Summary
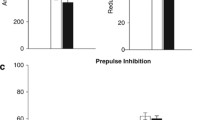
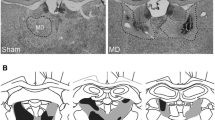
To study sensorimotor correlates of dopamine (DA) and gammaamino butyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission in the thalamus, we microinjected the DA agonist apomorphine (APO), the GABA agonist muscimol and vehicle into the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus (MdT) of rats and monitored catalepsy, sensorimotor asymmetries and the acoustic startle response. Unilateral MdT muscimol microinjections (50 ng) produced a lateralization of the removal of adhesive disks placed simultaneously on both forelegs in a tactile extinction task, but did not measurably influence any aspects of startle behavior. The sensorimotor asymmetry consisted of preferential orientation to the adhesive disk on the side ipsilateral to the microinjection. Vehicle and APO microinjections produced no significant behavioral results. In a follow-up study, unilateral MdT muscimol microinjections significantly depressed medial prefrontal cortical metabolism (measured by 2-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake) by 24%, but did not affect nucleus accumbens metabolic activity. Together, these findings are consistent with the concept that GABA-mediated inhibition of thalamocortical neurons in the MdT influences tactile extinction behavior, most likely by selectively suppressing excitatory input to the frontal cortex. The sensorimotor asymmetry observed in the present study resembles attentional and spatial memory deficits associated with frontal cortical lesions, and in conjunction with the 2-fluorodeoxyglucose results, suggests that elevated GABA neurotransmission in the thalamus may be involved in attentional and functional metabolic deficits in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizawa H, Kwak S, Shimizu T, Mannen T, Shibasaki H (1991) A case of adult onset pure pallidal degeneration. II. Analysis of neurotransmitter markers, with special reference to the termination of pallidothalamic tract in human brain. J Neurol Sci 102: 83–91
Beracochea DJ, Jaffard R, Jarrad LE (1989) Effects of anterior dorsomedial thalamic ibotenic lesions on learning and memory in rats. Behav Neural Biol 51: 364–376
Bogousslavsky J, Regli F, Uske A (1988) Thalamic infarcts: clinical syndromes, etiology and prognosis. Neurology 38: 837–848
Björklund A, Lindvall O (1984) Dopamine-containing systems in the CNS. In: Björklunde A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy, vol 2. Classical transmitters in the CNS, part I, A. Elsevier, New York, pp 55–78
Camps M, Cortes R, Gueye B, Probst A, Palacios JM (1989) Dopamine receptors in human brain: autoradiographic distribution of D 2 sites. Neuroscience 28: 275–290
Casselli RJ, Graff-Radford NR, Rezai K (1991) Thalamocortical diaschisis: single photon emission tomographic study of cortical blood flow changes after focal thalamic infarction. Neuropsychiatr Neuropsychol Behav Neurol 4: 193–214
Castaigne P, Lhermitte F, Buge A, Escourolle R, Hauw JJ, Lyon-Caen O (1980) Paramedian thalamic and midbrain infarcts: clinical and neuropathological study. Ann Neurol 10: 127–148
Condes-Lara M, Kesar S, Albe-Fessard D (1982) Comparison of caudate nucleus and substantia nigra control of medial thalamic cell activites in the rat. Neurosci Lett 31: 129–134
Crowne DP, Yeo CH, Russell IS (1981) The effects of unilateral frontal eye field lesions in the monkey: visual-motor guidance and avoidance behavior. Behav Brain Res 2: 165–167
Crowne DP, Richardson CM, Dawson KA (1986) Parietal and frontal eye field neglect in the rat. Behav Brain Res 22: 227–231
Dawson TM, Gehlert DR, Wamsley JK (1986) Quantitative autoradiographic localization of central D-1 and D-2 receptors. In: Breese JR, Creese I (eds) Neurobiology of central D1-dopamine receptors. Plenum Press, New York, pp 93–119
