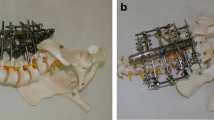
Abstract
In a study the results recorded in 34 surgically treated patients with specific or unspecific spondylodiscitis after dorsoventral one-stage instrumentation with CDI and anterior grafting (group 1) were compared with those obtained in a group of 38 patients treated with anterior CDH instrumentation in combination with anterior grafting (group 2). The mean observation periods were 48.4 (19–82) months in group 1 and 29.0 (8–54) months in group 2. In both groups the infection healed after fusion without a secondary operation. In group 1 the mean values for blood loss, operating time, length of hospital stay and fusion length (3.5 segments) were significant higher than those in group 2; in particular, the fusion length was shorter (1.3 segments) in group 2. Only 8 patients in group 1 were treated with postoperative external support. The mean preoperative segmental angle of 18.2° (group 1) was corrected by a mean of 11.9°, and the reposition loss during follow-up amounted to an average of 2.7°. Group 2 showed a mean preoperative segmental deformity angle of 13.4°, which was corrected by 11.6°, and the loss of reposition was 2.9° on average. Even in florid spondylodiscitis a short-range anterior fusion of the affected spinal segment can be performed with a primarystable implant, avoiding a second operation without an increased risk of infection-related dislocation. In the authors' own experience a secondary dorsal operation can be avoided except in the case segment L-5/S-1, the fast mobilization without external support allows a up-to-date treatment in this severe spinal disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliabadi, H, C Johnson, AS Cass, J Mayfild, K Vandenerink: Ureteral obstruction following the Dwyer procedure in a patient with an ileal loop urinary diversion. Spine 9 (1984) 819–821
Brown LP, KH Bridwell, RT Holt, J Jennings: Aortic erosion and laceration associated with the Dunn anterior spinal instrumentation. Orthop Trans 10 (1986) 16–17
Brussatis F, H Blümlein, TW Underlich: Ergebnisse nach Ausräumung und Fusion bei Spondylitiden. Z Orthop 121 (1983) 458–459
Buchner H, P Pink: Die Spondylitis tuberculosa. Orthopäde 10 (1981) 119–132
Chan FL, SP Chow: Retroperitoneal fibrosis after anterior spinal fusion. Clin Radiol 34 (1983) 331–335
Cleveland RH, V Gilsanz, RL Lebowitz, RH Wilkinson: Hydronephrosis from retroperitoneal fibrosis after anterior spine fusion J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 60a (1978) 996–997
Collert S: Osteomyelitis of the spine. Acta Orthop Scand 48 (1977) 283–290
Colton CL, AJ Hall: Atlas of orthopaedic surgical approaches. Butterworth-Heinemann, Stoneham 1991
Costerton JW, RT Irvin, KJ Cheng: The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 35 (1981) 299–324
Dick W, R Graf, E Morscher: Konservative und operative Therapie der Spondylitis. Therapiewoche 34 (1984) 448–152
Digby JM, JB Kersley: Pyogenic non-tuberculoss spinal infection. J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 61b (1979) 47–55
Dufek P, G Salis-Soglio Frhr von, Z Bozdech: Die unspezifische bakterielle Spondylitis — eine Analyse von 32 Fällen. Z Orthop 125 (1987) 225–261
Dunn HK: Anterior stabilisation of thoracolumbar injuries. Clin Orthop 189 (1984) 116–124
Dunn HK: Anterior spine stabilization and decompression for thoracolumbar injuries. Orthop Clin North Am 17 (1986) 113–119
Dunn HK, AU Daniels, GG McBride: Comparative assessment of spine stability achieved with a new anterior spine fixation system. Orthop Trans 4 (1980) 268–269
