Griffin AM, Bournsell MEG (1990) Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of DNA from the region of the thymidine kinase gene of infectious laryngotracheitis virus; potential evolutionary relationships between the herpesvirus subfamilies. J Gen Virol 71:841–850
Hanson LE (1984) Laryngotracheitis. In: Hofstad MS, Barnes HJ, Calnek BW, Reid WM, Yoder HW Jr (eds) Diseases of poultry, 8th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 444–451
Hattori M, Sakaki Y (1986) Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem 152: 232–238
Higgins DG, Bleasby AJ, Fuchs R (1992) CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci 8: 189–191
Honess RW, Roizman B (1974) Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Casacade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol 14: 8–19
Inchauspe G, Nagpal S, Ostrove JM (1989) Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of virus early and late genes. Virology 173: 700–709
Johnson MA, Prideaux CT, Kongsuwan K, Sheppard M, Fahey KJ (1991) Gallid herpesvirus 1 (infectious laryngotracheitis virus): cloning and physical maps of the SA-2 strain. Arch Virol 119: 181–198
Johnson MA, Tyack SG, Prideaux CT, Kongsuwan K, Sheppard M (1995) Complete nucleotide sequence of infectious laryngotracheitis virus (gallid herpesvirus 1) ICP4 gene. Virus Res (in press)
Kongsuwan K, Prideaux CT, Johnson MA, Sheppard M, Fahey KJ (1991) Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding infectious laryngotracheitis virus glycoprotein B. Virology 184:404–414
Kongsuwan K, Johnson MA, Prideaux CT, Sheppard M (1993) Identification of an infectious laryngotracheitis virus gene encoding an immunogenic protein with a predicted Mr of 32 kilodaltons. Virus Res 29: 125–140
Kongsuwan K, Prideaux CT, Johnson MA, Sheppard M, Rhodes S (1995) Nucleotide sequence analysis of an infectious laryngotracheitis virus gene corresponding to the US3 of HSV-1 and a unique gene encoding a 67 kDa protein. Arch Virol 140: 27–39
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1984) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157: 105–132
Leib DA, Bradbury JM, Hart CA, McCarthy K (1987) Genome isomerism in two alphaherpesviruses:Herpesvirus saimiri-1 (Herpesvirus tamarinus) and avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Arch Virol 93: 287–294
McCarthy AM, McMahan L, Schaffer PA (1989) Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 deletion mutants exhibit altered patterns of transcription and are DNA deficient. J Virol 63: 18–27
McGeoch DJ, Dalrymple MA, Davison AJ, Dolan A, Frame MC, McNab D, Perry LJ, Scott JE, Taylor P (1988) The complete DNA sequence of the unique long region of the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol 69: 1531–1574
Perry LJ, Rixon FJ, Everett RD, Frame MC, McGeoch DJ (1986) Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol 67: 2365–2380
Pogue-Guile KL, Spear PG (1987) The single base pair substitution responsible for theSyn phenotype of herpes simplex virus type 1, strain MP. Virology 157: 67–74
Roizman B (1982) The family Herpesviridae: general description, taxonomy and classification. In: Roizman B (ed) The herpesviruses, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York, pp 1–23
Roizman B, Desrosiers RC, Fleckenstein B, Lopez C, Minson AC, Studdert MJ (1992) The family Herpesviridae: an update. Arch Virol 123: 425–440
Rosenfeld PJ, Kelly TJ (1986) Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem 261: 1398–1408
Sacks WR, Greene CC, Aschman DP, Schaffer PA (1985) Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol 55: 796–805
Sandri-Goldin RM (1991) Analysis of the regulatory activities of the HSV-1 α protein ICP27, pp 77–103. In: Wagner EK (ed) Herpesvirus transcription and its regulation. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sawadogo M, Van Dyke MW (1991) A rapid method for the purification of deprotected oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 19: 674
Sinkovic B, Hunt S (1968) Vaccination of day-old chickens against infectious laryngotracheitis by conjunctival instillation. Aust Vet J 44: 55–57
Southern E (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Telford EAR, Watson MS, McBride K, Davison AJ (1992) The DNA sequence of equine herpesvirus-1. Virology 189: 304–316
Vaughan PJ, Thibault KJ, Hardwicke MA, Sandri-Goldin RM (1992) The herpes simplex virus immediate early protein ICP27 encodes a potential metal binding domain and binds zinc in vitro. Virology 189: 377–384
Zhao Y, Holden R, Harty RN, O'Callaghan DJ (1992) Identification and transcriptional analyses of the UL3 and UL4 genes of equine herpesvirus 1, homologues of the ICP27 and glycoprotein K genes of herpes simplex virus. J Virol 66: 5363–5372
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, M.A., Prideaux, C.T., Kongsuwan, K. et al. ICP27 immediate early gene, glycoprotein K (gK) and DNA helicase homologues of infectious laryngotracheitis virus (gallid herpesvirus 1) SA-2 strain. Archives of Virology 140, 623–634 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01309954
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01309954