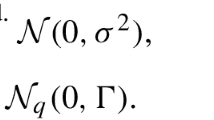Abstract
A method is presented for conducting a Hayman analysis of non-replicated diallel tables using a maximum-likelihood (ML) model-fitting approach, rather than a traditional analysis of variance (ANOVA) approach. Hayman's linear model for a diallel analysis is used to generate a table of expected cell means. This table of expected cell means is fit to a table of observed cell means, and the fit is assessed using a chi-square value. Often data collected from diallel crosses fail to meet the underlying assumptions of ANOVA. The ML method makes no assumptions about equal cell sizes or homogeneity of variance. Thus, the ML method for diallel analysis provides some statistical advantages over ANOVA methods. The ML method also offers the advantage of having the ability to analyze diallels with missing cells. Using the ML method, incomplete diallel tables can be analyzed, and the partitioning of all the sources of variation in a diallel table is still accomplished from the remaining crosses. These advantages make the ML method an attractive approach for extracting the maximum amount of information from a diallel table.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CERN (1977).MINUIT: A System for Function Minimization and Analysis of the Parameter Errors and Correlations, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland.
Crusio, W. E., Kerbusch, J. M. L., and van Abeelen, J. H. F. (1984). The replicated diallel cross: A generalized method of analysis.Biometrics 14:81–104.
Broadhurst, P. L. (1960). Application of biometrical genetics to the inheritance of behaviour. In Eysenck, H. J. (ed.),Experiments in Personality, Vol. 1. Psychogenetics and Psychopharmacology, Routledge and Kegan Paul, London, pp. 3–102.
Broadhurst, P. L. (1966). Stability and change in the inheritance of behaviour in rats: A further analysis of statistics from a diallel cross.Proc. Roy. Soc. B 165:450–472.
Falconer, D. S. (1989).Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Hayman, B. I. (1954a). The analysis of variance of diallel tables.Biometrics 10:235–244.
Hayman, B. I. (1954b). The theory and analysis of diallel crosses.Genetics 39:789–809.
Jones, R. M. (1965). Analysis of variance of the half-diallel table.Heredity 20:117–121.
Lynch, C. B., and Sulzbach, D. S. (1984). Quantitative genetic analysis of temperature regulation inMus musculus. II. Diallel analysis of individual traits.Evolution 38:527–540.
Schmidt, J. (1919). La valeur de l'individu à titre de générateur appreciée suivant la méthode du croisement diallèle.Compt. Rend. Lab. Carlsberg 14:1–33.
Snedecor, G. W. (1956).Statistical Methods Applied to Experiments in Agriculture and Biology, 5th ed., Iowa State College Press, Ames.
Wearden, S. (1964). Alternative analyses of the diallel cross.Heredity 19:669–680.
Wright, A. J. (1985). Diallel designs, analyses, and reference populations.Heredity 54:307–311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez, L.A., Fulker, D.W. & Cherny, S.S. A maximum-likelihood model-fitting approach to conducting a hayman analysis of diallel tables with complete or missing data. Behav Genet 23, 69–76 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067555
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067555