Summary
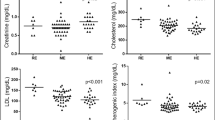
Cholinesterase activity measurement should be considered in relationship to its proposed use, whether for diagnostic information, a monitor of health status or because of its logistical and economic practicality. To prevent confusion one must consider that measurement of cholinesterase activity may confirm the existence of poisoning by an inhibitor, may measure an individual worker's overall exposure or his characteristic individual response. Where groups of workers are involved a group response may be derived to identify the magnitude of the response at some preset value of significance from which a biological threshold limit value may be established. The population at risk, the intensity and frequency of exposure dictate the frequency of sampling. Pesticide exposed workers are grouped according to confined and unconfined environments. Confined environments are those associated with manufacturing, formulating and warehousing of pesticidal products. Unconfined environments are those associated with application and postapplication exposures. All of the aforementioned factors must be considered before employing cholinesterase activity measurement as an index of exposure to pesticides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alles, G.A., Hawes, R.C.: Cholinesterases in the blood of man. J. Biol. Chem.133, 375 (1940)
American Conference Governmental Industrial Hygienists: Threshold limit values for chemical substances and physical agents in the workroom environment with intended changes for 1974, p.8 (1974)
Antopol, W., Tuchman, L., Schrifrin, A.: Cholinesterase activity of human sera with special reference to hyperthyroidism. Proc.Soc.Exp.Biol.& Med.38, 363 (1938)
El-Hawary, M.F.S.: Cholinesterase levels in normal Egyptians. Gaz.KasrEl-Aini Fac.Med.24, 247 (1958)
Federal Working Group on Pest Management: Guidelines on sampling and statistical methodologies for ambient pesticide monitoring, Washington, D.C., pp.IX-3 (1974)
Frawley, J.P., Fuyat, H.V., Hagan, E., Blake, J.R., Fitzhugh, O.G.: Marked potentiation in mammalian toxicity from simultaneous administration of two anti cholinesterase compounds. J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther.121, 96 (1957)
Kalow, W., Genest, K.: A method for the detection of atypical forms of human cholinesterases. Determination of dibucaine numbers. Can.J.Biochem.35, 339 (1957)
LaMotta, R.V., Williams, H.M., Whetstone, H.J.: Studies of cholinesterase activity. II. Serum cholinesterase in hepatitis and cirrhosis. Gastroenterology33, 50 (1957)
McArdle, B.: The serum cholinesterase in jaundice and diseases of the liver. Quart.J.Med.33 (N.S.9), 107 (1940)
McNeil, B.J., Keeler, E., Adelstein, S.J.: Primer on certain elements of medical decision making. N.Eng.J.Med.293, 211–215 (1975)
Milby, T.H., Bailey, J.B., Davies, J.E., Guthrie, F.E., Hays, H.W., Long, K.R., May, J., Wymer, W.H.: Occupational exposure to pesticides. Fed. Working Group on Pest Management, Washington, D.C., pp. 104–105 (1974)
Webb, E.C.: The nomenclature of multiple enzyme forms. Experimenta20, 592 (1964)
Wetstone, H.S., LaMotta, R.V., Middlebrook, L., Tennant, R., White, B.V.: Studies of cholinesterase activity\(\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{\bar N} \) liver function in pregnancy:values of certain standard liver function tests in pregnancy. Am.J.Obst. & Gynecol.76, 480 (1958)
White, B.V., Wetstone, H., LaMotta, R.: Serum cholinesterase activity in malignant neoplasms. Trans.Am.Clin.Climatol.Assoc.69, 176 (1957)
Williams, H.M., LaMotta, R.V., Wetstone, H.J.: Studies of cholinesterase in obstructive jaundice and neoplastic disease. Gastroenterology33, 58 (1957)
Wills, J.H.: The measurement and significance of changes in the cholinesterase activities of erythrocytes and plasma in man and animals. In: Critical reviews in toxicology, pp.153. New York: Chemical Rubber 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, K.R. Cholinesterase activity as a biological indicator of exposure to pesticides. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 36, 75–86 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01262314
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01262314