DiChiara G, Morelli M, Porceddu ML, Gessa GL (1979) Role of thalamic GABA in motor functions: catalepsy and ipsiversive turning after intrathalamic muscimol. Neuroscience 4: 1453–1465
Gallassi R, Morreale A, Montagna P, Gambetti P, Lugaresi E (1992) Fatal familial insomnia: neuropsychological study of a disease with thalamic degeneration. Cortex 28: 175–187
Gjedde A, Reith J, Dyve S, Léger G, Guttman M, Diksic M, Evans A, Kuwabara H (1991) Dopa decarboxylase activity of the living human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 2721–2725
Groenewegen HJ (1988) Organization of the afferent connections of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus in the rat, related to the mediodorsal-prefrontal topography. Neuroscience 24: 379–431
Herrera AJ, Machado A, Cano J (1993) Ageing and monoamine turnover in the lateral geniculate nucleus and visual cortex of the rat. Neurochem Int 22: 531–539
Houser CR, Vaughn JE, Barber RP, Roberts E (1980) GABA neurons are the major cell type of the nucleus reticularis thalami. Brain Res 200: 341–354
Isseroff A, Rosvold HE, Galkin TW, Goldman-Rakic PS (1982) Spatial memory impairements following damage to the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus in rhesus monkeys. Brain Res 232: 97–113
Janowski A, Neve KA, Taylor B, de Paulis T, Belknap JK (1992) Extrastriatal dopamine D 2 receptors: Distribution, pharmacological characterization and region-specific regulation by clozapine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261: 1282–1290
Jones EG (1985) The thalamus. Plenum Press, New York
Kennedy C, Des Rosiers MH, Sukarada O, Shinohara M, Reivich M, Jehle JW, Sokoloff L (1976) Metabolic mapping of the primary visual system of the monkey by means of the autoradiographic 14 C-deoxyglucose method. Proc Natl Acad Sci 73: 4230–4234
Kessler J, Markowitsch HJ, Otto B (1982) Subtle but distinct impairments of rats with chemical lesions in the thalamic mediodorsal nucleus, tested in a radial arm maze. J Comp Physiol Psychol 96: 712–720
Levant B, Grigoriadis DE, DeSouza EB (1992) Characterization of [3H]quinpirole binding to D2-like dopamine receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 262: 929–935
Levasseur M, Baron JC, Sette G, Legualt-Demare F, Pappata S, Mauguière F, Benoít N, Dinh ST, Degos JD, Laplane D, Mazoyer B (1992) Brain energy metabolism in bilateral paramedian thalamic infarcts: a positron emission tomography study. Brain 115: 795–807
Luria AR (1969) Frontal lobe syndromes. In: Vinken PJ, Martin JJ (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 2. Elsevier, New York, pp 725–757
Machida CA, Searles RP, Nipper V, Brown JA, Kozell LB, Neve KA (1992) Molecular cloning and expression of the rhesus macaque D 1 dopamine receptor gene. Mol Pharmacol 41: 652–659
Mansour A, Meador-Woodruff JH, Bunzow JR, Civelli O, Akil H, Watson SJ (1990) Localization of dopamine D 2 receptor mRNA and D 1 and D 2 receptor binding in the rat brain and pituitary: anin situ hybridization-receptor autoradiographic analysis. J Neurosci 10: 2587–2600
Marini G, Imeri L, Mancia M (1988) Changes in sleep-waking cycle induced by lesions of medialis dorsalis thalamic nuclei in the cat. Neurosci Lett 85: 223–227
McCormick DA (1992) Neurotransmitter actions in the thalamus and cerebral cortex and their role in neuromodulation of thalamocortical activity. Prog Neurobiol 39: 337–388
McGilchrist I, Goldstein LH, Jadresic D, Fenwick P (1993) Thalamo-frontal psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 163: 113–115
Meador-Woodruff JH, Mansour A, Grandy DK, Damask SP, Civelli O, Watson SJ (1992) Distribution of D 5 dopamine receptor mRNA in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 145: 209–212
Mennemeier M, Fennell E, Valenstein E, Heilman KM (1992) Contributions of the left intralaminar and medial thalamic nuclei to memory. Arch Neurol 49: 1050–1058