Dunn HK, EM Globe, GG McBride, AU Daniels: An implant system for anterior spine stabilization. Orthop Trans 5 (1981) 433–434
Dwyer AF, AC Yau, L Hsu, JP O'Brien, AR Hodgson: Deep paravertebral infection following Dwyer anterior spinal instrumentation. A report of three cases. Spine 1 (1976) 201–206
Eichenauer M, EO van der Lan, A Mostegl: Vorwiegend ambulant-konservative Behandlung der unkomplizierten Spondylitis tuberculosa. Therapiewoche 37 (1987), 122–131
Eismont FJ, HH Bohlman, PL Soni, VM Goldberg, AA Freehafer: Pyogenic and fungal vertebral osteomyelitis with paralysis. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 65a (1983) 19–29
Enderle A, E Schmitt, L Zichner: Zur Diagnostik herdförmiger Wirbelsäulenerkrankungen — eine kritische Betrachtung. Z Orthop 119 (1981) 193–205
Eysel P, C Hopf, A Diop, F Lavaste: Die mehrsegmentale ventrale Stabilisierung der Lendenwirbelsäule: eine vergleichende biomechanische Studie. Z Orthop 133 (1995) 242–248
Flynn JC, CT Price: Sexual complications of anterior fusion of the lumbar spine. Spine 9 (1984) 489–492
Giehl JP, K Zielke, HP Hack: Die ventrale Derotationsspondylodese Bach Zielke. Orthopäde 18 (1989) 101–117
Gristina AG, JW Costerton: Bacterial adherence and the glycocalyx and their role in musculoskeletal infection. Orthop Clin North Am 15 (1985) 517–535
Gristina AG, M Oga, LX Webb, DC Hobgood: Bacterial adherence and the pathogenesis of osteomyelitis. Science 228 (1985) 990–993
Harmon PH: A simplified surgical technic for anterior lumbar discectomy and fusion. Avoidance of complications. Anatomy of the retroperitoneal veins. Clin Orthop 37 (1964) 130–144
Heine J, M Immenkamp, HH Matthiass: Ergebnisse der operativen Behandlung der Spondylitis tuberculosa. Z Orthop 121 (1983) 457–461
Hodgson AR, FE Stock: Anterior spine fusion for the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 42a (1960) 295–310
Hope C, P Eysel, J Dubousset: CDH preliminary report on a new anterior spinal instrumentation. Eur Spine J 4 (1995) 194–199
Ito H, J Tsuchiy, G Asami: A new radical operation for Potts disease. J Bone Jt Surg 16 (1934) 499–511
Jäger M, HH Springer: Die entzündlichen Erkrankungen der Wirbelsäule. Orthopäde 10 (1981) 106–113
Jendrisak MD: Spontaneous abdominal aortic rupture from erosion by a lumbar spine fixation device. A case report. Surgery 99 (1986) 631–633
Johnson RM, EJ McGuire: Urogenital complications of anterior approaches to the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop 154 (1981) 114–118
Kaneda K: Anterior approach and Kaneda instrumentation for lesions of the thoracic and lumbar spine. In:Bridwell KH, RL Dewald (eds.): Textbook of spinal surgery. Lippincott, Philadelphia, 1981
Kemp HBS, JW Jackson, JD Jeremiah, AJ Hall: Pyogenic infections occurring primarily in intervertebral discs. J Bone Jt Sung [Br] 55b (1973) 699–714
Kemp HBS, JW Jackson, JD Jeremiah, J Cook: Anterior fusion of the spine for infective lesions in adults. J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 55b (1973) 715–734
King DM, KM Mayo: Infective lesion of the vertebral column. Clin Orthop 96 (1973) 248–253
Kirkaldy-Willis WH, TG Thomas: Anterior approaches in the diagnosis and treatment of infections of the vertebral bodies. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 47a (1965) 87–110
Krödel A, H Stürz: Differenzierte operative und konservative Therapie der Spondylitis und Spondylodiscitis. Z Orthop 127 (1989) 587–596
La Rocca H: Infections of the spine. Clin Neurosurg 25 (1978) 296–304
