Summary
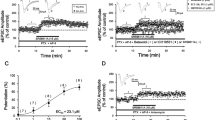
We investigated how the L-type calcium channel blockade (CCB) with nifedipine affects the cyclic AMP responses to noradrenaline or isoproterenol in cerebral cortical slices from rats receiving antidepressant treatments that induce (electroconvulsive shock, imipramine) or do not induce (amitriptyline) β-downregulation. To assess the role of protein kinase C (PKC) in receptor crosstalk under CCB conditions, the cyclic AMP responses were tested also in the presence of a PKC activator, TPA. CCB alone induced no changes, but modulated the action of those antidepressants that down regulate the β-adrenergic system. Chronic ECS and imipramine treatments were differently affected. ECS, under conditions of CCB, down regulated the response to isoproterenol in the presence of TPA, while imipramine ceased to block the TPA-potentiation of cyclic AMP responses. Thus, CCB affects the processes related to the antidepressant-induced changes on the crosstalk between α1- and β-adrenergic receptors, depending on the specific properties of the antidepressant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antkiewicz-Michaluk L, Michaluk J, Romańska I, Vetulani J (1990) Effect of repetitive electroconvulsive treatment on sensitivity to pain and on [3H]nitrendipine binding sites in cortical and hippocampal membranes. Psychopharmacology 101: 240–243
Antkiewicz-Michaluk L, Romańska I, Michaluk J, Vetulani J (1991) Role of calcium channels in effects of antidepressant drugs on responsiveness to pain. Psychopharmacology 105: 269–274
Azzi A, Boscoboinik D, Hensey C (1992) The protein kinase C family. Eur J Biochem 208: 547–557
Banarjee SP, Kung LS, Riggi SJ, Chanda SK (1977) Development of β-adrenergic receptor subsensitivity by antidepressants. Nature 268: 455–456
Bazzi MD, Nelsestuen GL (1987) Role of substrate in determining the phospholipid specificity of protein kinase C activation. Biochemistry 26: 5002–5008
Bergstrom DA, Kellar KJ (1979) Effect of electroconvulsive shock on monoaminergic receptor binding sites in rat brain. Nature 278: 464–466
Berridge MJ, Irvine RF (1990) Inositol phosphates and cell signaling. Nature 341: 197–205
Birnbaumer LG (1990) Proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 30: 675–705
Borbe HO, Zierenberg O (1985) Amitriptylinoxide: receptor-binding profile compared with other antidepressant drugs. Pharmacopsychiatry 18: 314–319
Bouvier M, Leeb-Lundberg LMF, Benovic JL, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ (1987) Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. II. Effects of agonist occupancy on phosphorylation of α1- and β2-adrenergic receptors by protein kinase C and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 262: 3106–3113
Brunello N, Barbaccia ML, Chuang DM, Costa E (1982) Down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors following repeated injections of desmethylimipramine: permissive role of serotonergic axons. Neuropharmacology 21: 114–1149
Czyrak A, Mogilnicka E, Maj J (1989) Dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists as antidepressant drugs in mice and rats. Neuropharmacology 28: 229–233
Daly JW, Padgett W, Creveling CR, Cantacuzene D, Kirk KL (1980) Fluoroepinephrines: specific agonists for the activation of alpha and beta adrenergic-sensitive cyclic AMP-generating system in rat slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 212: 382–389
De Lorenzo RJ (1982) Calmodulin modulation of calcium signal in synaptic transmission. In: Bradford HF (ed) Neurotransmitter interaction and compartmentation. Plenum, New York, pp 101–120
Delgado-Escueta AV, Victor S, Davidson D (1980) The effects of electroshock convulsion on calcium transport within synaptic terminals. J Neurochem 34: 1140–1148
Duman RS, Enna SJ (1987) Modulation of receptor-mediated cyclic AMP production in brain. Neuropharmacology 26: 981–986
Geoffroy M, Mogilnicka E, Nielsen M, Rafaelsen OJ (1988) Effect of nifedipine on the shuttlebox escape deficit induced by inescapable shock in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 154: 277–283