Mogenson GJ, Wu M (1988) Disruption of food hoarding by injections of procaine into mediodorsal thalamus, GABA into subpallidal region and haloperidol into accumbens. Brain Res Bull 20: 247–251
Montaron MF, Buser P (1988) Relationships between nucleus medialis dorsalis, pericruciate cortex, ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens in cat: an electrophysiological study. Exp Brain Res 69: 559–566
Muramoto O, Kanazawa I, Nissato S (1984) Nuclear distribution of glutamate, gamaaminobutyrate and aspartate within the normal human thalamus. Neuroscience 13: 733–742
Neave N, Sahgal A, Aggleton JP (1993) Lack of effect of dorsomedial thalamic lesions on automated tests of spatial memory in the rat. Behav Brain Res 55: 39–49
Oke A, Adams RN (1987) Elevated thalamic dopamine: possible link to sensory dysfunctions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13: 589–604
Oke A, Lewis R, Adams RN (1980) Hemispheric asymmetry of norepinephrine distribution in the rat thalamus. Brain Res 188: 269–272
Oke A, Solnick J, Adams RN (1983) Catecholamine distribution patterns in the rat thalamus. Brain Res 269: 180–183
Romo R, Cheramy A, Godeheu G, Glowinski J (1986) In vivo presynaptic control of dopamine release in the cat caudate nucleus-I opposite changes in neuronal activity and release invoked from thalamic motor nuclei. Neuroscience 19: 1067–1079
Schallert T, Upchurch M, Lobough N, Farrar R, Spirduso W, Gilliam P, Vaughn D, Wilcox RE (1982) Tactile extinction: distinguishing between sensorimotor and motor asymmetries in rats with unilateral nigrostriatal damage. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 16: 455–462
Schwartz ML, Mrzljak L (1992) Serotonergic, noradrenergic, and dopaminergic innervation of the primate mediodorsal thalamic nucleus. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18: 1418
Slotnik BM, Kaneko N (1981) Role of the dorsomedial thalamic nucleus in olfactory discrimination learning rats. Science 214: 91–92
Speedie LJ, Heilman KM (1982) Amnestic disturbance following infarction of the left dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus. Neuropsychologica 20: 597–604
Speedie LJ, Heilman KM (1983) Anterograde memory deficits for visuospatial material after infarction of the right thalamus. Arch Neurol 40: 183–186
Steriade M, Jones EG, Llinas RR (1990) Thalamic oscillations and signaling. Wiley, New York
Stokes KA, Best PJ (1988) Dorsomedial thalamic lesions impair radial maze performance in the rat. Behav Neurosci 102: 294–300
Szelies B, Herholz K, Pawlik G, Karbe H, Hebold I, Wolf-Dieter H (1991) Widespread functional effects of discrete thalamic infarction. Arch Neurol 48: 178–182
Vives F, Mogenson JM (1985) Electrophysiological evidence that the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus is a relay between the ventral pallidum and the medial prefrontal cortex. Brain Res 344: 329–337
Wilcox RE, Mikula J, Levitt RA (1979) Periaqueductal gray naloxone microinjections in morphine-dependent rats: hyperalgesia without “classical” withdrawal. Neuropharmacology 18: 639–641
Young KA, Wilcox RE (1991) Characterization of D 2 receptors and dopamine levels in the thalamus of the rat. Life Sci 48: 1845–1852
Young KA, Randall PK, Wilcox RE (1991) Dose and time response analysis of apomorphines effect on prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle. Behav Brain Res 42: 43–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, K.A., Hicks, P.B., Randall, P.K. et al. Behavioral and frontal cortical metabolic effects of apomorphine and muscimol microinjections into the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus. J. Neural Transmission 98, 119–132 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01277015
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01277015