Summary
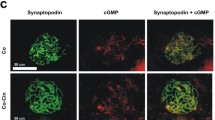
Glomerular basement membrane thickening is thought to be due to increased collagen synthesis and abnormal cross linking. Based upon the observation that the incorporation of distinct proline analogues leads to increased degradation of the newly abnormally formed collagen we administered cis 3 hydroxyproline orally to streptozotocin diabetic rats.
Measuring glomerular basement membrane thickness we found in the treated group significantly lower values. The solubility of collagen in the treated group was significantly increased, indicating the mechanism of action of the proline analogue. The collagen content of kidneys in the treated group was reduced as well correlating with the basement membrane thickness. Provided the absence of toxicity of cis 3 hydroxyproline its pharmaceutical use for the inhibition of basement membrane proliferation seems promising.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brownlee H, Spiro RG (1979) Glomerular basement membrane metabolism in the diabetic rat. Diabetes 28: 121–129
Dixit SN (1979) Isolation and characterization of two alpha chain size collageneous polypeptide chains C and D from glomerular basement membranes. FEBS Lett 106: 379–387
Häusler J (1981) Darstellung von cis und trans C3 substituierten Prolinverbindungen. Liebig's Ann Chem: 1073–1092
Jimenez SA, Rosenbloom J (1974) Decreased thermal stability of collagens containing proline analogues. Arch Biochem Biophys 163: 459–465
Lämmli UK (1970) A cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–682
Lubec G, Kitz K, Adamiker D (1980) Immunochemical and morphological differences between the immature and mature glomerular basement membrane. Renal Physiol 2: 79–82
Lubec G, Leban H, Peyroux J, Sternberg M, Pollak A (1982) Reduced collagenolytic activity in rats with streptozotocin diabetes. Nephron 30: 357–360
Lubec G, Bartosch B, Mallinger R, Frisch H, Graef I (1990) The effect of substance L on glucose mediated collagen cross links in the db/db mouse. Nephron 86: 676–685
Lubec G, Vycudilik W, Mallinger R, Häusler J, Popow C, Lubec B (1991) Antigenic changes of the glomerular basement membrane after the incorporation of hydroxyproline isomers. Renal Physiol 15: 33–40
Prokop DJ, Kivirikko K, Tuderman L, Guzman NA (1979) The biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders. N Engl J Med 301: 77–85
Riley D, Kerr JS, Berg RA, Ianni BD, Pietra GG, Edelman NH, Prockop DJ (1981) Prevention of bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis in the hamster by cis 4 hydroxyproline. Am Rev Resp Dis 123: 388–393
Schnider GL, Kohn RR (1981) Effects of age and diabetes mellitus on the solubility and non-enzymatic glycosylation of human skin collagen. J Clin Invest 67: 1630–1635
Uitto J, Ryhänen L, Tan EML, Oikarinen AI, Zaragoza EJ (1984) Pharmacological inhibition of excessive collagen deposition in fibrotic diseases. Fed Proc 43: 2815–2820
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lubec, B., Sternberg, M., Mallinger, R. et al. Cis 3 hydroxyproline reduces glomerular basement membrane thickness and collagen type IV synthesis in diabetic rats. Amino Acids 4, 249–254 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00805826
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00805826