Grega DS, Werz MA, Macdonald RL (1987) Forskolin and phorbol esters reduce the same potassium conductance of mouse neurons in culture. Science 235: 345–348
Hall H, Ögren SO (1981) Effects of antidepressant drugs on different receptors in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol 70: 393–407
Hullett FJ, Potkin SG, Levy AB, Ciasca R (1988) Depression associated with nifedipine-induced calcium channel blockade. Am J Psychiatry 145: 1277–1279
Höschl C, Kozeny J (1988) Verapamil in affective disorders a controlled, double-blind study. Biol Psychiatry 25: 128–140
Janowsky A, Okada F, Manier DH, Applegate CD, Sulser F, Steranka LR (1982) Role of serotonergic input in the regulation of the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system. Science 218: 900–901
Karbon EW, Shenolikar S, Enna SJ (1986) Phorbol esters enhance neurotransmitter-stimulated cyclic AMP production in rat brain slices. J Neurochem 47: 1566–1575
Katada T, Gilman AG, Watanabe Y, Bauer S, Jakobs KH (1985) Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem 151: 431–437
Kostowski W, Dyr W, Puciłowski O (1990) Activity of diltiazem and nifedipine in some animal models of depression. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 42: 121–127
Lasoń W, Przewłocki R (1993) The effect of chronic treatment with imipramine on the G roteins mRNA level in the rat hippocampus — an interaction with a calcium channel antagonist. Pol J Pharmacol 45: 219–226
Leeb-Lundberg LMF, Cotecchia S, Lomasney JW, DeBernardis JF, Lefkowitz RJ, Caron MG (1985) Phorbol esters promote α1-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation and receptor uncoupling from inositol phospholipid metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 5651–5655
Li PP, Warsh JJ, Sibony D, Chiu A (1988) Assessment of rat brain alpha 1-adrenoceptor binding and activation of inositol phospholipid turnover following chronic imipramine treatment. Neurochem Res 13: 1111–1118
Manji HK, Lenox RH (1994) Long-term action of lithium: a role for transcriptional and postranscriptional factors regulated by protein kinase C. Synapse 16: 11–28
Martin P, Laurent S, Massol J, Childs M, Puech AJ (1989) Effects of dihydropyridine drugs on reversal by imipramine of helpless behavior in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 162: 185–188
Middlemiss D (1985) The calcium channel activator, Bay K8644, enhances K + evoked efflux of acetylcholine and noradrenaline from brain slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 331: 114–116
Miller RJ (1987) Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science 235: 46–52
Mogilnicka E, Czyrak A, Maj J (1987) Dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists reduce immobility in the mouse behavioral despair test; antidepressants facilitate nifedipine action. Eur J Pharmacol 138: 413–416
Nalepa I (1994) The effect of psychotropic drugs on the interaction of protein kinase C with second messenger systems in the rat cerebral cortex. Pol J Pharmacol 46: 1–14
Nalepa I, Vetulani J (1991a) Involvement of protein kinase C in the mechanisms of in vitro effects of imipramine on generation of second messengers by noradrenaline in the cerebral cortical slices of the rat. Neuroscience 44: 585–590
Nalepa I, Vetulani J (1991b) Different mechanisms of β-adrenoceptor downregulation by chronic imipramine and electroconvulsive treatment: possible role for protein kinase C. J Neurochem 57: 904–910
Nalepa I, Vetulani J (1993a) Enhancement of the responsiveness of cortical adrenergic receptors by chronic administration of an atypical antidepressant citalopram. J Neurochem 60: 2029–2035
Nalepa I, Vetulani J (1993b) The effect of calcium channel blockade on the action of chronic ECT and imipramine on responses of α- and β-adrenoceptors in the rat cerebral cortex. Pol J Pharm 45: 201–205
Nalepa I, Vetulani J (1994) The responsiveness of cerebral cortical adrenergic receptors after chronic administration of atypical antidepressant mianserin. J Psychiat Neurosci 19: 120–128