Leong JCY: Anterior spinal fusion for low back syndrome. In:Floman Y (ed): Disorders of lumbar spine, Aspen, Gaithersburg, Md 1990
Lifeso RM, P Weaver, EH Harder: Tuberculous spondylitis in adults. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 67a (1985) 1405–1413
Manner G, K Parsch: Spondylitis und Spondylodiszitis beim Kind. Z Orthop 121 (1983) 455–456
Martin NS: Tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 52b (1970) 613–621
McMaster WC, I Silber: An urological complication of Dwyer instrumentation. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 57a (1975) 710–711
Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine: A 10-year assessment of controlled trials of inpatient and outpatient treatment and of plaster-of-Paris jackets for tuberculosis of the spine in children on standard chemotherapy. J Bone Surg [Br] 67b (1985) 103–110
Meurer A, P Eysel, J Heine: Ergebnisse der operativen Behandlung der Spondylitis tuberculosa. Z Orthop 133 (1995) 227–23
Nasca JR, RB McElvein: Aspergillus fumigatus osteomyelitis of the thoracic spine treated by excision and interbody fusion. Spine 10 (1985) 848–851
Oga M, Y Sugioka, CD Hobgood, AG Gristina, QN Myrvik: Surgical biomaterials and differential colonization byStaphylococcus epidermidis. Biomaterials 9 (1988) 285–289
Oga M, T Arizono, M Takasita, Y Sugioka: Evaluation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis. Spine 18 (1993) 1890–1894
Parthasarathy R: Madras study of tuberculosis of spine. Assessment and follow-up. In: Shanmugasundaram TK (ed): Current concepts in bone and joint tuberculosis. International Bone and Joint Tuberculosis Club, Madras, 1985
Peters KM, B Schwanitz, KW Zilkens: Spondylodiszitis — eine häufig spät gestellte Diagnose. Orthop Praxis 28 (1992) 108–112
Rajasekaran S, TK Shanmugasundaram: Prediction of the angle of Gibbus deformity in tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 69 (1987) 503–509
Rajasekaran S, S Soundarapandian: Progression of kyphosis in tuberculosis of the spine treated by anterior arthrodesis. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 71a (1989) 1314–1323
Robinson BHB, MHJ Lessof: Osteomyelitis of the spine. Guys Hosp Rep 110 (1972) 303–309
Schulze W: Entzündliche Wirbelsäulenprozesse. Die Wirbelsäule in Forschung und Praxis 83 (1979) 147–150
Silber I, W McMaster: Retroperitoneal fibrosis with hydronephrosis as a complication of the Dwyer procedure. J Pediatr Surg 12 (1977) 255–257
Stevenson FH, CW Manning: Tuberculosis of the spine treated conservatively with chemotherapy. Tubercle 43 (1962) 406–410
Stolke D, V Seifert, U Kunz: Die postoperative Discitis intervertebralis lumbalis. Z Orthop 126 (1988) 666–670
Wedge JH, AF Oryschak, DE Robertson, WH Kirkaldy-Willis: Atypical manifestations of spinal infections. Clin Orthop 123 (1977) 155–263
Woolsey RM: Aortic laceration after anterior spinal fusion. Surg Neurol 25 (1986) 267–268
Zielke K: Ventrale Derotationsspondylodese — Irrtümer und Ergebnisse nach vier Jahren. Z Orthop 118 (1980) 626
Zielke K: Ventrale Derotationsspondylodese, Behandlungsergebnisse bei idiopathischen Lumbalskoliosen. Z Orthop 120 (1982) 320–329
Zielke K, R Stunkat, F Beaujean: Ventrale Derotationsspondylodese. Vorläufiger Ergebnisbericht über 26 operierte Fälle. Arch Orthop Unfallchir 85 (1976) 257–277
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hopf, C., Meurer, A., Eysel, P. et al. Operative treatment of spondylodiscitis —what is the most effective approach?. Neurosurg. Rev. 21, 217–225 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01105775
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01105775