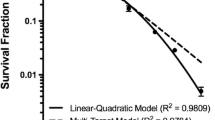
Summary
Responses of the S/S variant of the L5178Y murine leukemic lymphoblast, the photoreceptor cell of the rabbit retina and the lenticular epithelium of the rabbit to heavy ions (20Ne,28Si,40Ar and56Fe) are described and discussed primarily from the standpoint of the need for a comprehensive theory of cellular radiosensitivity from which a general theory of tissue radiosensitivity can be constructed.
The radiation responses of the very radiosensitive, repair-deficient S/S variant during the G1- and early S phases of the cell cycle were found to be unlike those of normally radioresistant cells in culture: the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) did not increase with the linear energy transfer (LET∞) of the incident radiation. Such behavior could be anticipated for a cell which is lacking the repair system that operates in other (normal) cells when they are exposed to ionizing radiations in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. The S/S variant does exhibit a peak of radioresistance to X-photons mid-G1 + 8 h into the cell cycle, however, and as the LET∞ was increased, the repair capacity responsible for that radioresistance was reduced progressively.
Sensory cells (photoreceptors) in the retina of the New Zealand white (NZW) rabbit are very radioresistant to ionizing radiations, and several years elapsed after localized exposure (e.g., 5–10 Gy) to heavy ions (20Ne,40Ar) before photoreceptor cells were lost from the retina. During the first few weeks after such irradiations, damage to DNA in the photoreceptor cells was repaired to a point where it could not be demonstrated by reorienting gradient sedimentation under alkaline conditions, a technique that can detect DNA damage produced by <0.1 Gy of X-photons. Restitution of DNA structure was not permanent, however, and months or years later, butbefore loss of photoreceptor cells from the retina could be detected, progressive deterioration of the DNA structure began.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lett JT, Bergtold DS, Keng PC (1986) Effects of LET∞ on the fate of DNA damage induced in rabbit sensory cells in situ: fundamental aspects. In: Chappas C, Simic MG, Grossman L, Upton AC (eds) Mechanisms of DNA Damage and Repair: Implications for Carcinogenesis and Risk Assessment. Plenum Press, New York (in press)
Lea DE (1946) Actions of radiations on living cells. Cambridge University Press, London
Nagasawa H, Cox AB, Lett JT (1980) The radiation responses of synchronous L5178Y S/ S cells and their significance for radiobiological theory. Proc R Soc London 211:25–49
Lett JT, Bergtold DS, Cox AB, Keng PC, Okayasu R (1984) Further evidence that the survival of irradiated mammalian cells is controlled by temporal processes. Br J Cancer 49, Suppl VI:163–168
Lett JT, Cox AB, Keng PC, Lee AC, Su CM, Bergtold DS (1980) Late degeneration in rabbit tissues after irradiation by heavy ions. Life Sci Space Res XVIII:131–142
Keng PC, Lett JT (1981) Effects of heavy ions on rabbit tissues: Loss of electroretinogram and DNA repair in retinal photoreceptor cells. Int J Radiat Biol 39:655–664
Cox AB, Keng PC, Glass NL, Lett JT (1981) Effects of heavy ions on rabbit tissues: Alopecia. Int J Radiat Biol 40:645–657
Keng PC, Lee AC, Cox AB, Bergtold DS, Lett JT (1982) Effects of heavy ions on rabbit tissues: Cataractogenesis. Int J Radiat Biol 41:127–137
Cox AB, Keng PC, Lee AC, Lett JT (1982) Effects of heavy ions on rabbit tissues: Damage to the forebrain. Int J Radiat Biol 42:355–367
Keng PC, Bergtold DS, Lett JT (1983) Effects of heavy ions on rabbit tissues: Analysis of low levels of DNA damage in retinal photoreceptor cells. Int J Radiat Biol 43:219–229
Cox AB, Ainsworth EJ, Jose JG, Lee AC, Lett JT (1983) Cataractogenesis from high-LET radiation and the Casarett model. Adv Space Res 3:211–219
Bergtold DS, Cox AB, Su CM, Lett JT (1983) Late skin damage in rabbits and monkeys after exposure to particulate radiations. Adv Space Res 3:221–229
Lett JT, Cox AB, Bergtold DS, Lee AC, Pickering JE (1984) Late effects from particulate radiations in primate and rabbit tissues. Adv Space Res 4:251–256
Cox AB, Kraft LM (1984) Quantitation of heavy-ion damage to the mammalian brain: Some preliminary findings. Adv Space Res 4:247–250
Lett JT, Cox AB, Lee AC (1985) Some perspectives on cataractogenesis from heavy charged particles. Radiat Res 104: S 201-S 207
Lett JT (1981) Measurement of single-strand breaks by sedimentation in alkaline sucrose gradients. In: Friedberg EC, Hanawalt PC (eds) DNA repair. A laboratory manual of research procedures, vol 1, Part B. Marcel Dekker, New York, Basel, pp 363–378
Bergtold DS, Lett JT (1985) Alterations in chromosomal DNA and aging: An overview. In: Sohal RS, Birnbaum L, Cutler RG (eds) Molecular biology of aging: gene stability and gene expression. Raven Press, New York (in press)
Worgul BV, Merriam GR Jr, Szechter A, Srinivasan BD (1976) Lens epithelium and radiation cataract. Arch Ophthalmol 94:996–999
Friedberg EC, Ehmann UK, Williams JI (1979) Human diseases associated with defective DNA repair. In: Lett JT, Adler H (eds) Advances in Radiation Biology, vol 8. Academic Press, New York, pp 86–174
Barendsen GW (1968) Responses of cultured cells, tumours and normal tissues to radiations of different linear energy transfer. In: Ebert M, Howard A (eds) Current Topics in Radiation Research, vol 4. North-Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam, pp 293–356
Blakely EA, Ngo FQH, Curtis SB, Tobias CA (1984) Heavy-ion radiobiology: Cellular studies. In: Lett JT (ed) Advances in Radiation Biology, vol 11. Academic Press, New York, pp 295–389
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lett, J.T., Cox, A.B. & Bergtold, D.S. Cellular and tissue responses to heavy ions: Basic considerations. Radiat Environ Biophys 25, 1–12 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209679
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209679