Nalepa I, Chalecka-Franaszek E, Vetulani J (1993) The antagonistic effect of separate and consecutive chronic treatment with imipramine and ECS on the regulation of α1-adrenoceptor activity by protein kinase C. Pol J Pharmacol 45: 521–532
Nalepa I, Chalecka-Franaszek E, Vetulani J (1996) Modulation by mianserin pretreatment of the chronic electroconvulsive shock effects on the adrenergic system in the cerebral cortex of the rat. Human Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 11: 273–282
Nowak G, Przegaliński E (1988) Long-term effect of antidepressant drugs and electroconvulsive shock on brain α1-adrenoceptors following destruction of noradrenergic or serotonergic nerve terminals. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 40: 393–400
Reuter H, Stevens CF, Tsiern RW, Yellen G (1982) Properties of single calcium channels in cardiac cell culture. Nature 297: 501–504
Rouot B, Brabet P, Homburger V, Toutant M, Bockaert J (1987) Go a major brain GTP binding protein in search of a function: purification, immunological and biochemical characteristics. Biochimie 69: 339–349
Salomon Y, Londos C, Rodbell M (1974) A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem 58: 541–548
Schatzman KC, Wise BC, Kuo JF (1981) Phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase: inhibition by antipsychotic drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 98: 669–676
Shimizu H, Daly J, Crevelling CR (1969) A radioisotopic method for measuring formation of adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate in incubated slices of brain. J Neurochem 16: 1609–1619
Snoek GT, Feijen A, Hage WJ, Van Rotterdam W, De Laat SW (1988) The role of hydrophobic interaction in the phospholipid-dependent activation of protein kinase C. Biochem J 255: 629–637
Sugden D, Klein DC (1988) Activators of protein kinase C act at a postreceptor site to amplify cyclic AMP production in rat pinealocytes. J Neurochem 50: 149–155
Sullivan R, Melnick DA, Malech HL, Meshulam T, Simons ER, Lazzari KG, Proto PJ, Gadenne AS, Leavitt JL, Griffin JD (1987) The effects of phorbol myristate acetate and chemotactic peptide on transmembrane potentials and cytosolic free calcium in mature granulocytes evolve sequentially as the cells differentiate. J Biol Chem 262: 1274–1281
Vanecek J, Sugden D, Weller JL, Klein DC (1986) See-saw signal processing in pinealocytes involves reciprocal changes in the alpha 1-adrenergic component of the cyclic GMP response and the beta-adrenergic component of the cyclic AMP response. J Neurochem 47 (3): 678–686
Vetulani J (1991) The development of our understanding of the mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 43: 323–338
Vetulani J, Sulser F (1975) Action of various antidepressant treatment reduces reactivity of noradrenergic cyclic AMP generating system in limbic forebrain. Nature 257: 495–496
Vetulani J, Nalepa I (1996) The effect of chronic administration of amitriptyline on the effects of subsequent electroconvulsive treatment on responsiveness of α1- and β-adrenoceptors in the rat cortical slices. J Neural Transm 103: 363–376
Vetulani J, Antkiewicz-Michaluk L, Rokosz-Pelc A, Pilc A (1983) Chronic electroconvulsive treatment enhances the density of [3H]prazosin binding sites in the central nervous system of the rat. Brain Res 27: 392–395
Vetulani J, Antkiewicz-Michaluk L, Rokosz-Pelc A (1984) Chronic administration of antidepres sant drugs increases the density of cortical3H-prazosin binding sites in the rat. Brain Res 310: 360–362
Wise H, Halliday CA (1985) Why is amitriptyline much weaker than desipramine at decreasing β-adrenoceptor numbers? Eur J Pharmacol 110: 137–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nalepa, I., Kowalska, M., Kreiner, G. et al. Does Ca2+ channel blockade modulate the antidepressant-induced changes in mechanisms of adrenergic transduction?. J. Neural Transmission 104, 535–547 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01277670
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01277670